感谢您阅读本文,欢迎“一键三连”。作者定会不负众望,按时按量创作出更优质的内容。
❤️ 1. 毕业设计专栏,毕业季咱们不慌,上千款毕业设计等你来选。
决策树算法是一种常用于分类和回归任务的监督学习算法。它通过树状模型对数据进行决策,是数据挖掘和机器学习中常见的技术之一。本文将详细介绍决策树算法的原理、构建过程,并通过伪代码和Java代码实现一个具体案例。
一、决策树算法原理
1.1 什么是决策树
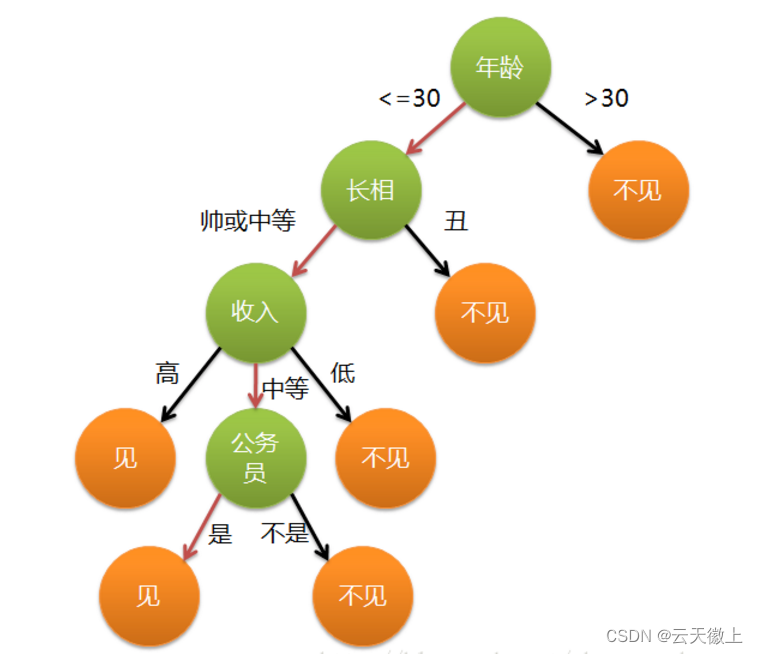
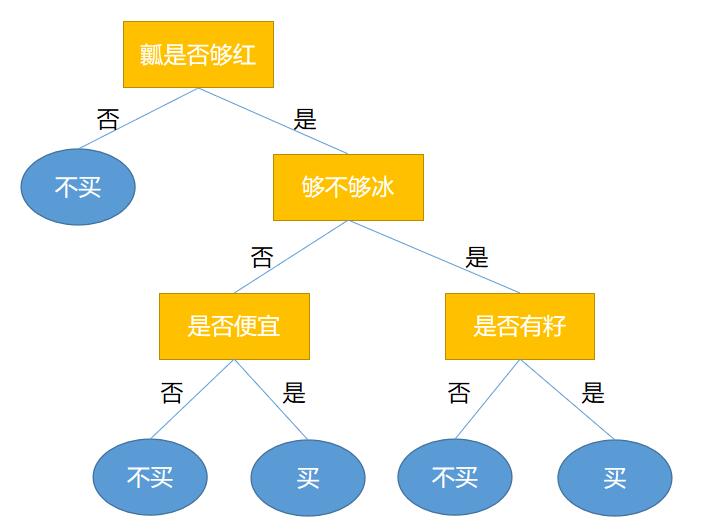
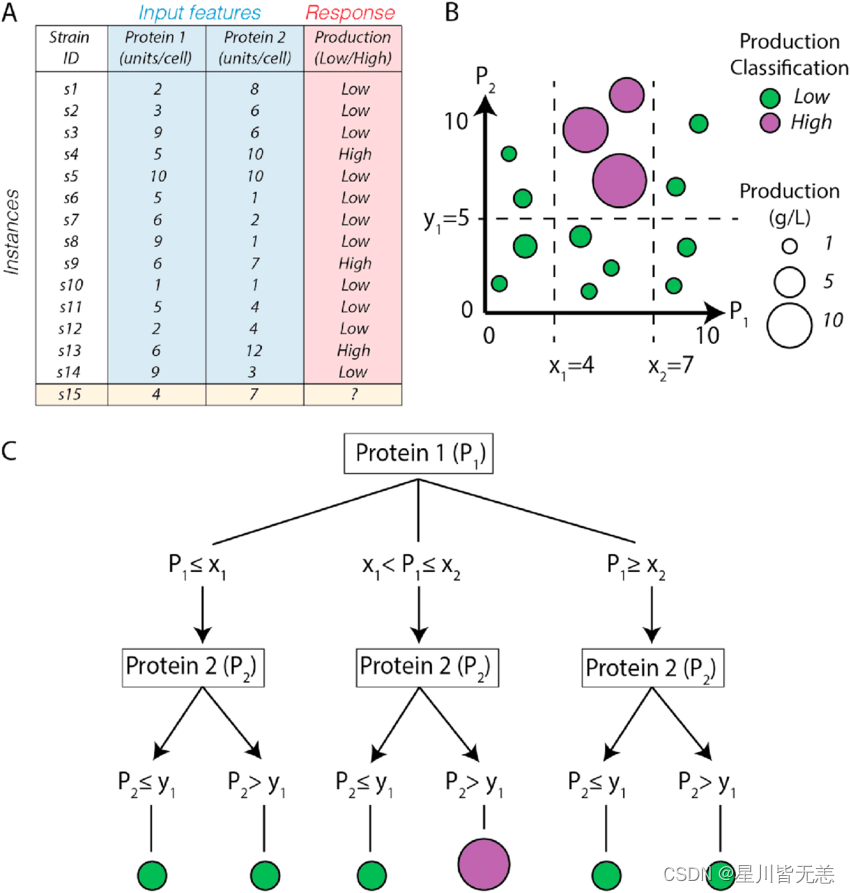
决策树是一种树状结构,其中每个内部节点表示对某个属性的测试,每个分支表示测试结果的某个值,每个叶节点表示一个类别或回归值。决策树的目标是通过分裂数据集来形成一棵能够最大限度地减少数据集中的不纯度的树。
1.2 决策树的构建
决策树的构建过程可以通过以下几个步骤完成:
- 选择最佳属性:选择一个属性作为当前节点的分裂标准。常用的方法有信息增益、基尼指数等。
- 分裂数据集:根据选定的属性将数据集分裂成子集。
- 递归构建子树:对每个子集递归应用上述步骤,直到满足停止条件(如所有实例属于同一类别,或没有更多属性可分)。
1.3 决策树的优缺点
优点:
- 简单直观,易于理解和解释。
- 既适用于分类,也适用于回归任务。
- 不需要特征归一化。
缺点:
- 容易过拟合,尤其是在数据量较小或噪音较多的情况下。
- 对于连续变量,需要对其进行分割处理。
二、决策树算法伪代码
Algorithm: Decision Tree Learning
Input: DataSet D, AttributeList A
Output: Decision Tree T
Function DecisionTree(D, A):
1. Create a node N
2. If all instances in D belong to the same class:
return N as a leaf node with that class label
3. If A is empty:
return N as a leaf node with the most common class label in D
4. Select the attribute a* from A that best splits D (based on criteria like information gain)
5. Label node N with attribute a*
6. For each possible value v of a*:
6.1 Create a child node
6.2 Split the data set D into subsets Dv where a* = v
6.3 If Dv is empty:
Add a leaf node to N with the most common class label in D
6.4 Else:
Recursively apply DecisionTree(Dv, A - {a*}) and attach the subtree to N
7. Return N三、Java 实现
下面是使用 Java 实现决策树算法的代码示例。
3.1 决策树节点类
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
// 决策树节点类
class TreeNode {
String attribute; // 属性名称
Map<String, TreeNode> children; // 子节点
String label; // 类别标签
// 构造函数,叶节点
public TreeNode(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
// 构造函数,决策节点
public TreeNode(String attribute, Map<String, TreeNode> children) {
this.attribute = attribute;
this.children = children;
}
}3.2 决策树算法类
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class DecisionTree {
// 构建决策树
public static TreeNode buildTree(List<Map<String, String>> data, List<String> attributes) {
if (data.isEmpty()) {
return null; // 数据为空,返回null
}
// 检查所有实例是否具有相同的标签
Set<String> labels = data.stream().map(d -> d.get("label")).collect(Collectors.toSet());
if (labels.size() == 1) {
return new TreeNode(labels.iterator().next()); // 所有实例具有相同的标签,创建叶节点
}
if (attributes.isEmpty()) {
// 返回一个具有最常见标签的叶节点
String commonLabel = getMostCommonLabel(data);
return new TreeNode(commonLabel);
}
String bestAttribute = selectBestAttribute(data, attributes); // 选择最佳属性
Map<String, List<Map<String, String>>> partitions = partitionData(data, bestAttribute); // 分割数据
Map<String, TreeNode> children = new HashMap<>();
for (String value : partitions.keySet()) {
List<String> newAttributes = new ArrayList<>(attributes);
newAttributes.remove(bestAttribute); // 删除已使用的属性
children.put(value, buildTree(partitions.get(value), newAttributes)); // 递归构建子树
}
return new TreeNode(bestAttribute, children); // 返回根节点
}
// 选择最佳属性(此处使用简单的方法,实际中应使用信息增益等更复杂的方法)
private static String selectBestAttribute(List<Map<String, String>> data, List<String> attributes) {
return attributes.get(0);
}
// 分割数据集
private static Map<String, List<Map<String, String>>> partitionData(List<Map<String, String>> data, String attribute) {
return data.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(d -> d.get(attribute)));
}
// 获取最常见的标签
private static String getMostCommonLabel(List<Map<String, String>> data) {
return data.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(d -> d.get("label"), Collectors.counting()))
.entrySet().stream().max(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()).get().getKey();
}
// 打印决策树
public static void printTree(TreeNode node, String indent) {
if (node.label != null) {
System.out.println(indent + "Label: " + node.label); // 叶节点
} else {
System.out.println(indent + "Attribute: " + node.attribute); // 决策节点
for (String value : node.children.keySet()) {
System.out.println(indent + " Value: " + value);
printTree(node.children.get(value), indent + " ");
}
}
}
// 主方法,测试决策树
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 示例数据集
List<Map<String, String>> data = new ArrayList<>();
data.add(Map.of("color", "red", "shape", "round", "label", "apple"));
data.add(Map.of("color", "yellow", "shape", "round", "label", "apple"));
data.add(Map.of("color", "red", "shape", "oblong", "label", "banana"));
data.add(Map.of("color", "yellow", "shape", "oblong", "label", "banana"));
List<String> attributes = List.of("color", "shape"); // 属性列表
TreeNode tree = buildTree(data, attributes); // 构建决策树
printTree(tree, ""); // 打印决策树
}
}四、使用场景
决策树广泛应用于许多实际场景中,以下是一些典型的应用场景:
- 医疗诊断:决策树可用于医疗诊断,通过输入病人的症状和体征,决策树可以帮助医生做出诊断决定。
- 信用评估:银行和金融机构使用决策树模型来评估贷款申请人的信用评分,决定是否批准贷款。
- 市场营销:企业可以利用决策树来分析消费者行为,根据消费者的特征进行精准营销,提升转化率。
- 制造业故障诊断:通过分析机器的运行数据,决策树可以帮助识别潜在的故障,进行预防性维护。
- 文本分类:决策树可用于文本分类任务,例如垃圾邮件过滤,通过分析邮件的内容来确定其类别。
五、总结
决策树是一种直观且功能强大的机器学习算法,广泛应用于分类和回归任务中。本文详细介绍了决策树的原理、构建步骤,并通过伪代码和Java代码展示了决策树的实现方法。此外,还介绍了决策树在实际中的应用场景。通过本教程,你将深入理解决策树的基本原理和实际应用,掌握构建决策树模型的方法和技巧。希望本文能对你学习和应用决策树算法有所帮助。
感谢您阅读本文,欢迎“一键三连”。作者定会不负众望,按时按量创作出更优质的内容。
❤️ 1. 毕业设计专栏,毕业季咱们不慌,上千款毕业设计等你来选。