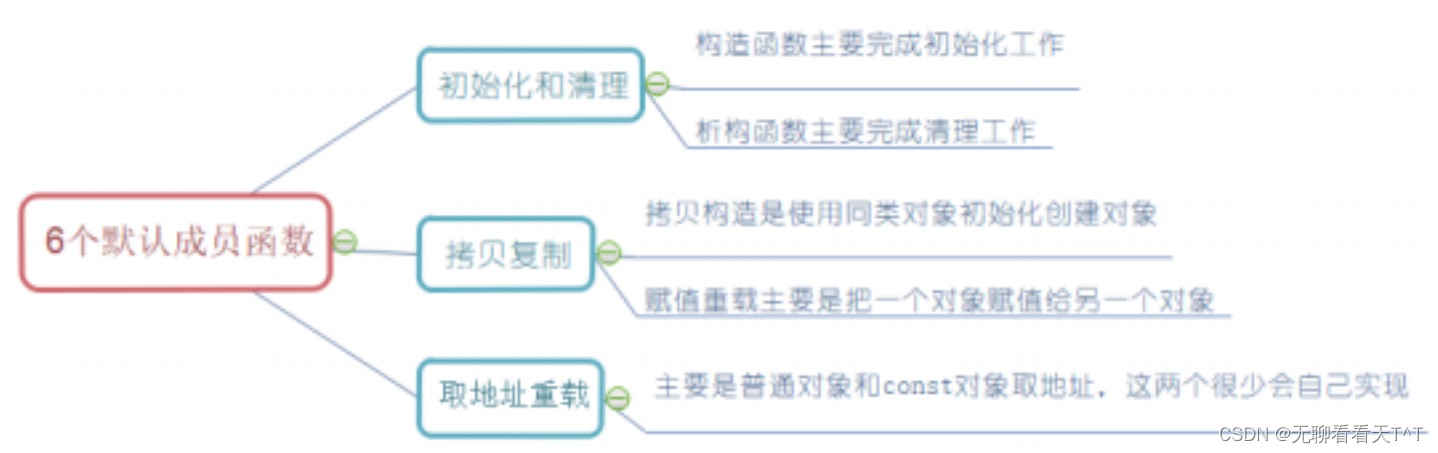
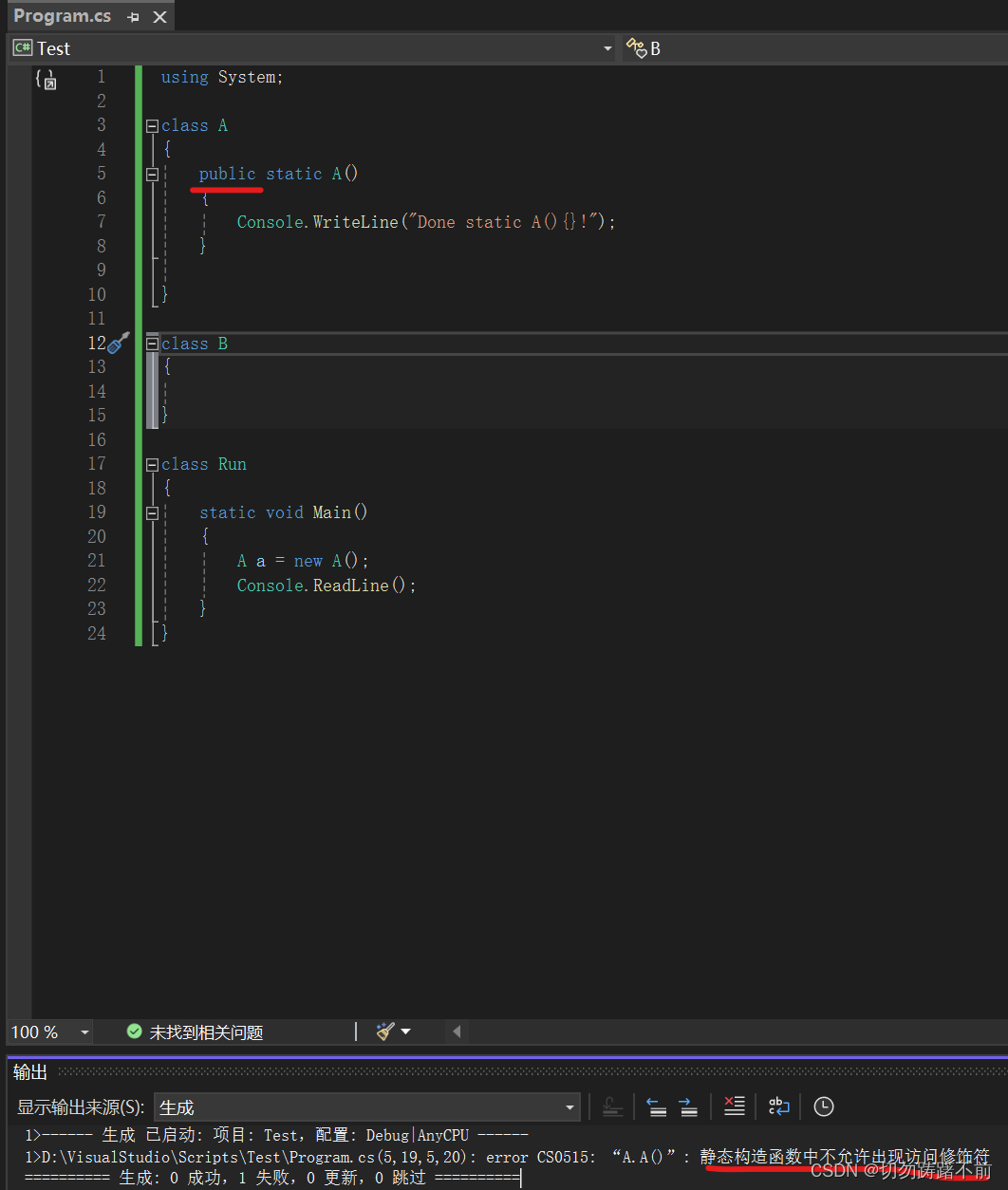
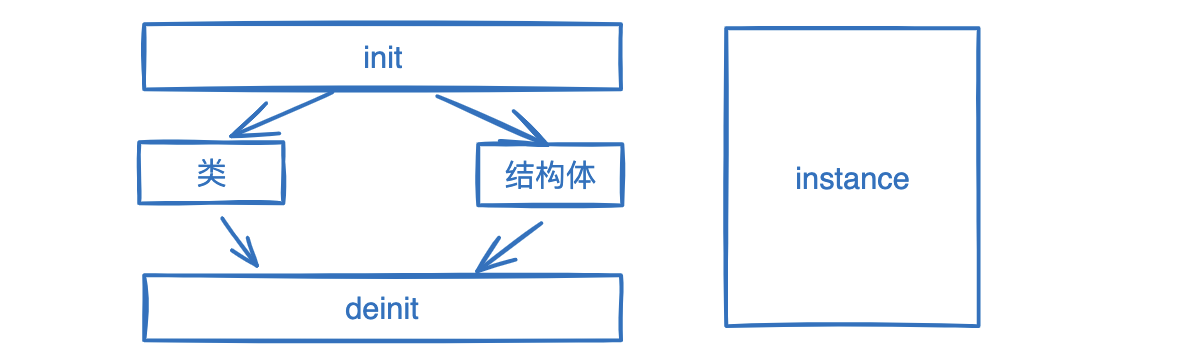
Swift的初始化是一个有大量规则的固定过程。初始化是设置类型实例的操作,包括给每个存储属性初始值,以及一些其他准备工作。完成这个过程后,实例就可以使用了。 简单来讲就是类的构造函数,基本语法如下:
注意:初始化不仅只针对类,也对结构体有效。类和结构体通用
对象初始化函数定义
类的初始化
init是关键字,参数个数0~N个,这个是和Objective-C语言是有点不太一样的。
class CustomType {
init(someValue: SomeType) { //init是关键字,参数个数0~N个
// 初始化代码
}
}
如果不显示声明初始化函数的话,默认为init(){}。
结构体初始化
默认初始化函数
swift为结构体提供了两种默认的构造函数,一种是空属性的,另一种是全属性的。所以像下面的代码两种调用方式都可以。
//Town.swift
struct Town { //定义了一个名为Town的结构体
//定义了两个属性
var population = 5422
var numberOfStoplights = 4
//定义实例方法
func printDescription() {
print("Population: \(population); number of stop lights: \(numberOfStoplights)")
}
//定义修改方法,需要添加mutating关键字
mutating func changePopulation(by amount: Int) {
population += amount
}
}
测试代码
var town = Town()
var town = Town(population:10000, numberOfStoplights:10)
自定义初始化函数
如果自定义了构造函数,上述两种默认构造函数就全不能用了。
struct Town {
//因为删除了默认值,所以不能和自动类型识别了,需要手动指定属性类型
let region: String
var numberOfStoplights: Int
var population: Int {
didSet(oldPopulation) {
print("The population has changed to \(population) from \(oldPopulation).")
}
}
/*下面是自定义的初始化方法,这里的?号表示可失败的初始化方法也可以用!号来代替,也可以不写
1.可失败的意思一般用于参数检查,如果检查失败则返回一个nil值。然后在程序调用时也用myTown?这种方式调用,会更安全;
2. guard 就是一个关键字,用于确保可以提前返回
*/
init?(region: String, population: Int, stoplights: Int) {
//可失败就体现在这里,参数如果不合适,则直接返回nil(创建失改),这种特性比较好用,在其它语言中一种会用抛异常的方式或工厂的方式来实现。
guard population > 0 else {
return nil
}
self.region = region
self.population = population
numberOfStoplights = stoplights
}
//初始化方法2:N/A表示空字符串值传入
init?(population: Int, stoplights: Int) {
self.init(region: "N/A", population: population, stoplights: stoplights)
}
var townSize: Size {
get {
precondition(self.population >= 0, "Town cannot have negative population.")
switch self.population {
case 0...10_000:
return Size.small
case 10_001...100_000:
return Size.medium
default:
return Size.large
}
}
}
enum Size {
case small
case medium
case large
}
func printDescription() {
print("Population: \(population); number of stop lights: \(numberOfStoplights); region: \(region)")
}
mutating func changePopulation(_ amount: Int) {
population += amount
}
}
测试调用
var myTown = Town(population: 5, stoplights: 4)
myTown?.printDescription()
let ts = myTown?.townSize
print(ts) //Optional(swiftcommandtool.Town.Size.small)
对象初始化
类的初始化需要注意继承的问题,默认时类只会提供一个空的构造函数方法,这是和结构体不一样的地方
- 指定初始化方法,用于给类的所有属性设置初始值;程序代码没有任何修饰关键字,可以有多个;
- 便捷初始化方法,只是一种标识,一般会委托给指定初始化方法来实现;用关键字convenience修饰,可以有多个;
- 类的必需初始化方法,一个类要求其子类必须提供特定的初始化方法;
- 反初始化方法,在类的实例销毁时执行内存清理过程;用deinit定义,一个类只能有一个此方法
因为默认的初始化方法必须给所有属性设置初始值,则便捷初始化方法则不需要。
默认初始化方法
类的默认初始化方法也是int(){},与结构体不同,类没有默认的成员初始化方法。这解释了为什么之前要给类设置默认值:这样可以利用自带的空初始化方法。比如:let fredTheZombie = Zombie(),其中的空圆括号表示这是一个默认初始化方法。
自定义构造函数
父类
class Monster {
var town: Town?
var name: String
var victimPool: Int {
get {
return town?.population ?? 0
}
set(newVictimPool) {
town?.population = newVictimPool
}
}
//自定义的初始化方法, required 表示所有子类都必须实现此构造方法,否则程序会报错
required init(town: Town?, monsterName: String) {
self.town = town
name = monsterName
}
func terrorizeTown() {
if town != nil {
print("\(name) is terrorizing a town!")
} else {
print("\(name) hasn't found a town to terrorize yet...")
}
}
}
子类
默认情况下子类不会自动继承父类的初始化方法,目的是希望避免子类在不经意间提供了无法为所有属性赋值的初始化方法,但在下列两种场景中子类会继承父类的初始化方法:
- 子类没有定义任何自定义的初始化方法;
- 如果子类复写了父类所有指定的初始化方法,也会继承父类的所有便捷初始化方法;
class Zombie: Monster {
class var spookyNoise: String {
return "Brains..."
}
var walksWithLimp: Bool
private(set) var isFallingApart: Bool
//子类特有的初始化方法
init(limp: Bool, fallingApart: Bool, town: Town?, monsterName: String) {
walksWithLimp = limp
isFallingApart = fallingApart
super.init(town: town, monsterName: monsterName)
}
//convenience 关键字用来表示快捷初始化方法
convenience init(limp: Bool, fallingApart: Bool) {
self.init(limp: limp, fallingApart: fallingApart, town: nil, monsterName: "Fred")
if walksWithLimp {
print("This zombie has a bad knee.")
}
}
//复写父类的初始化方法,可以省略overrid关键字
required init(town: Town?, monsterName: String) {
walksWithLimp = false
isFallingApart = false
super.init(town: town, monsterName: monsterName) //调用父类构造函数
}
final override func terrorizeTown() {
if !isFallingApart {
town?.changePopulation(-10)
}
}
}
程序调用
//调用Zombie指定初始化方法:init(limp: Bool, fallingApart: Bool, town: Town?, monsterName: String)
//The population has changed to 999995 from 1000005.
//Population: 999995; number of stop lights: 4; region: N/A
var fredTheZombie: Zombie? = Zombie(limp: false, fallingApart: false, town: myTown, monsterName: "Fred")
fredTheZombie?.terrorizeTown()
fredTheZombie?.town?.printDescription()
//调用快捷初始化方法:convenience init(limp: Bool, fallingApart: Bool)
//This zombie has a bad knee.
var convenientZombie = Zombie(limp: true, fallingApart: false)
//Victim pool: Optional(999995)
//The population has changed to 500 from 999995.
//Victim pool: Optional(500)
print("Victim pool: \(fredTheZombie?.victimPool)")
fredTheZombie?.victimPool = 500
print("Victim pool: \(fredTheZombie?.victimPool)")
//调用反初始化方法
//Brains...
//Zombie named Fred is no longer with us.
print(Zombie.spookyNoise)
fredTheZombie = nil
初始化函数参数
初始化的函数参数也和普通函数一样,支持内、外名称加类型这种,也支持一些特殊特性,比如下面的_用法,隐藏外部参数名称。
struct WeightRecordInLBS {
let weight: Double
//用_来指定
init(_ pounds: Double) {
weight = pounds
}
init(kilograms kilos: Double) {
weight = kilos * 2.20462
}
}
//
let wr = WeightRecordInLBS(185)
对象的销毁(反向初始化)
反初始化(deinitialization)是在类的实例没用之后将其清除出内存的过程。从概念上讲,反初始化就是初始化的反面。只有引用类型可以反初始化,值类型不行。 在Swift中,实例被清除出内存之前会调用反初始化方法。这提供了销毁实例前最后做一些维 护工作的机会。
deinit {
print("Zombie named \(name) is no longer with us.")
}


![[lesson<span style='color:red;'>22</span>]对象<span style='color:red;'>的</span><span style='color:red;'>销毁</span>](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7d1b075e67ec44e68fb2404176dd9d2c.png#pic_center)