目录
3-37、xlrd.sheet.Sheet.cell_xf_index方法
5、博客个人主页


在Excel中,通常所说的“情侣键”并非官方术语,而是对某些常用且经常成对出现的快捷键的一种形象化的称呼。其中,最为人熟知和广泛使用的“情侣键”是“Ctrl+C”和“Ctrl+V”。
1、Ctrl+C:这个快捷键的作用是“拷贝”或“复制”。当你在Excel中选中某个单元格、一行、一列或整个工作表的内容后,按下Ctrl+C键,这些内容就会被复制到计算机的剪贴板中,等待下一步的粘贴操作。
2、Ctrl+V:这个快捷键的作用是“粘贴”。在你按下Ctrl+C键将内容复制到剪贴板后,可以通过按下Ctrl+V键将这些内容粘贴到Excel中的另一个位置,这两个操作经常是连续进行的,因此Ctrl+C和Ctrl+V就像一对“情侣”,总是成对出现。
除了这对常见的“情侣键”外,Excel中还有许多其他的快捷键可以帮助用户更高效地完成各种操作。然而,这些快捷键通常并没有像Ctrl+C和Ctrl+V那样形成特定的“情侣”关系。
然而,今天我不再展开介绍“情侣键”,而是要重点推介Python中的“情侣库”,即xlrd和xlwt两个第三方库。
一、xlrd库的由来
xlrd库是一种用于在Python中读取Excel文件的库,它的名称中的"xl"代表Excel,"rd"代表读取,其开发者是John Machin(注:库名字符拆分诠释,只是一种猜测)。
xlrd最初是在2005年开始开发的,是基于Python的开源项目(下载:xlrd库官网下载)。
由于Excel文件在数据处理和分析中的重要性,xlrd库填补了Python在处理Excel文件方面的空白,使得用户可以方便地在Python环境中读取Excel文件的内容,并进行进一步的数据操作和分析。
二、xlrd库优缺点
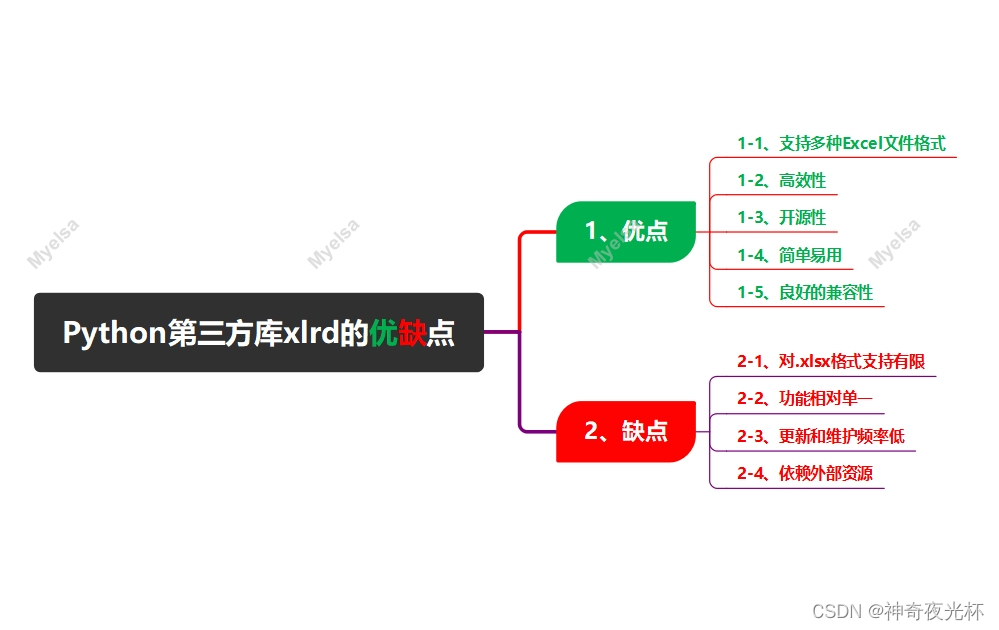
1、优点
1-1、支持多种Excel文件格式
xlrd库支持多种Excel文件格式,包括`.xls`和`.xlsx`(在旧版本中),这使得无论数据存储在哪种格式的Excel文件中,用户都可以使用xlrd库来读取。
1-2、高效性
xlrd库使用C语言编写,因此其性能非常高,即使面对非常大的Excel文件,xlrd也可以快速地读取其中的数据。
1-3、开源性
xlrd是完全开源的,可以在GitHub等平台上找到其源代码,这使得任何人都可以根据自己的需求对其进行修改和扩展。
1-4、简单易用
xlrd提供了简单直接的API来获取单元格数据、行列数等,使得从Excel文件中读取数据变得简单而高效。
1-5、良好的兼容性
xlrd库适配多种Python版本,包括Python 2.7(不包括3.0-3.3)或Python 3.4及以上版本,这为用户提供了广泛的兼容性选择。
2、缺点
2-1、对.xlsx格式支持有限
在xlrd 1.2.0之后的版本中(大约从2020年开始),xlrd库不再支持`.xlsx`文件格式,这限制了xlrd在新版Excel文件(主要是`.xlsx`格式)上的应用。
2-2、功能相对单一
xlrd库主要专注于从Excel文件中读取数据,而不提供写入或修改Excel文件的功能,这使得在处理需要写入或修改Excel文件的任务时,用户需要结合其他库(如`openpyxl`或`xlwt`)使用。
2-3、更新和维护频率低
由于xlrd库主要关注于读取Excel文件的功能,并且随着`.xlsx`格式的普及,其使用范围逐渐缩小,因此,xlrd库的更新和维护频率可能相对较低。
2-4、依赖外部资源
在某些情况下,xlrd库可能需要依赖外部资源或库来完全发挥其功能,这可能会增加用户在使用xlrd库时的复杂性和不确定性。
总之,xlrd库在读取Excel文件方面具有高效、开源和简单易用等优点,但在对`.xlsx`格式的支持、功能单一以及更新和维护频率等方面存在一些缺点,用户在选择使用xlrd库时需要根据自己的需求进行权衡和选择。
三、xlrd库的版本说明
xlrd库适配的Python版本根据库的不同版本而有所不同。以下是针对几个主要版本的说明:
1、xlrd 1.2.0版本
1-1、适配Python>=2.7(不包括3.0-3.3)或Python>=3.4。
1-2、该版本支持xlsx文件格式,并且是一个广泛使用的版本,因为它能够处理小到中等大小的Excel文件,并且具有较好的性能表现。
2、xlrd 2.0.1版本
2-1、适配Python>=2.7(不包括3.0-3.5)或Python>=3.6。
2-2、该版本不再支持xlsx文件格式,仅支持旧版的xls文件格式,因为在xlrd 2.0版本之后,xlrd移除了对xlsx格式的支持。
3、xlrd3(非官方名称)
xlrd3是xlrd的开源扩展库,提供了对xlsx文件格式的支持,然而,请注意,xlrd3并不是xlrd的官方名称(下载:GitHub - Dragon2fly/xlrd3)。
四、如何学好xlrd库?
1、获取xlrd库的属性和方法
用print()和dir()两个函数获取xlrd库所有属性和方法的列表
# ['Book', 'FILE_FORMAT_DESCRIPTIONS', 'FMLA_TYPE_ARRAY', 'FMLA_TYPE_CELL', 'FMLA_TYPE_COND_FMT', 'FMLA_TYPE_DATA_VAL',
# 'FMLA_TYPE_NAME', 'FMLA_TYPE_SHARED', 'Operand', 'PEEK_SIZE', 'Ref3D', 'XLDateError', 'XLRDError', 'XLS_SIGNATURE',
# 'XL_CELL_BLANK', 'XL_CELL_BOOLEAN', 'XL_CELL_DATE', 'XL_CELL_EMPTY', 'XL_CELL_ERROR', 'XL_CELL_NUMBER', 'XL_CELL_TEXT', 'ZIP_SIGNATURE',
# '__VERSION__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__path__',
# '__spec__', '__version__',
# 'biff_text_from_num', 'biffh', 'book', 'cellname', 'cellnameabs', 'colname', 'compdoc', 'count_records', 'decompile_formula',
# 'dump', 'dump_formula', 'empty_cell', 'error_text_from_code', 'evaluate_name_formula', 'formatting', 'formula', 'info',
# 'inspect_format', 'oBOOL', 'oERR', 'oNUM', 'oREF', 'oREL', 'oSTRG', 'oUNK', 'okind_dict', 'open_workbook', 'open_workbook_xls',
# 'os', 'pprint', 'rangename3d', 'rangename3drel', 'sheet', 'sys', 'timemachine', 'xldate', 'xldate_as_datetime', 'xldate_as_tuple', 'zipfile']2、获取xlrd库的帮助信息
用help()函数获取xlrd库的帮助信息
Help on package xlrd:
NAME
xlrd
DESCRIPTION
# Copyright (c) 2005-2012 Stephen John Machin, Lingfo Pty Ltd
# This module is part of the xlrd package, which is released under a
# BSD-style licence.
PACKAGE CONTENTS
biffh
book
compdoc
formatting
formula
info
sheet
timemachine
xldate
FUNCTIONS
count_records(filename, outfile=<_io.TextIOWrapper name='<stdout>' mode='w' encoding='utf-8'>)
For debugging and analysis: summarise the file's BIFF records.
ie: produce a sorted file of ``(record_name, count)``.
:param filename: The path to the file to be summarised.
:param outfile: An open file, to which the summary is written.
dump(filename, outfile=<_io.TextIOWrapper name='<stdout>' mode='w' encoding='utf-8'>, unnumbered=False)
For debugging: dump an XLS file's BIFF records in char & hex.
:param filename: The path to the file to be dumped.
:param outfile: An open file, to which the dump is written.
:param unnumbered: If true, omit offsets (for meaningful diffs).
inspect_format(path=None, content=None)
Inspect the content at the supplied path or the :class:`bytes` content provided
and return the file's type as a :class:`str`, or ``None`` if it cannot
be determined.
:param path:
A :class:`string <str>` path containing the content to inspect.
``~`` will be expanded.
:param content:
The :class:`bytes` content to inspect.
:returns:
A :class:`str`, or ``None`` if the format cannot be determined.
The return value can always be looked up in :data:`FILE_FORMAT_DESCRIPTIONS`
to return a human-readable description of the format found.
open_workbook(filename=None, logfile=<_io.TextIOWrapper name='<stdout>' mode='w' encoding='utf-8'>, verbosity=0, use_mmap=True, file_contents=None, encoding_override=None, formatting_info=False, on_demand=False, ragged_rows=False, ignore_workbook_corruption=False)
Open a spreadsheet file for data extraction.
:param filename: The path to the spreadsheet file to be opened.
:param logfile: An open file to which messages and diagnostics are written.
:param verbosity: Increases the volume of trace material written to the
logfile.
:param use_mmap:
Whether to use the mmap module is determined heuristically.
Use this arg to override the result.
Current heuristic: mmap is used if it exists.
:param file_contents:
A string or an :class:`mmap.mmap` object or some other behave-alike
object. If ``file_contents`` is supplied, ``filename`` will not be used,
except (possibly) in messages.
:param encoding_override:
Used to overcome missing or bad codepage information
in older-version files. See :doc:`unicode`.
:param formatting_info:
The default is ``False``, which saves memory.
In this case, "Blank" cells, which are those with their own formatting
information but no data, are treated as empty by ignoring the file's
``BLANK`` and ``MULBLANK`` records.
This cuts off any bottom or right "margin" of rows of empty or blank
cells.
Only :meth:`~xlrd.sheet.Sheet.cell_value` and
:meth:`~xlrd.sheet.Sheet.cell_type` are available.
When ``True``, formatting information will be read from the spreadsheet
file. This provides all cells, including empty and blank cells.
Formatting information is available for each cell.
Note that this will raise a NotImplementedError when used with an
xlsx file.
:param on_demand:
Governs whether sheets are all loaded initially or when demanded
by the caller. See :doc:`on_demand`.
:param ragged_rows:
The default of ``False`` means all rows are padded out with empty cells so
that all rows have the same size as found in
:attr:`~xlrd.sheet.Sheet.ncols`.
``True`` means that there are no empty cells at the ends of rows.
This can result in substantial memory savings if rows are of widely
varying sizes. See also the :meth:`~xlrd.sheet.Sheet.row_len` method.
:param ignore_workbook_corruption:
This option allows to read corrupted workbooks.
When ``False`` you may face CompDocError: Workbook corruption.
When ``True`` that exception will be ignored.
:returns: An instance of the :class:`~xlrd.book.Book` class.
DATA
FILE_FORMAT_DESCRIPTIONS = {'xls': 'Excel xls', 'xlsb': 'Excel 2007 xl...
FMLA_TYPE_ARRAY = 4
FMLA_TYPE_CELL = 1
FMLA_TYPE_COND_FMT = 8
FMLA_TYPE_DATA_VAL = 16
FMLA_TYPE_NAME = 32
FMLA_TYPE_SHARED = 2
PEEK_SIZE = 8
XLS_SIGNATURE = b'\xd0\xcf\x11\xe0\xa1\xb1\x1a\xe1'
XL_CELL_BLANK = 6
XL_CELL_BOOLEAN = 4
XL_CELL_DATE = 3
XL_CELL_EMPTY = 0
XL_CELL_ERROR = 5
XL_CELL_NUMBER = 2
XL_CELL_TEXT = 1
ZIP_SIGNATURE = b'PK\x03\x04'
__VERSION__ = '2.0.1'
biff_text_from_num = {0: '(not BIFF)', 20: '2.0', 21: '2.1', 30: '3', ...
empty_cell = empty:''
error_text_from_code = {0: '#NULL!', 7: '#DIV/0!', 15: '#VALUE!', 23: ...
oBOOL = 3
oERR = 4
oNUM = 2
oREF = -1
oREL = -2
oSTRG = 1
oUNK = 0
okind_dict = {-2: 'oREL', -1: 'oREF', 0: 'oUNK', 1: 'oSTRG', 2: 'oNUM'...
VERSION
2.0.1
FILE
e:\python_workspace\pythonproject\lib\site-packages\xlrd\__init__.py3、用法精讲
3-33、xlrd.cellname函数
3-33-1、语法
cellname(rowx, colx)
Utility function: ``(5, 7)`` => ``'H6'``3-33-2、参数
3-33-2-1、rowx(必须):一个整数,表示单元格的行号(从0开始计数)。
3-33-2-2、colx(必须):一个整数,表示单元格的列号(从0开始计数)。
3-33-3、功能
用于将单元格的行号和列号转换为Excel单元格的引用格式(如A1、B2等)。
3-33-4、返回值
返回值是一个字符串,表示Excel单元格的引用格式,如"A1", "B2", "C3"等,这个函数根据给定的行号rowx(从0开始)和列号colx(从0开始)来生成对应的Excel单元格引用。
3-33-5、说明
3-33-5-1、 行号和列号都是从0开始的,与Excel中从1开始的计数方式不同。
3-33-5-2、如果列号大于25(即Z列之后),xlrd.cellname会将列号转换为相应的多个字母的组合(如 AA、AB等)。
3-33-6、用法
# 33、xlrd.cellname函数
import xlrd
# 注意:这里并没有真正打开一个Excel文件,只是示例使用xlrd.cellname函数
rowx = 0 # 第1行在Python中索引为0
colx = 0 # 第1列在Python中索引为0
cell_name = xlrd.cellname(rowx, colx)
print(cell_name) # 输出:A13-34、xlrd.cellnameabs函数
3-34-1、语法
cellnameabs(rowx, colx, r1c1=0)
Utility function: ``(5, 7)`` => ``'$H$6'``3-34-2、参数
3-34-2-1、rowx(必须):一个整数,表示单元格的行号(从0开始计数)。
3-34-2-2、colx(必须):一个整数,表示单元格的列号(从0开始计数)。
3-34-2-3、r1c1(可选):表示是否更改Excel公式引用单元格的方式,默认为0,即用字母代表列,用数字代表行的方式。
3-34-3、功能
用于根据给定的行号和列号生成Excel单元格的绝对引用格式字符串。这个函数在处理需要保持引用不变的Excel公式时非常有用。
3-34-4、返回值
返回一个字符串,表示绝对单元格引用的格式,如$A$1、$B$2等。
3-34-5、说明
3-34-5-1、r1c1=0:用字母代表列,用数字代表行的方式。
3-34-5-2、r1c1=1:行列都使用数字的方式。
3-34-6、用法
# 34、xlrd.cellnameabs函数
import xlrd
# 注意:这里并没有真正打开一个Excel文件,只是示例使用xlrd.cellnameabs函数
rowx = 0 # 第1行在Python中索引为0
colx = 0 # 第1列在Python中索引为0
cell_name_abs = xlrd.cellnameabs(rowx, colx)
print(cell_name_abs) # 输出:$A$13-35、xlrd.colname函数
3-35-1、语法
colname(colx)
Utility function: ``7`` => ``'H'``, ``27`` => ``'AB'``
3-35-2、参数
3-35-2-1、colx(必须):一个整数,表示单元格的列号(从0开始计数)。
3-35-3、功能
用于根据给定的列索引(从0开始)返回对应的列名(即Excel中的列标签,如'A', 'B', 'C'等)。
3-35-4、返回值
返回一个字符串,表示与给定列索引对应的Excel列名。
3-35-5、说明
3-35-5-1、列索引是从0开始的,而Excel中的列标签(如'A', 'B', 'C'等)是从1开始的。但在使用xlrd.colname时,你需要使用基于0的索引。
3-35-5-2、如果列索引超出了Excel中的列数范围(即大于或等于16384,因为Excel 2007及更高版本支持最多16384列),xlrd.colname函数可能会返回一个不可预料的值或引发错误。
3-35-6、用法
# 35、xlrd.colname函数
import xlrd
# 假设我们有一个Excel文件,并想要获取其第一列的列名
# 注意:这里并没有真正打开一个Excel文件,只是示例使用xlrd.colname函数
col_index = 0 # 第一列的索引
column_name = xlrd.colname(col_index)
print(column_name) # 输出:A
col_index = 27
column_name = xlrd.colname(col_index)
print(column_name) # 输出:AB3-36、xlrd.count_records函数
3-36-1、语法
count_records(filename, outfile=<_io.TextIOWrapper name='<stdout>' mode='w' encoding='utf-8'>)
For debugging and analysis: summarise the file's BIFF records.
ie: produce a sorted file of ``(record_name, count)``.
:param filename: The path to the file to be summarised.
:param outfile: An open file, to which the summary is written.3-36-2、参数
3-36-2-1、filename(必须):指定要打开的Excel文件的路径和文件名。
3-36-2-2、outfile(可选):用于输出日志的文件对象,默认值为None,即不输出日志。
3-36-3、功能
用于计算Excel文件中工作表(sheet)的总记录数。
3-36-4、返回值
返回一个整数,表示所有工作表中记录的总数。
3-36-5、说明
outfile=<_io.TextIOWrapper name='<stdout>' mode='w' encoding='utf-8'>是一个在Python中表示文件或流对象的字符串描述。具体讲,这涉及到Python的io模块的TextIOWrapper类。
让我们分解这个描述:
3-36-5-1、io.TextIOWrapper
这是Python内部用于处理文本文件或文本流的类。当你使用如open()函数打开一个文件以文本模式(例如'r'、'w'、'a'等)时,你通常会得到一个TextIOWrapper的实例。
3-36-5-2、name='<stdout>'
这表示该流或文件对象与标准输出(`stdout`)相关联。在Python中,sys.stdout是一个常用的文件对象,它代表了程序的标准输出,通常连接到终端或命令行界面。
3-36-5-3、mode='w'
这表示该文件或流以写入模式打开。在写入模式下,你可以向文件或流写入数据,但通常不能读取数据(除非文件是以追加模式'a'打开的)。
3-36-5-4、encoding='utf-8'
这指定了文本数据的编码方式。`utf-8`是一种常用的编码方式,能够表示世界上大多数语言的字符。
3-36-6、用法
# 36、xlrd.count_records函数
import xlrd
# 指定Excel文件的路径
filename = r'E:\360Downloads\test.xls'
# 调用xlrd.count_records函数计算记录数
total_records = xlrd.count_records(filename)
# 打印总记录数
print(f'Total records in the file: {total_records}')3-37、xlrd.sheet.Sheet.cell_xf_index方法
3-37-1、语法
cell_xf_index(self, rowx, colx)
XF index of the cell in the given row and column.
This is an index into :attr:`~xlrd.book.Book.xf_list`.
.. versionadded:: 0.6.13-37-2、参数
3-37-2-1、self(必须):一个对实例对象本身的引用,在类的所有方法中都会自动传递。
3-37-2-2、rowx(必须):一个整数,表示行索引。
3-37-2-3、colx(必须):一个整数,表示列索引。
3-37-3、功能
用于获取指定行和列的单元格的格式(XF)索引。
3-37-4、返回值
返回一个索引值。要获取实际的格式信息,你需要使用这个索引值去访问xf_list列表。
3-37-5、说明
如果你想要检查Excel文件中的格式信息,xlrd库提供了一个参数formatting_info,将其设置为True,它可以在打开工作簿时收集有关单元格格式的信息。
3-37-5-1、xf_index是单元格的扩展格式索引(XF Index),它指向xf_list中的具体格式信息。
3-37-5-2、xf_list是包含所有扩展格式的列表,通过索引可以获取具体的格式对象xf,该对象包含字体、颜色、边框等详细的格式信息。
3-37-6、用法
# 37、xlrd.sheet.Sheet.cell_xf_index方法
import xlrd
# 打开文件,同时获取格式信息
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(r'E:\360Downloads\test.xls', formatting_info=True)
# 选择工作表
sheet = workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
# 获取单元格的格式信息
cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)
xf_index = cell.xf_index
xf = workbook.xf_list[xf_index]
# 输出格式信息
print(f"Cell XF Index: {xf_index}")
print(f"Cell Font Index: {xf.font_index}")
print(f"Cell Background Color: {xf.background.pattern_colour_index}")