枚举
基础概念:
枚举(Enum)是一种用户定义的数据类型,用于定义一个有限集合的命名常量。在C++中,枚举类型可以通过关键字enum来定义。
下面是一个简单的枚举类型的定义示例:
#include <iostream> enum Color { RED, GREEN, BLUE }; int main() { Color c = RED; if(c == RED) { std::cout << "The color is red" << std::endl; } else if(c == GREEN) { std::cout << "The color is green" << std::endl; } else if(c == BLUE) { std::cout << "The color is blue" << std::endl; } return 0; }在上面的示例中,我们定义了一个枚举类型Color,其中包含了三个枚举常量RED、GREEN和BLUE。在main函数中,我们声明了一个Color类型的变量c,并将其赋值为RED。然后通过if语句来判断c的值,并输出相应的颜色信息。
枚举类型的常量默认从0开始递增,也可以手动指定初始值,例如:
enum Fruit { APPLE = 1, ORANGE, BANANA };在这个示例中,APPLE的值为1,ORANGE的值为2,BANANA的值为3。
枚举类型的常量可以直接通过枚举类型名访问,也可以通过枚举类型名加作用域解析运算符::来访问,例如:
Color c = Color::RED;
练习1:特别数的和
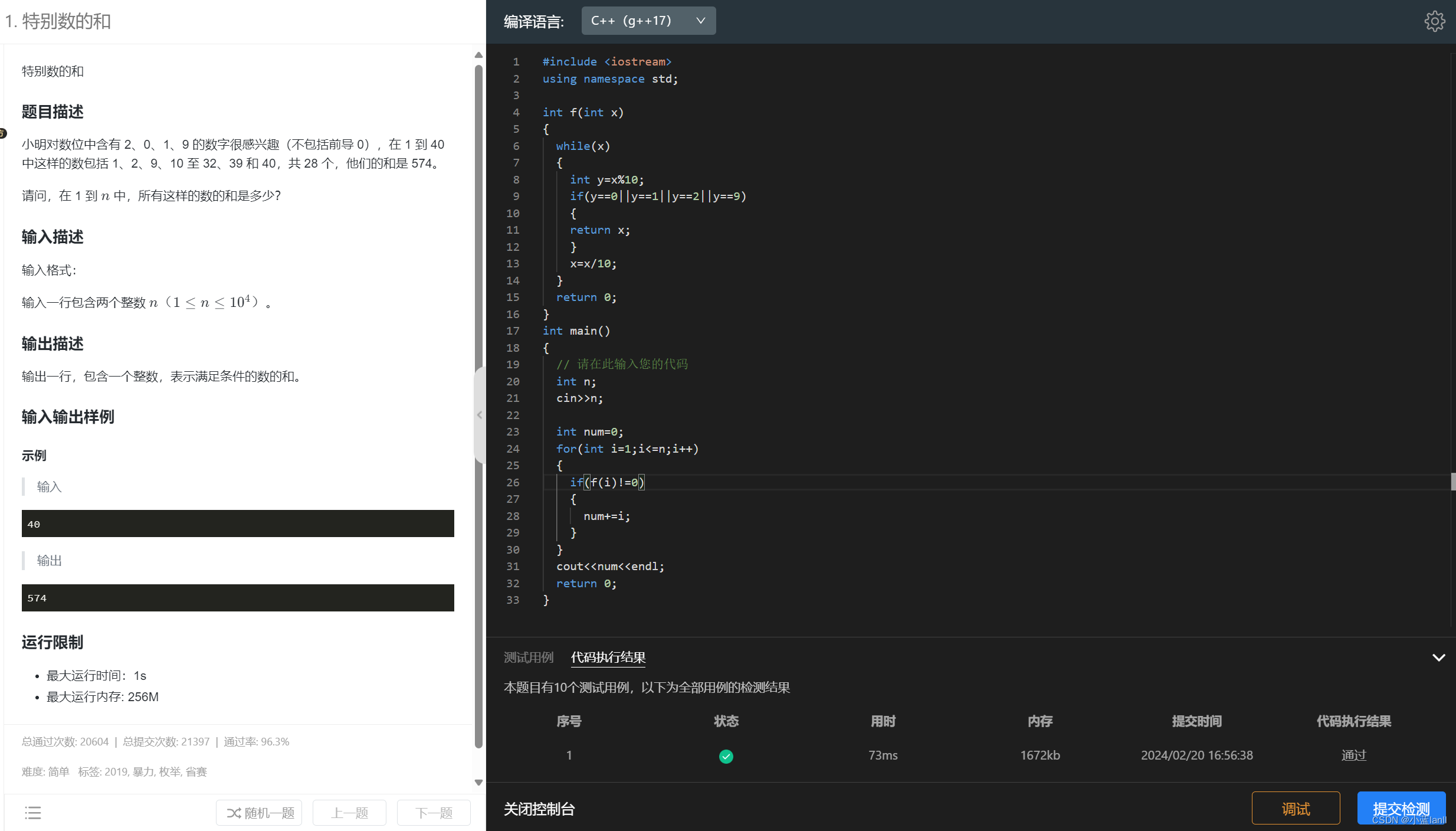
解析:
```cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 定义一个函数f,用于判断一个整数是否包含数字0、1、2、9
int f(int x)
{
while(x)
{
int y=x%10; // 取出x的个位数
if(y==0||y==1||y==2||y==9) // 判断个位数是否为0、1、2、9
{
return x; // 如果包含0、1、2、9,返回原整数x
}
x=x/10; // 去掉x的个位数,继续判断下一位
}
return 0; // 如果x不包含0、1、2、9,返回0
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n; // 输入一个整数n
int num=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(f(i)!=0) // 调用函数f判断i是否包含0、1、2、9
{
num+=i; // 如果包含,则将i加到num中
}
}
cout<<num<<endl; // 输出结果num
return 0;
}
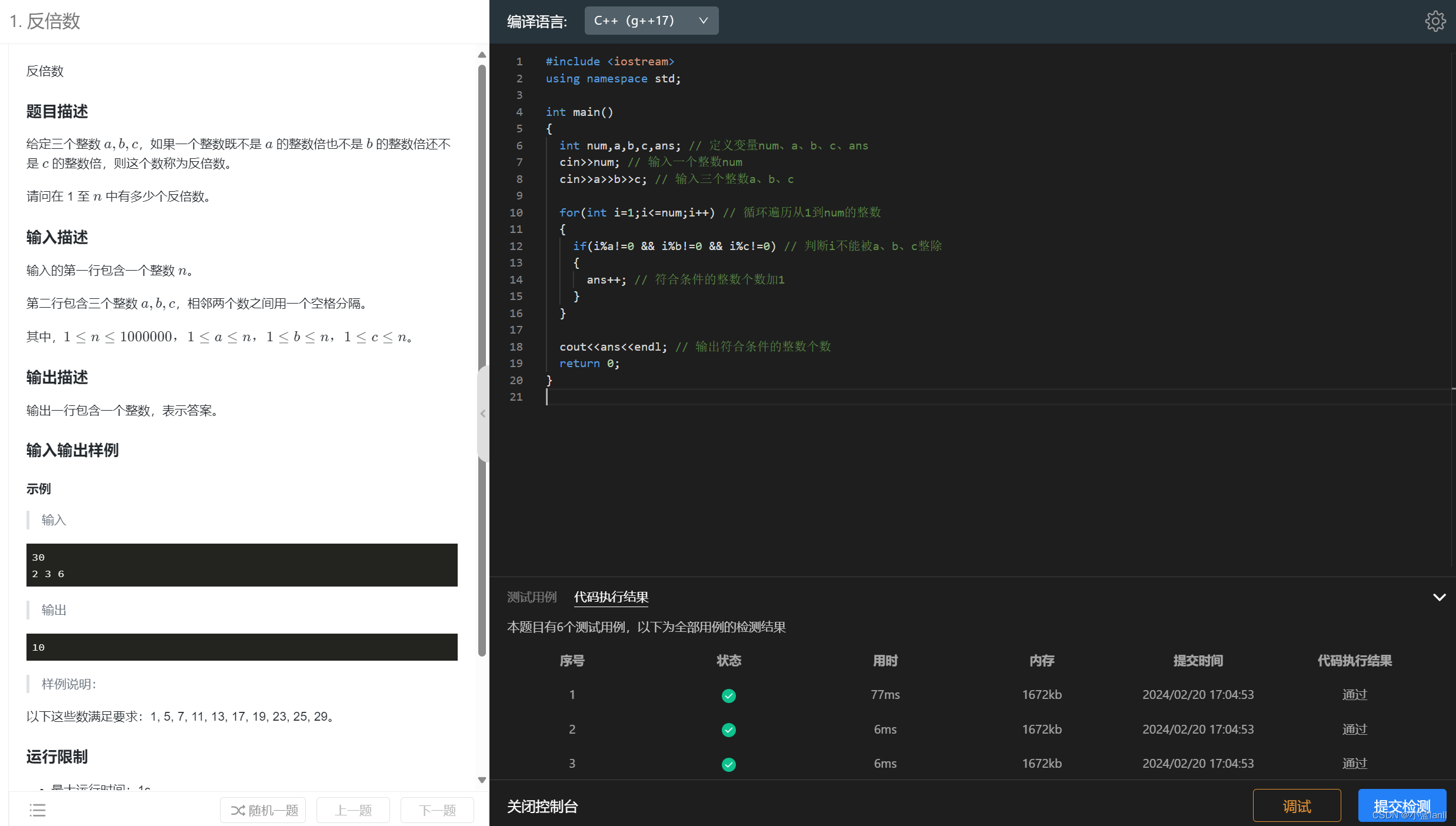
练习2:反倍数
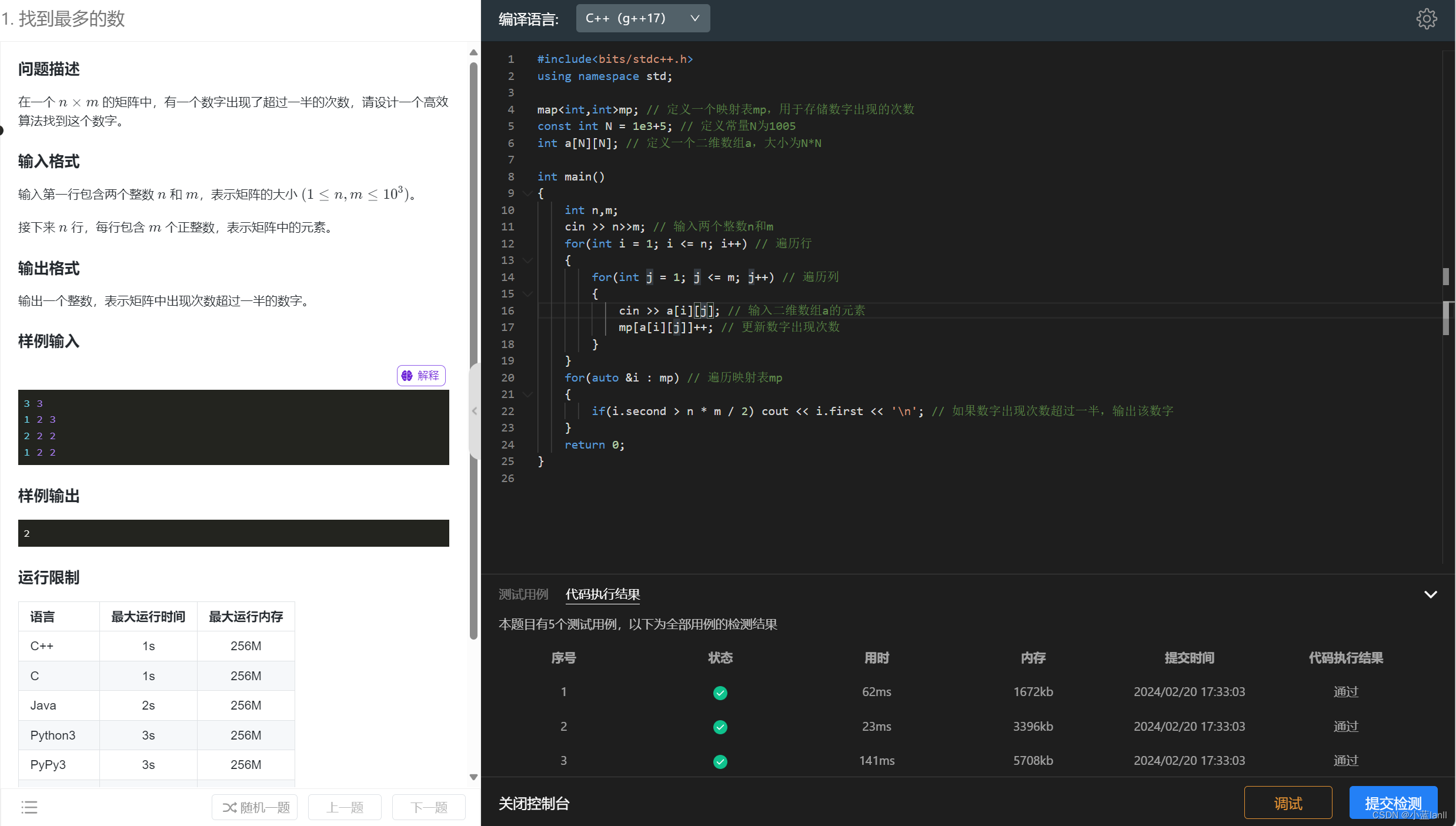
练习3:找到最多的数
双指针
基础概念:
双指针算法是一种常用的解决问题的技巧,主要用于在数组或链表中寻找一些特定的结构。双指针算法通常有两种类型:快慢指针和左右指针。下面分别介绍这两种类型的双指针算法。
- 快慢指针: 快慢指针算法通常用于解决链表中的问题,例如判断链表是否有环、找到链表的中间节点等。
示例代码:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; struct ListNode { int val; ListNode* next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} }; bool hasCycle(ListNode* head) { ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head; while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (slow == fast) { return true; // 链表中存在环 } } return false; // 链表中不存在环 } int main() { // 创建一个有环的链表 ListNode* head = new ListNode(3); head->next = new ListNode(2); head->next->next = new ListNode(0); head->next->next->next = new ListNode(-4); head->next->next->next->next = head->next; // 使链表形成环 cout << hasCycle(head) << endl; // 输出1,表示链表中存在环 return 0; }
- 左右指针: 左右指针算法通常用于解决数组中的问题,例如在有序数组中寻找两个数使它们的和等于目标值等。
示例代码:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& numbers, int target) { int left = 0; int right = numbers.size() - 1; while (left < right) { int sum = numbers[left] + numbers[right]; if (sum == target) { return {left + 1, right + 1}; // 返回找到的两个数的下标(从1开始) } else if (sum < target) { left++; } else { right--; } } return {}; // 没有找到符合条件的两个数 } int main() { vector<int> numbers = {2, 7, 11, 15}; int target = 9; vector<int> result = twoSum(numbers, target); for (int num : result) { cout << num << " "; } return 0; }以上是双指针算法的两种常见类型及其示例代码。双指针算法通常能够在O(n)的时间复杂度内解决问题,是解决一些数组和链表相关问题的高效方法。
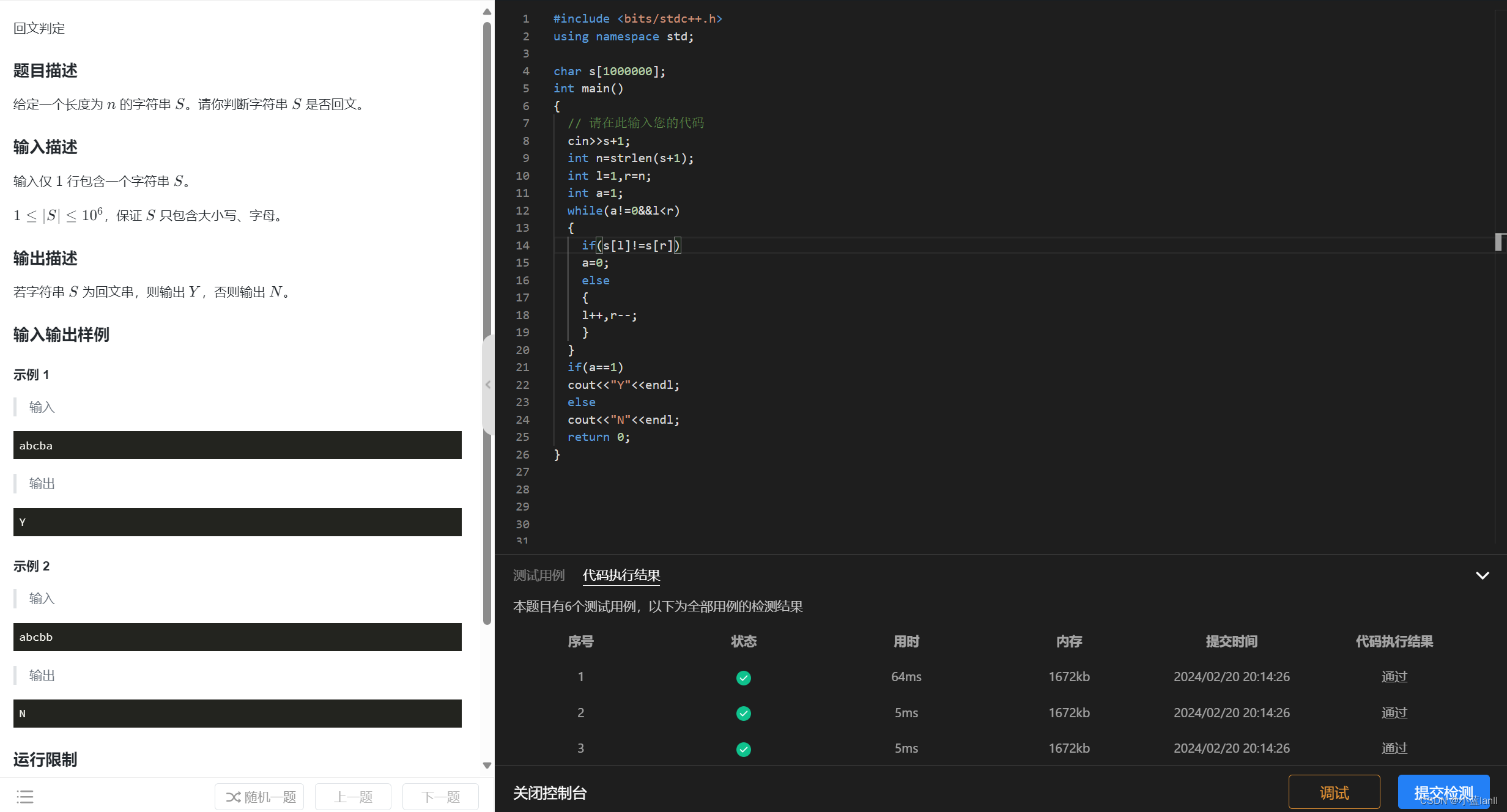
练习1:回文判定





![[<span style='color:red;'>蓝</span><span style='color:red;'>桥</span><span style='color:red;'>杯</span> 2019 国 <span style='color:red;'>C</span>] 数正方形(找规律,<span style='color:red;'>枚</span><span style='color:red;'>举</span>)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f71dabdffdd14bc2b544d971b60c6c42.png)






















![Sora 的工作原理(及其意义) [译]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/3a668f81737504ce0521b4b4900cb574.webp?x-oss-process=image/format,png)