文章目录
一、栈的概念
1.栈的定义
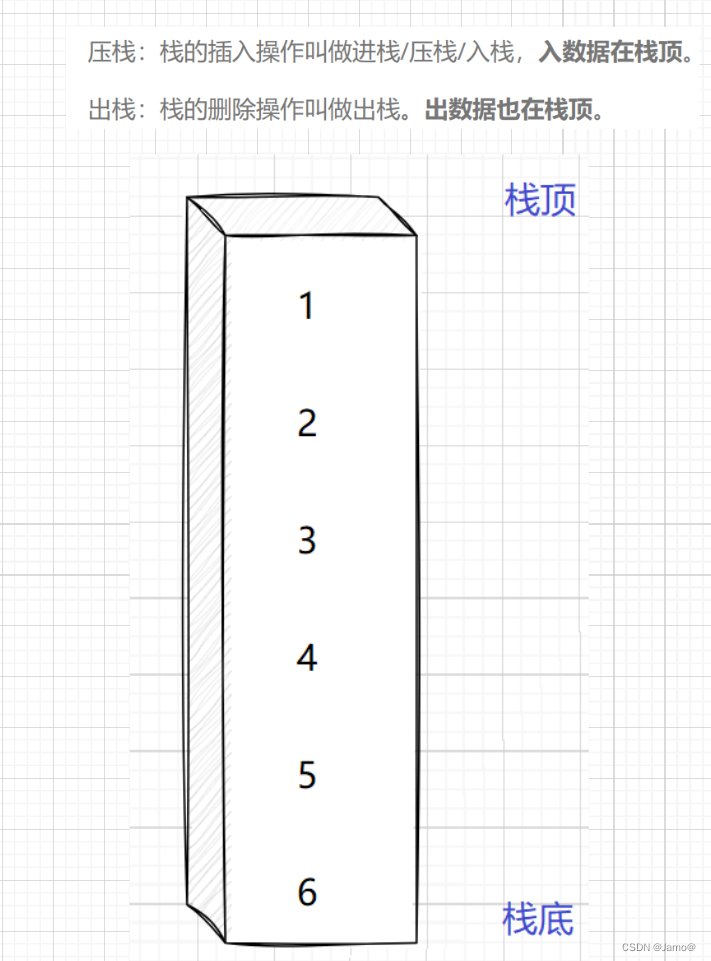
栈(Stack):只允许在一端进行插入或删除的线性表。首先栈是一种线性表,但限定这种线性表只能在某一端进行插入和删除操作。
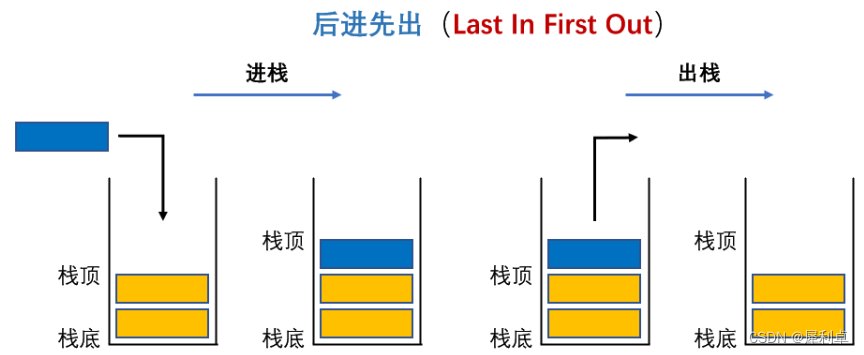
他是一种”先进后出“的数据结构

栈顶(Top):线性表允许进行插入删除的那一端。
栈底(Bottom):固定的,不允许进行插入和删除的另一端。
空栈:不含任何元素的空表
2.栈的常见基本操作
- InitStack(&S):初始化一个空栈S。
- StackEmpty(S):判断一个栈是否为空,若栈为空则返回true,否则返回false。
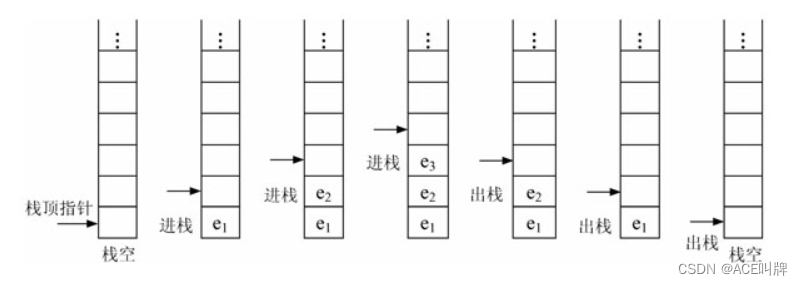
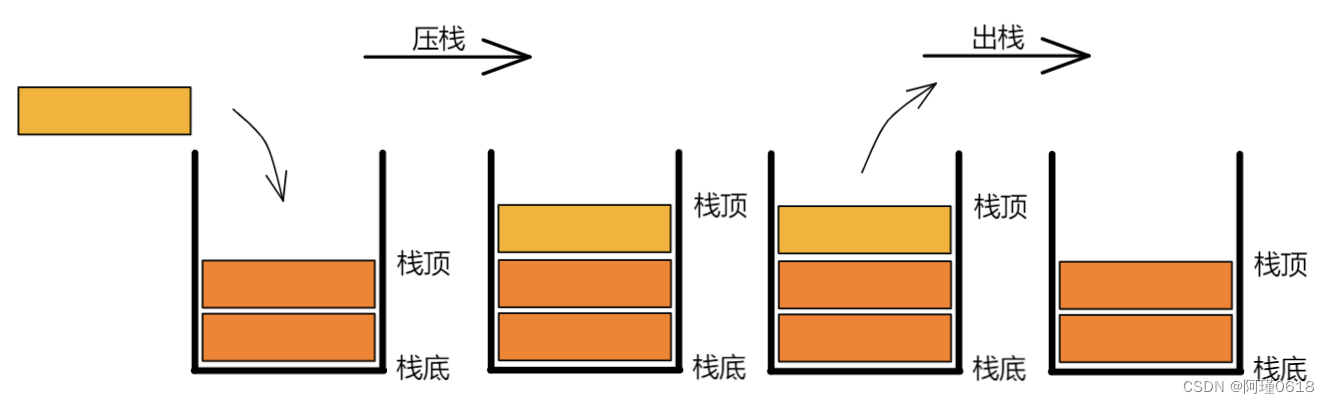
- Push(&S, x):进栈(栈的插入操作),若栈S未满,则将x加入使之成为新栈顶。
- Pop(&S, &x):出栈(栈的删除操作),若栈S非空,则弹出栈顶元素,并用x返回。
- GetTop(S, &x):读栈顶元素,若栈S非空,则用x返回栈顶元素。
- DestroyStack(&S):栈销毁,并释放S占用的存储空间(“&”表示引用调用)。
二、栈的顺序存储结构
1.栈的顺序存储结构
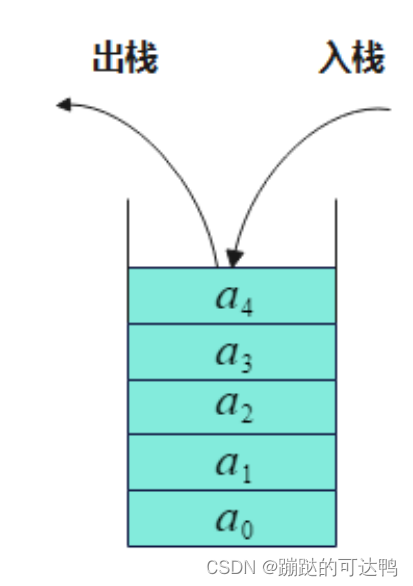
采用顺序存储的栈称为顺序栈,它利用一组地址连续的存储单元存放自栈底到栈顶的数据元素,同时附设一个指针(top)指示当前栈顶元素的位置。若存储栈的长度为StackSize,则栈顶位置top必须小于StackSize。当栈存在一个元素时,top等于0,因此通常把空栈的判断条件定位top等于-1。
若现在有一个栈,StackSize是5,则栈的普通情况、空栈、满栈的情况分别如下图所示:

2.共享栈(两栈共享空间)(双端栈)
(1)共享栈概念
利用栈底位置相对不变的特征,可让两个顺序栈共享一个一维数组空间,将两个栈的栈底分别设置在共享空间的两端,两个栈顶向共享空间的中间延伸,如下图所示:
两个栈的栈顶指针都指向栈顶元素,top0=-1时0号栈为空,top1=MaxSize时1号栈为空;仅当两个栈顶指针相邻(top0+1=top1)时,判断为栈满。当0号栈进栈时top0先加1再赋值,1号栈进栈时top1先减一再赋值出栈时则刚好相反。
双端栈是线性表的一种,更是栈的一个特殊分类,可用借用动态数组+栈的组合实现。
(2)特点
双端栈的特点是可以从两个方向进行操作,即从左侧插入和删除元素,也可以从右侧插入和删除元素。这使得双端栈在某些场景下可以提供更灵活的操作和更高的效率。
(3)实例
使用Java的Deque实现双端栈的演示实例:
public class DequeStack {
private Deque<Integer> deque;
public DequeStack() {
deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
}
public void push(int item) {
deque.push(item);
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
return deque.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
return deque.peek();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return deque.isEmpty();
}
public int size() {
return deque.size();
}
}
在这个示例中,我们使用了Java的Deque,具体是ArrayDeque实现类。ArrayDeque是基于可调整大小的数组实现的双端队列,可以在队列的两端进行插入和删除操作。我们将其作为双端栈的底层数据结构来实现。
通过双端栈,我们可以在栈顶和栈底进行元素的插入和删除操作。例如:
DequeStack stack = new DequeStack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
System.out.println(stack.peek()); // 输出:2
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // 输出:4
stack.push(5);
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // 输出:5
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // 输出:3
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // 输出:2
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty()); // 输出:true
三、栈的链式存储结构
1.链栈
采用链式存储的栈称为链栈,链栈的优点是便于多个栈共享存储空间和提高其效率,且不存在栈满上溢的情况。通常采用单链表实现,并规定所有操作都是在单链表的表头进行的。这里规定链栈没有头节点,Lhead指向栈顶元素
如下图所示。

对于空栈来说,链表原定义是头指针指向空,那么链栈的空其实就是top=NULL的时候。
2.性能比较
链栈的进栈push和出栈pop操作都很简单,时间复杂度均为O(1)。
对比一下顺序栈与链栈,它们在时间复杂度上是一样的,均为O(1)。
空间:1.顺序栈需要确定一个连续的长度,可能会存在内存浪费现象
优点:定位方便
2.链栈要求每个元素都要有指针域,会增加内存开销
对栈的长度无限制
如果栈的使用过程中元素变化不可预料,有时很小,有时非常大,那么最好是用链栈,反之,如果它的变化在可控范围内,建议使用顺序栈会更好一些。
四、Stack的常用方法
| 方法名称 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| public Stack() | 构造方法 | 创建Stack对象 |
| public E Stack(E item) | 普通方法 | 入栈 |
| public synchronized E pop() | 普通方法 | 出栈 |
| public synchronized E peek() | 普通方法 | 获取栈顶元素 |
| public boolean empty() | 普通方法 | 判断栈是否为空 |
| public synchronized int search(Object o) | 普通方法 | 基于栈顶位置(索引为1,索引自栈顶向栈底自增) 查找对象o,如果找到了返回索引值,否则返回-1 |
代码
public class MyStack {
public int[] elem; //数组 -> 栈空间
public int usedSize;//有效数据
public MyStack(){
this.elem = new int[5];
this.usedSize = 0;
}
//入栈
public void push(int val){
//如果栈满了就进行扩容
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize] = val;
usedSize++;
}
//判断栈是否满
public boolean isFull(){
return usedSize==this.elem.length;
}
//出栈
public int pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new NullPointerException("栈为空!");
}
int oldVal = this.elem[usedSize-1];
this.usedSize--;
return oldVal;
}
//判断栈是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize==0;
}
//读取栈顶元素
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new NullPointerException("栈为空!");
}
return this.elem[usedSize-1];
}
}
测试类
public class TestDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);//入栈
myStack.push(2);
myStack.push(3);
myStack.push(4);
System.out.println(myStack.peek());//获取栈顶元素
System.out.println(myStack.pop());//出栈
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.isEmpty());//判断栈是否为空,如果为空返回true,否则返回false
}
}
运行结果:
4
4
3
2
1
true
五、栈的使用

在集合框架中,Stack(栈)是一个普通的类,实现了List接口,具体框架图如下:

注意:
- Stack实现了RandomAccess接口,表明Stack支持随机访问
- Stack实现了Cloneable接口,表明Stack是可以clone的
- Stack实现了Serializable接口,表明Stack是支持序列化的
- Vector(向量)是一个封装了动态大小数组的顺序容器(Sequence Container)。跟任意其它类型容器一样,它能够存放各种类型的对象。可以简单的认为,向量是一个能够存放任意类型的动态数组。
- Vector 与 ArrayList 基本是一致的,不同的是Vector是线程安全的,会在可能出现线程安全的方法前面使用 synchronized 关键字。
六、栈的几种实现方式
1.基于简单数组的实现方式
使用简单数组作为底层数据结构来实现栈,通过将栈顶元素的索引存储在变量中,实现压栈和弹栈操作,每次压栈时将元素添加到数组末尾,每次弹栈时将栈顶元素从数组中删除。由于数组的长度是固定的,需要提前定义栈的最大容量。
public class ArrayStack {
private int[] stack;
private int top;
public ArrayStack(int capacity) {
stack = new int[capacity];
top = -1;
}
public void push(int item) {
if (top == stack.length - 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is full");
}
stack[++top] = item;
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
return stack[top--];
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
return stack[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
}
2.基于动态数组的实现方式
使用动态数组(如ArrayList)作为底层数据结构来实现栈,通过在动态数组的尾部进行插入和删除操作来实现栈的功能。当栈容量不足时,动态数组可以自动进行扩容,当栈元素减少时,动态数组可以自动进行缩容。这种实现方式提供了动态调整容量的特性。
public class DynamicArrayStack {
private ArrayList<Integer> stack;
public DynamicArrayStack() {
stack = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void push(int item) {
stack.add(item);
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
return stack.remove(stack.size() - 1);
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
return stack.get(stack.size() - 1);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
3.基于链表的实现方式
使用链表作为底层数据结构来实现栈,链表的头部或尾部作为栈顶,每次插入和删除操作都在链表的头部进行,通过修改引用来实现栈的操作。链表实现的栈可以动态增加和缩小容量,不需要提前定义栈的最大容量,但相对于数组实现,需要更多的空间开销。
public class LinkedListStack {
private Node top;
private class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public LinkedListStack() {
top = null;
}
public void push(int item) {
Node newNode = new Node(item);
if (isEmpty()) {
top = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = top;
top = newNode;
}
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
int item = top.data;
top = top.next;
return item;
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
return top.data;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == null;
}
}
基于数组的实现与基于链表的实现的区别
(1)基于数组的实现
- 各个操作都是常数时间开销
- 每隔一段时间进行的倍增操作的时间开销较大
(2) 基于链表实现的栈:
- 栈规模的增加和减小都很容易
- 各个操作都是常数时间开销
- 每个操作都需要使用额外的空间和时间开销来处理指针
4.基于队列的实现方式
使用队列作为底层数据结构来实现栈,可以使用两个队列来模拟栈的操作。当压栈时,将元素添加到非空队列中;当弹栈时,将非空队列中的元素依次弹出并放入另一个空队列中,直到剩下最后一个元素,即栈顶元素,然后弹出。这种实现方式可以保持栈顶元素总是在队列的尾部,模拟了栈的后进先出(LIFO)特性。
public class QueueBasedStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue1;
private Queue<Integer> queue2;
private int top;
public QueueBasedStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int item) {
queue1.add(item);
top = item;
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
while (queue1.size() > 1) {
top = queue1.remove();
queue2.add(top);
}
int item = queue1.remove();
Queue<Integer> tempQueue = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = tempQueue;
return item;
}
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stack is empty");
}
return top;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}


























![[计网04] 传输层和应用层 笔记 总结 万字详解](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8c536ed4c04d49fd844aeac865ddd7aa.png)