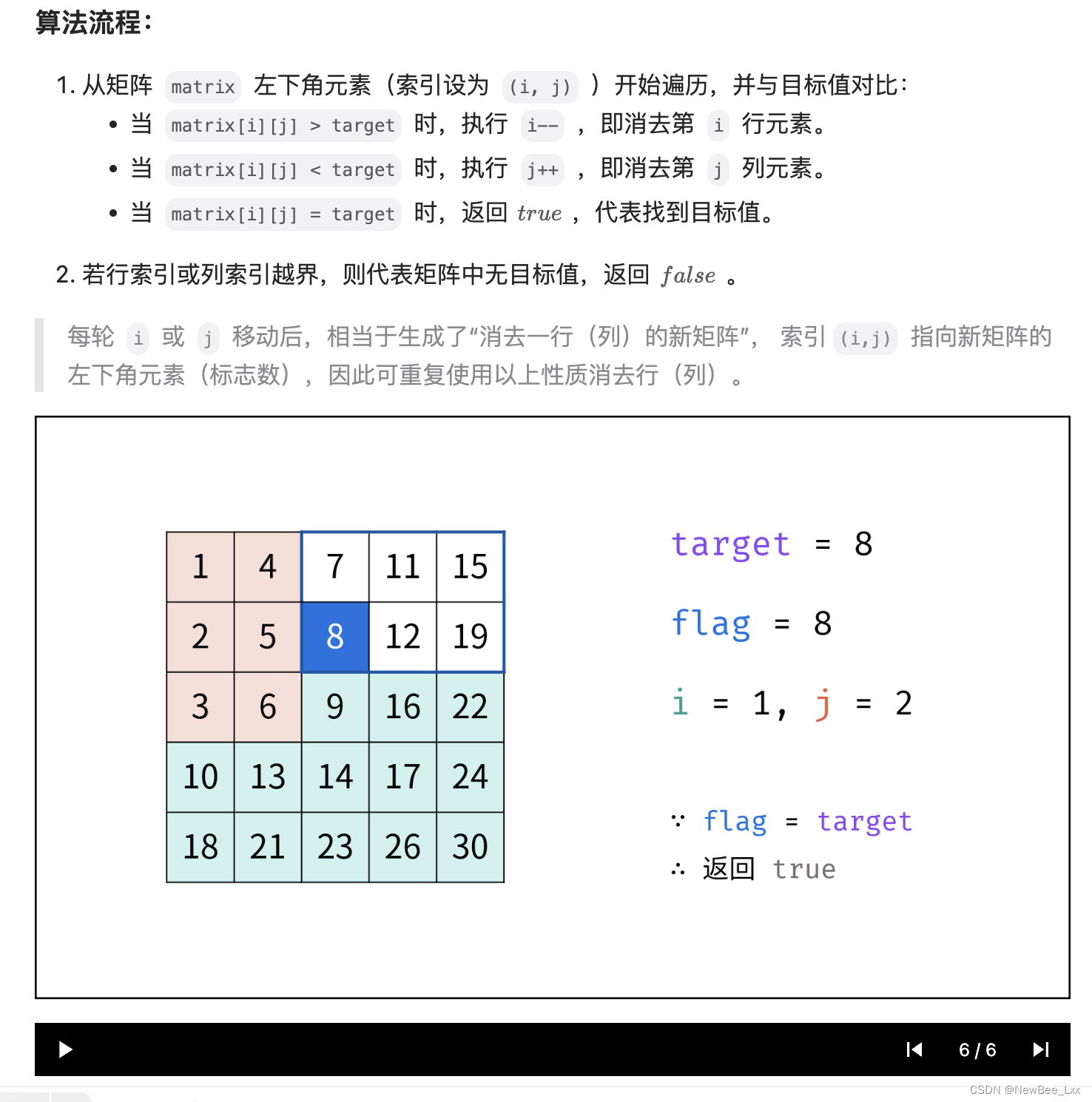
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
法一:迭代,while循环,注意要获取next给变量,得先判断非null,
需要4个变量, n0是前,n1 n2是交换的两,n3是n2的下一个可能为空,这种先把变量保存起来,动链表的时候就不会丢啦
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dum = ListNode(next = head)
n0 = dum
# 迭代,需要3个变量
while n0.next and n0.next.next:
n1 = n0.next
n2 = n1.next
n3 = n2.next # 可null
n0.next = n2
n2.next = n1
n1.next = n3
n0 = n1
return dum.next
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
法二:递归,三个变量,每次返回头节点
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 递归
# 终止条件 head or head head.next == null
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
# 3个变量
n1 = head
n2 = n1.next
n3 = n2.next
n2.next = n1
n1.next = self.swapPairs(n3)
return n2
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
快慢指针
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 删除节点,需要找到前面一个节点
# 但凡考虑头节点特殊情况,加dum虚拟哨兵节点
fast = slow = dum = ListNode(next=head)
for _ in range(n):
fast = fast.next
while fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
t = slow.next
slow.next = t.next
t.next = None
return dum.next
时间复杂度:O(n) 只需要一次循环
空间复杂度:O(1)
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
法一:双指针
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
curA = dumA = ListNode(next = headA)
curB = dumB = ListNode(next = headB)
cntA = 0
cntB = 0
while curA.next:
curA = curA.next
cntA += 1
while curB.next:
curB = curB.next
cntB += 1
curA = dumA
curB = dumB
if cntA - cntB > 0:
for _ in range(cntA - cntB):
curA = curA.next
else:
for _ in range(cntB - cntA):
curB = curB.next
while curA.next != curB.next and curA.next != None:
curA = curA.next
curB = curB.next
return curA.next
# return curA.next if curA.next != None else None

法二:
相交部分长度c,走完a,再走一段b-c,就到了相交的head,对于b,走完b再走一段a-c,也到了相交的head,两个走的长度都一样,如果==就返回,(这个可能是Head也可能没有相交就纯None。
自问:什么时候相遇?
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
A = headA
B = headB
while A != B:
A = A.next if A != None else headB
B = B.next if B != None else headA
return A
相等时有两个情况,到了相交的节点 or 没有相交都是None
142.环形链表II
快慢指针
快指针速度是慢指针的两倍,环长为b,前面直的部分长度为a,当慢指针到达入环的节点时,(走了一段直a)快指针的路径是他的两倍,(在环里走了a),实。接下来他们的速度差还是两倍,快的在前面,慢的在后面,两个的距离越来越大,慢的看做静止,快的相对于慢的走b-a次就能追上慢的,此时慢的也走了b-a次。这是快慢指针的第一次相遇。慢指针再走a次就能到达环的入口,再来第三个指针从head开始和慢指针同速前进,就会在head第二次相遇
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
fast = head
while fast != slow:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
return fast
return

注意
slow = fast = res = ListNode(next = head)
while fast != slow: # 这么写while不会执行
法二:集合法
set:无序不重复,可以看在不在
版本二)集合法
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
visited = set()
while head:
if head in visited:
return head
visited.add(head)
head = head.next
return None