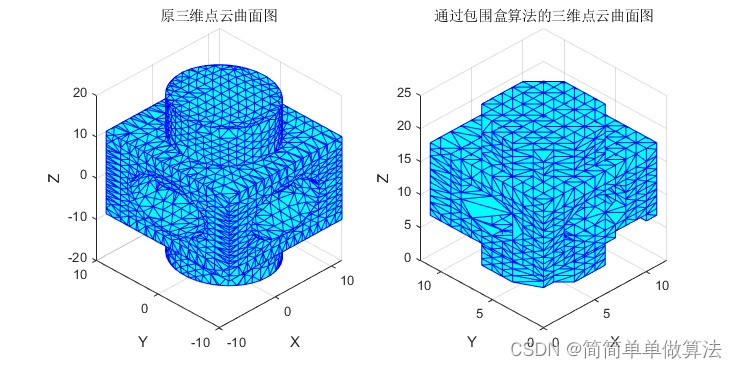
最小包围盒
包围盒计算步骤
1.利用PCA主元分析法获得点云的三个主方向,获取质心,计算协方差,获得协方差矩阵,求取协方差矩阵的特征值和特长向量,特征向量即为主方向。
2.利用计算得到的主方向和质心,将输入点云转换至原点,且主方向与坐标系方向重回,建立变换到原点的点云的包围盒。
3.给输入点云设置主方向和包围盒,通过输入点云到原点点云变换的逆变换实现。
最小包围盒顶点坐标计算步骤
1.输入点云转换至原点后,计算变换后点云的最大最小x,y,z轴的坐标,此时(max.x,max.y,max.z),(max.x,min.y,max.z),(max.x,max.y,min.z),(min.x,max.y,max.z),(min.x,max.y,min.z),(min.x,min.y,max.z),(min.x,min.y,max.z),(min.x,min.y,min.z)
即为变换后点云的包围盒,也是原始输入点云包围盒顶点坐标经过变化后的坐标.
2.将上述求得的6个包围盒坐标逆变换回输入点云的坐标系,即得到原始输入点云的包围盒顶点坐标
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/filters/project_inliers.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/filters/radius_outlier_removal.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/extract_clusters.h>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <pcl/common/transforms.h>
#include <pcl/common/common.h>
#include <pcl/common/time.h>
#include <pcl/common/angles.h>
#include <pcl/registration/transformation_estimation_svd.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
typedef struct myPointType
{
double x; //mm world coordinate x
double y; //mm world coordinate y
double z; //mm world coordinate z
int num; //point num
};
// Get N bits of the string from back to front.
char* Substrend(char* str, int n)
{
char* substr = (char*)malloc(n + 1);
int length = strlen(str);
if (n >= length)
{
strcpy(substr, str);
return substr;
}
int k = 0;
for (int i = length - n; i < length; i++)
{
substr[k] = str[i];
k++;
}
substr[k] = '\0';
return substr;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// create point cloud
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("E:\\***\\cloud_cluster_1.pcd", *cloud);
// start calculating time
pcl::StopWatch time;
Eigen::Vector4f pcaCentroid;
pcl::compute3DCentroid(*cloud, pcaCentroid);
Eigen::Matrix3f covariance;
pcl::computeCovarianceMatrixNormalized(*cloud, pcaCentroid, covariance);
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::Matrix3f> eigen_solver(covariance, Eigen::ComputeEigenvectors);
Eigen::Matrix3f eigenVectorsPCA = eigen_solver.eigenvectors();
Eigen::Vector3f eigenValuesPCA = eigen_solver.eigenvalues();
eigenVectorsPCA.col(2) = eigenVectorsPCA.col(0).cross(eigenVectorsPCA.col(1)); //校正主方向间垂直
eigenVectorsPCA.col(0) = eigenVectorsPCA.col(1).cross(eigenVectorsPCA.col(2));
eigenVectorsPCA.col(1) = eigenVectorsPCA.col(2).cross(eigenVectorsPCA.col(0));
std::cout << "特征值va(3x1):\n" << eigenValuesPCA << std::endl;
std::cout << "特征向量ve(3x3):\n" << eigenVectorsPCA << std::endl;
std::cout << "质心点(4x1):\n" << pcaCentroid << std::endl;
/*
// 另一种计算点云协方差矩阵特征值和特征向量的方式:通过pcl中的pca接口,如下,这种情况得到的特征向量相似特征向量
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloudPCAprojection (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PCA<pcl::PointXYZ> pca;
pca.setInputCloud(cloudSegmented);
pca.project(*cloudSegmented, *cloudPCAprojection);
std::cerr << std::endl << "EigenVectors: " << pca.getEigenVectors() << std::endl;//计算特征向量
std::cerr << std::endl << "EigenValues: " << pca.getEigenValues() << std::endl;//计算特征值
*/
Eigen::Matrix4f tm = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
Eigen::Matrix4f tm_inv = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
tm.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = eigenVectorsPCA.transpose(); //R.
tm.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = -1.0f * (eigenVectorsPCA.transpose()) * (pcaCentroid.head<3>());// -R*t
tm_inv = tm.inverse();
std::cout << "变换矩阵tm(4x4):\n" << tm << std::endl;
std::cout << "逆变矩阵tm'(4x4):\n" << tm_inv << std::endl;
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr transformedCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>);
pcl::transformPointCloud(*cloud, *transformedCloud, tm);
PointType min_p1, max_p1;
Eigen::Vector3f c1, c;
pcl::getMinMax3D(*transformedCloud, min_p1, max_p1);
c1 = 0.5f * (min_p1.getVector3fMap() + max_p1.getVector3fMap());
std::cout << "型心c1(3x1):\n" << c1 << std::endl;
Eigen::Affine3f tm_inv_aff(tm_inv);
pcl::transformPoint(c1, c, tm_inv_aff);
Eigen::Vector3f whd, whd1;
whd1 = max_p1.getVector3fMap() - min_p1.getVector3fMap();
whd = whd1;
float sc1 = (whd1(0) + whd1(1) + whd1(2)) / 3; //点云平均尺度,用于设置主方向箭头大小
std::cout << "width1=" << whd1(0) << endl;
std::cout << "heght1=" << whd1(1) << endl;
std::cout << "depth1=" << whd1(2) << endl;
std::cout << "scale1=" << sc1 << endl;
const Eigen::Quaternionf bboxQ1(Eigen::Quaternionf::Identity());
const Eigen::Vector3f bboxT1(c1);
const Eigen::Quaternionf bboxQ(tm_inv.block<3, 3>(0, 0));
const Eigen::Vector3f bboxT(c);
//变换到原点的点云主方向
PointType op;
op.x = 0.0;
op.y = 0.0;
op.z = 0.0;
Eigen::Vector3f px, py, pz;
Eigen::Affine3f tm_aff(tm);
pcl::transformVector(eigenVectorsPCA.col(0), px, tm_aff);
pcl::transformVector(eigenVectorsPCA.col(1), py, tm_aff);
pcl::transformVector(eigenVectorsPCA.col(2), pz, tm_aff);
PointType pcaX;
pcaX.x = sc1 * px(0);
pcaX.y = sc1 * px(1);
pcaX.z = sc1 * px(2);
PointType pcaY;
pcaY.x = sc1 * py(0);
pcaY.y = sc1 * py(1);
pcaY.z = sc1 * py(2);
PointType pcaZ;
pcaZ.x = sc1 * pz(0);
pcaZ.y = sc1 * pz(1);
pcaZ.z = sc1 * pz(2);
//初始点云的主方向
PointType cp;
cp.x = pcaCentroid(0);
cp.y = pcaCentroid(1);
cp.z = pcaCentroid(2);
PointType pcX;
pcX.x = sc1 * eigenVectorsPCA(0, 0) + cp.x;
pcX.y = sc1 * eigenVectorsPCA(1, 0) + cp.y;
pcX.z = sc1 * eigenVectorsPCA(2, 0) + cp.z;
PointType pcY;
pcY.x = sc1 * eigenVectorsPCA(0, 1) + cp.x;
pcY.y = sc1 * eigenVectorsPCA(1, 1) + cp.y;
pcY.z = sc1 * eigenVectorsPCA(2, 1) + cp.z;
PointType pcZ;
pcZ.x = sc1 * eigenVectorsPCA(0, 2) + cp.x;
pcZ.y = sc1 * eigenVectorsPCA(1, 2) + cp.y;
pcZ.z = sc1 * eigenVectorsPCA(2, 2) + cp.z;
//Rectangular vertex
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr transVertexCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>);//存放变换后点云包围盒的6个顶点
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr VertexCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>);//存放原来点云中包围盒的6个顶点
transVertexCloud->width = 6;
transVertexCloud->height = 1;
transVertexCloud->is_dense = false;
transVertexCloud->points.resize(transVertexCloud->width * transVertexCloud->height);
transVertexCloud->points[0].x = max_p1.x;
transVertexCloud->points[0].y = max_p1.y;
transVertexCloud->points[0].z = max_p1.z;
transVertexCloud->points[1].x = max_p1.x;
transVertexCloud->points[1].y = max_p1.y;
transVertexCloud->points[1].z = min_p1.z;
transVertexCloud->points[2].x = max_p1.x;
transVertexCloud->points[2].y = min_p1.y;
transVertexCloud->points[2].z = min_p1.z;
transVertexCloud->points[3].x = min_p1.x;
transVertexCloud->points[3].y = max_p1.y;
transVertexCloud->points[3].z = max_p1.z;
transVertexCloud->points[4].x = min_p1.x;
transVertexCloud->points[4].y = min_p1.y;
transVertexCloud->points[4].z = max_p1.z;
transVertexCloud->points[5].x = min_p1.x;
transVertexCloud->points[5].y = min_p1.y;
transVertexCloud->points[5].z = min_p1.z;
pcl::transformPointCloud(*transVertexCloud, *VertexCloud, tm_inv);
// 逆变换回来的角度
cout << whd1(0) << " " << whd1(1) << " " << whd1(2) << endl;
auto euler = bboxQ1.toRotationMatrix().eulerAngles(0, 1, 2);
std::cout << "Euler from quaternion in roll, pitch, yaw" << std::endl << euler / 3.14 * 180 << std::endl << std::endl;
//Output time consumption
std::cout << "运行时间" << time.getTime() << "ms" << std::endl;
//visualization
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer;
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointType> tc_handler(transformedCloud, 0, 255, 0); //设置点云颜色
//Visual transformed point cloud
viewer.addPointCloud(transformedCloud, tc_handler, "transformCloud");
viewer.addCube(bboxT1, bboxQ1, whd1(0), whd1(1), whd1(2), "bbox1");
viewer.setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_REPRESENTATION, pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_REPRESENTATION_WIREFRAME, "bbox1");
viewer.setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, "bbox1");
viewer.addArrow(pcaX, op, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, false, "arrow_X");
viewer.addArrow(pcaY, op, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, false, "arrow_Y");
viewer.addArrow(pcaZ, op, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, false, "arrow_Z");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointType> color_handler(cloud, 255, 0, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud, color_handler, "cloud");
viewer.addCube(bboxT, bboxQ, whd(0), whd(1), whd(2), "bbox");
viewer.setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_REPRESENTATION, pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_REPRESENTATION_WIREFRAME, "bbox");
viewer.setShapeRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, "bbox");
viewer.addArrow(pcX, cp, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, false, "arrow_x");
viewer.addArrow(pcY, cp, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, false, "arrow_y");
viewer.addArrow(pcZ, cp, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, false, "arrow_z");
viewer.addCoordinateSystem(0.5f * sc1);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
viewer.addPointCloud(VertexCloud, "temp_cloud");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 10, "temp_cloud");
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
实验结果


总结
- 实验环境:pcl1.11.0+vs2019+win10
- 点云包围盒在碰撞检测时,可以使用包围盒来提前排除大部分不在关注区域内的点云。
- 顶点坐标精确描述了点云的位置。
- 点云主轴方向可做帮助识别点云的旋转状态,此外,在点云处理中,通常需要将不同视角或不同时间采集的点云数据进行配准和对齐,主轴方向是一种常用的参考依据。