vue3 .2看一遍就会的setup语法糖
起初vue3.0暴露变量必须return出来,template才能使用
vue3.2中,只需要在script标签上加上setup属性,组件在编译的过程中代码运行的上下文是在setup0函数中,无需retuen template 可之间使用
文件结构
<template>
// Vue2中,template标签中只能有一个根元素,在Vue3中没有此限制
// ...
</template>
<script setup>
// ...
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
// 支持CSS变量注入v-bind(color)
</style>data
<script setup>
import { reactive, ref, toRefs } from 'vue'
// ref声明响应式数据,用于声明基本数据类型
const name = ref('Jerry')
// 修改
name.value = 'Tom'
// reactive声明响应式数据,用于声明引用数据类型
const state = reactive({
name: 'Jerry',
sex: '男'
})
// 修改
state.name = 'Tom'
// 使用toRefs解构
const {name, sex} = toRefs(state)
// template可直接使用{{name}}、{{sex}}
</script>method
<script setup>
import { computed, ref } from 'vue'
const count = ref(1)
// 通过computed获得doubleCount
const doubleCount = computed(() => {
return count.value * 2
})
</script>Watch
<script setup>
import { watch, reactive } from 'vue'
const state = reactive({
count: 1
})
// 声明方法
const changeCount = () => {
state.count = state.count * 2
}
// 监听count
watch(
() => state.count,
(newVal, oldVal) => {
console.log(state.count)
console.log(`watch监听变化前的数据:${oldVal}`)
console.log(`watch监听变化后的数据:${newVal}`)
},
{
immediate: true, // 立即执行
deep: true // 深度监听
}
)
</script>props父传子
子组件
<template>
<span>{{props.name}}</span>
// 可省略【props.】
<span>{{name}}</span>
</template>
<script setup>
// import { defineProps } from 'vue'
// defineProps在<script setup>中自动可用,无需导入
// 需在.eslintrc.js文件中【globals】下配置【defineProps: true】
// 声明props
const props = defineProps({
name: {
type: String,
default: ''
}
})
</script>父组件
<template>
<child name='Jerry'/>
</template>
<script setup>
// 引入子组件(组件自动注册)
import child from './child.vue'
</script>emit子传父
子组件
<template>
<span>{{props.name}}</span>
// 可省略【props.】
<span>{{name}}</span>
<button @click='changeName'>更名</button>
</template>
<script setup>
// import { defineEmits, defineProps } from 'vue'
// defineEmits和defineProps在<script setup>中自动可用,无需导入
// 需在.eslintrc.js文件中【globals】下配置【defineEmits: true】、【defineProps: true】
// 声明props
const props = defineProps({
name: {
type: String,
default: ''
}
})
// 声明事件
const emit = defineEmits(['updateName'])
const changeName = () => {
// 执行
emit('updateName', 'Tom')
}
</script>父组件
<template>
<child :name='state.name' @updateName='updateName'/>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
// 引入子组件
import child from './child.vue'
const state = reactive({
name: 'Jerry'
})
// 接收子组件触发的方法
const updateName = (name) => {
state.name = name
}
</script>v-model
子组件
<template>
<span @click="changeInfo">我叫{{ modelValue }},今年{{ age }}岁</span>
</template>
<script setup>
// import { defineEmits, defineProps } from 'vue'
// defineEmits和defineProps在<script setup>中自动可用,无需导入
// 需在.eslintrc.js文件中【globals】下配置【defineEmits: true】、【defineProps: true】
defineProps({
modelValue: String,
age: Number
})
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue', 'update:age'])
const changeInfo = () => {
// 触发父组件值更新
emit('update:modelValue', 'Tom')
emit('update:age', 30)
}
</script>父组件
<template>
// v-model:modelValue简写为v-model
// 可绑定多个v-model
<child
v-model="state.name"
v-model:age="state.age"
/>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
// 引入子组件
import child from './child.vue'
const state = reactive({
name: 'Jerry',
age: 20
})
</script>nextTick
<script setup>
import { nextTick } from 'vue'
nextTick(() => {
// ...
})
</script>子组件ref变量和defineExpose
在标准写法中,子组件的数据都是默认隐式暴露给父组件的,单在script-setup模式下,所有数据只是默认给return给template使用,不会暴露到组件外,所以父组件式无法直接通过挂载ref变量获取子组件的数据。
如果要调用子组件的数据,需要在子组件显示的暴露出来,才能正确的拿到,这个操作,就是由defineExpose来完成。
总结:子组件里面的方法 父组件是可以使用的通过ref可以使用
子组件
<template>
<span>{{state.name}}</span>
</template>
<script setup>
import { defineExpose, reactive, toRefs } from 'vue'
// 声明state
const state = reactive({
name: 'Jerry'
})
// 声明方法
const changeName = () => {
// 执行
state.name = 'Tom'
}
// 将方法、变量暴露给父组件使用,父组见才可通过ref API拿到子组件暴露的数据
defineExpose({
// 解构state
...toRefs(state),
changeName
})
</script>父组件
<template>
<child ref='childRef'/>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, nextTick } from 'vue'
// 引入子组件
import child from './child.vue'
// 子组件ref
const childRef = ref('childRef')
// nextTick
nextTick(() => {
// 获取子组件name
console.log(childRef.value.name)
// 执行子组件方法
childRef.value.changeName()
})
</script>插槽slot
子组件
<template>
<!-- 匿名插槽 -->
<slot/>
<!-- 具名插槽 -->
<slot name='title'/>
<!-- 作用域插槽 -->
<slot name="footer" :scope="state" />
</template>
<script setup>
import { useSlots, reactive } from 'vue'
const state = reactive({
name: '张三',
age: '25岁'
})
const slots = useSlots()
// 匿名插槽使用情况
const defaultSlot = reactive(slots.default && slots.default().length)
console.log(defaultSlot) // 1
// 具名插槽使用情况
const titleSlot = reactive(slots.title && slots.title().length)
console.log(titleSlot) // 3
</script>父组件
<template>
<child>
<!-- 匿名插槽 -->
<span>我是默认插槽</span>
<!-- 具名插槽 -->
<template #title>
<h1>我是具名插槽</h1>
<h1>我是具名插槽</h1>
<h1>我是具名插槽</h1>
</template>
<!-- 作用域插槽 -->
<template #footer="{ scope }">
<footer>作用域插槽——姓名:{{ scope.name }},年龄{{ scope.age }}</footer>
</template>
</child>
</template>
<script setup>
// 引入子组件
import child from './child.vue'
</script>路由useRoute和useRouter
useRoute:用于返回当前路由信息对象用于接收路由参数
useRouter:于返回当前路由实例,常用于实现路由跳转
<script setup>
import { useRoute, useRouter } from 'vue-router'
// 必须先声明调用
const route = useRoute()
const router = useRouter()
// 路由信息
console.log(route.query)
// 路由跳转
router.push('/newPage')
</script>路由导航守卫
<script setup>
import { onBeforeRouteLeave, onBeforeRouteUpdate } from 'vue-router'
// 添加一个导航守卫,在当前组件将要离开时触发。
onBeforeRouteLeave((to, from, next) => {
next()
})
// 添加一个导航守卫,在当前组件更新时触发。
// 在当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用。
onBeforeRouteUpdate((to, from, next) => {
next()
})
</script>store
Vue3 中的Vuex不再提供辅助函数写法
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
import { key } from '../store/index'
// 必须先声明调用
const store = useStore(key)
// 获取Vuex的state
store.state.xxx
// 触发mutations的方法
store.commit('fnName')
// 触发actions的方法
store.dispatch('fnName')
// 获取Getters
store.getters.xxx
</script>生命周期
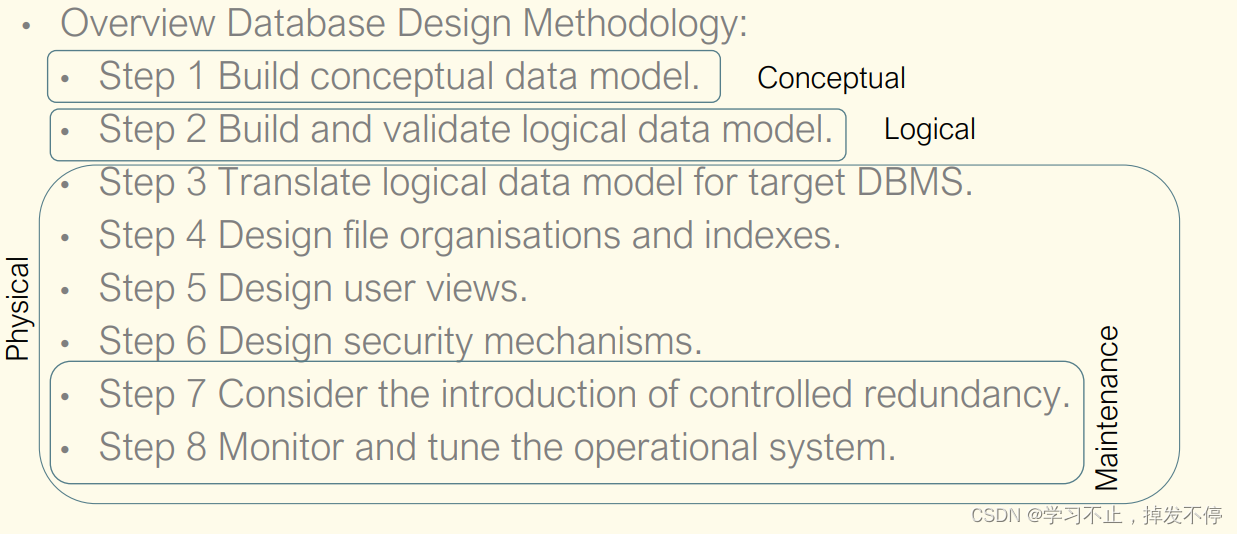
- 通过在生命周期钩子前面加上 “on” 来访问组件的生命周期钩子。
- 下表包含如何在 Option API 和 setup() 内部调用生命周期钩子
| OPtion API | setup中 |
| beforeCreate | 不需要 |
| create | 不需要 |
| beforeMount | onbeforeMount |
| mounted | onMounted |
| beforeUpdate | onBeforeUpdate |
| updated | onUpdated |
| beforeUnmount | onBeforeUnmount |
| unmounted | onUnmounted |
| errorCaptured | onErrorCaptured |
| renderTracked | onRenderTracked |
| renderTriggered | onRenderTriggered |
| activated | onActivated |
| deactivated | onDeactivated |
CSS变量注入
<template>
<span>Jerry</span>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
const state = reactive({
color: 'red'
})
</script>
<style scoped>
span {
// 使用v-bind绑定state中的变量
color: v-bind('state.color');
}
</style>原型绑定与组件内使用
main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
const app = createApp(App)
// 获取原型
const prototype = app.config.globalProperties
// 绑定参数
prototype.name = 'Jerry'组件内使用
<script setup>
import { getCurrentInstance } from 'vue'
// 获取原型
const { proxy } = getCurrentInstance()
// 输出
console.log(proxy.name)
</script>对await的支持
不必再配合async就可以直接使用await了,这种情况下,组件的setup会自动编程async,seyup.
<script setup>
const post = await fetch('/api').then(() => {})
</script>定义组件的name
<script>
//用单独的<script>块来定义
export default {
name: 'ComponentName',
}
</script>provide和inject
父组件
<template>
<child/>
</template>
<script setup>
import { provide } from 'vue'
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
// 引入子组件
import child from './child.vue'
let name = ref('Jerry')
// 声明provide
provide('provideState', {
name,
changeName: () => {
name.value = 'Tom'
}
})
// 监听name改变
watch(name, () => {
console.log(`name变成了${name}`)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(name.value) // Tom
}, 1000)
})
</script>子组件
<script setup>
import { inject } from 'vue'
// 注入
const provideState = inject('provideState')
// 子组件触发name改变
provideState.changeName()
</script>Vue3中使用echarts
// 安装
cnpm i echarts --save
// 组件内引入
import * as echarts from 'echarts'pinia的使用
概述
现有用户对vuex更熟悉,他是Vue之前的官方状态管理库,由于pina再生态系统中能够承担相同的职责能做的更好,因此vuex现在处于维护模式,它仍然可以工作,但不再接受新的功能,对于新的应用,建议使用Pina
事实上 Pina最初正式为了探索vuex的下一个版本开发的,因此整合了核心团队关于vuex 5的许多想法,最终,我们意识到Pina已经实现了我们想要再vuex 5中提供的大部分内容,因此决定将其作为新的官方推荐。
相比于vuex Pina提供了更简介的直接的API ,并提供了组合式风格的API,最重要的是,再使用TypeScript 时它提供了更完善的类型推导
安装
yarn add pinia
# or with npm
npm install pinia创建一个 pinia 实例
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
const pinia = createPinia()
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(pinia)
app.mount('#app')定义一个store
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
//您可以将`defineStore()`的返回值命名为任意名称,
//但最好使用store的名称,并用“use”将其包围
//(例如`useUserStore`、`useCartStore`和`useProductStore`)
//第一个参数是应用程序中存储的唯一id
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
// 其他选项...
})
//定义一个完整的store
//与 Vue 的选项 API 类似,我们也可以传递带有属性的选项对象。state actions getters
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({ count: 0, name: 'Eduardo' }),
getters: {
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
},
actions: {
increment() {
this.count++
},
},
})
//您可以将 视为store的属性,也可以将其视为store的属性,
//state => data
//getters => computed
//actions => methods
//这样会更容易记忆
// 还有另一种可能的语法来定义存储。与 Vue 合成 API 的设置函数类似,我们可以传入一个函数来定义反应式属性和方法,并返回一个包含我们要公开的属性和方法的对象。
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
const count = ref(0)
const name = ref('Eduardo')
const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2)
function increment() {
count.value++
}
return { count, name, doubleCount, increment }
})使用
import { useCounterStore } from '@/stores/counter'
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
export default {
setup() {
const store = useCounterStore()
//结构并赋予响应性
const { name, doubleCount } = storeToRefs(store)
return {
// you can return the whole store instance to use it in the template
store,
}
},
}state
//给 state 加上类型推导
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {
state: () => {
return {
userList: [] as UserInfo[],
user: null as UserInfo | null,
}
},
})
interface UserInfo {
name: string
age: number
}
//或者给整个state加上类型推导
interface State {
userList: UserInfo[]
user: UserInfo | null
}
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {
state: (): State => {
return {
userList: [],
user: null,
}
},
})
interface UserInfo {
name: string
age: number
}访问state
const store = useStore()
store.count++重置状态
const store = useStore()
store.$reset()getters
定义
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
getters: {
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
},
})
//添加类型约束
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
getters: {
// automatically infers the return type as a number
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
},
// the return type **must** be explicitly set
doublePlusOne(): number {
// autocompletion and typings for the whole store ✨
return this.doubleCount + 1
},
},
})访问
<template>
<p>Double count is {{ store.doubleCount }}</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
setup() {
const store = useCounterStore()
return { store }
},
}
</script>访问其他getter
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
getters: {
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
doubleCountPlusOne() {
// autocompletion ✨
return this.doubleCount + 1
},
},
})将参数传递给获取者
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
getters: {
getUserById: (state) => {
return (userId) => state.users.find((user) => user.id === userId)
},
},
})
//组件中使用
<script>
export default {
setup() {
const store = useStore()
return { getUserById: store.getUserById }
},
}
</script>
<template>
<p>User 2: {{ getUserById(2) }}</p>
</template>actions
定义
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
actions: {
// 因为我们依赖“this”,所以不能使用箭头函数
increment() {
this.count++
},
randomizeCounter() {
this.count = Math.round(100 * Math.random())
},
},
})
//与 getter 一样,操作通过完全键入(和自动完成✨)支持来访问整个商店实例。与 getter 不同,操作可以是异步的
import { mande } from 'mande'
const api = mande('/api/users')
export const useUsers = defineStore('users', {
state: () => ({
userData: null,
// ...
}),
actions: {
async registerUser(login, password) {
try {
this.userData = await api.post({ login, password })
showTooltip(`Welcome back ${this.userData.name}!`)
} catch (error) {
showTooltip(error)
// let the form component display the error
return error
}
},
},
}) 使用
export default {
setup() {
const store = useCounterStore()
store.randomizeCounter()
},
}


















![[DS]Polar靶场web(二)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/32846b2739924b6182f8fc43f356e388.png)