一、组合模式
1-1、意图
将对象组合成树型结构,以表示"部分-整体"的层次结构。Composite使得用户对单个对象和组
合对象的使用具有一致性。
示例:对象:文件、文件夹

1-2、结构

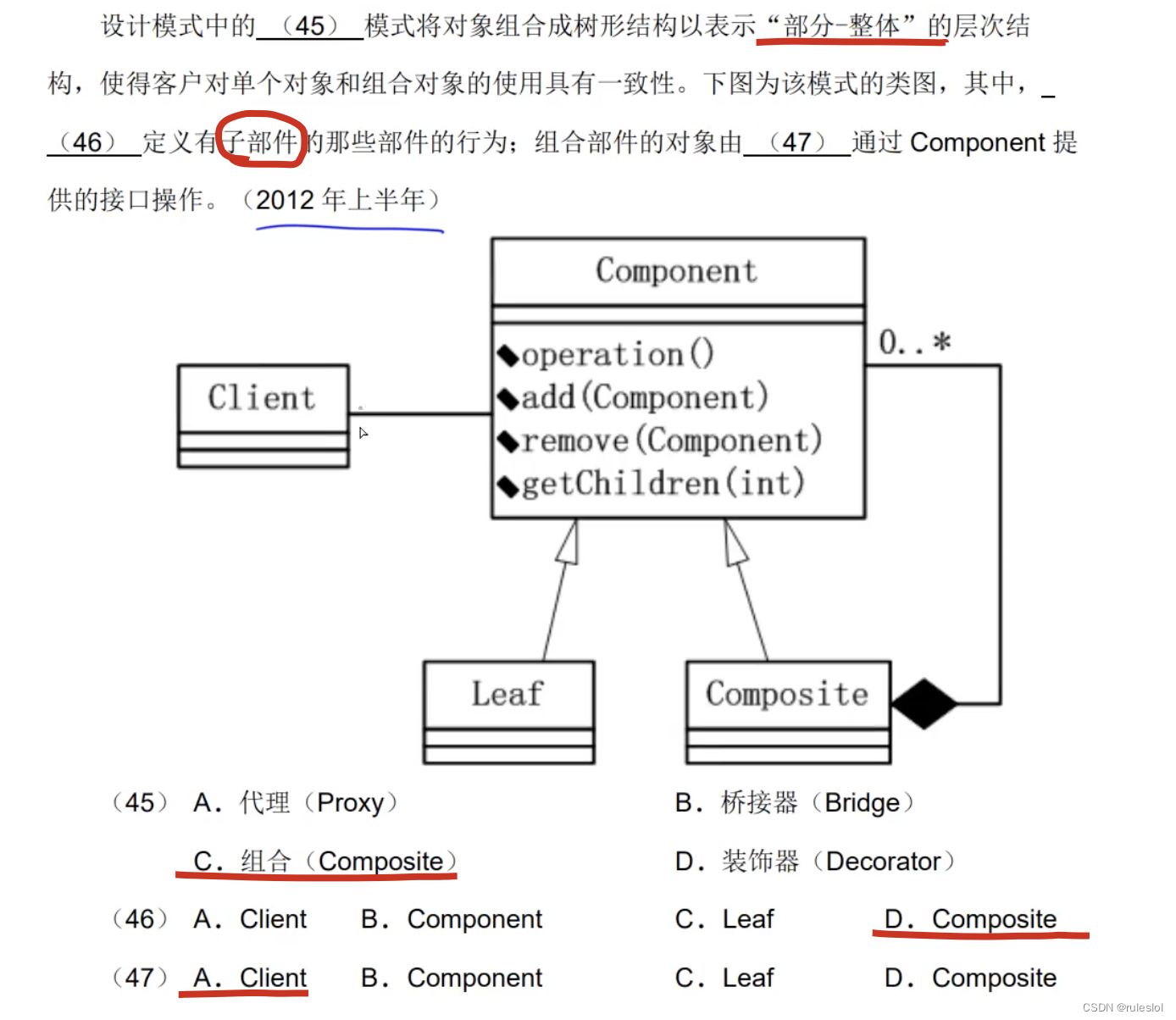
- Component 为组合中的对象声明接口;在适当情况下实现所有类共有接口的默认行为;声明一个接口用于访问和管理 Component 的子组件;(可选) 在递归结构中定义一个接口,用于访问一个父组件,并在合适的情况下实现它。
- Leaf 在组合中表示叶结点对象,叶结点没有子结点: 在组合中定义图元对象的行为。
- Composite 定义有子组件的那些组件的行为;存储子组件;在 Component 接口中实现与子组件有关的操作。
- Client 通过 Component 接口操纵组合组件的对象。
1-3、代码实现
abstract class AbstractFile {
protected String name;
public void printName(){
System.out.println(name);
}
public abstract boolean Add(AbstractFile file);
public abstract boolean remove(AbstractFile file);
public abstract List<AbstractFile> getChild();
}// 文件夹
public class Folder extends AbstractFile {
private List<AbstractFile> childrenList = new ArrayList<AbstractFile>();
public Folder(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean Add(AbstractFile file) {
return childrenList.add(file);
}
@Override
public boolean remove(AbstractFile file) {
return childrenList.remove(file);
}
@Override
public List<AbstractFile> getChild() {
return childrenList;
}
}
// 文件
public class File extends AbstractFile {
public File(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean Add(AbstractFile file) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean remove(AbstractFile file) {
return false;
}
@Override
public List<AbstractFile> getChild() {
return null;
}
}
// 客户端
public class CompositePattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractFile rootFolder = new Folder("rootFolder");
AbstractFile folderA = new Folder("Folder A");
AbstractFile folderB = new Folder("Folder B");
AbstractFile fileC = new File("File C");
AbstractFile fileD = new File("File D");
AbstractFile fileE = new File("File E");
rootFolder.Add(folderA);
rootFolder.Add(folderB);
rootFolder.Add(fileC);
folderB.Add(fileD);
folderB.Add(fileE);
print(rootFolder);
}
static void print(AbstractFile file){
file.printName();
List<AbstractFile> allFile = file.getChild();
if(allFile == null){
return;
}
for(AbstractFile fileChild : allFile){
/*System.out.println("==========");
fileChild.printName();*/
print(fileChild);// 递归
}
}
}
1-4、适用性
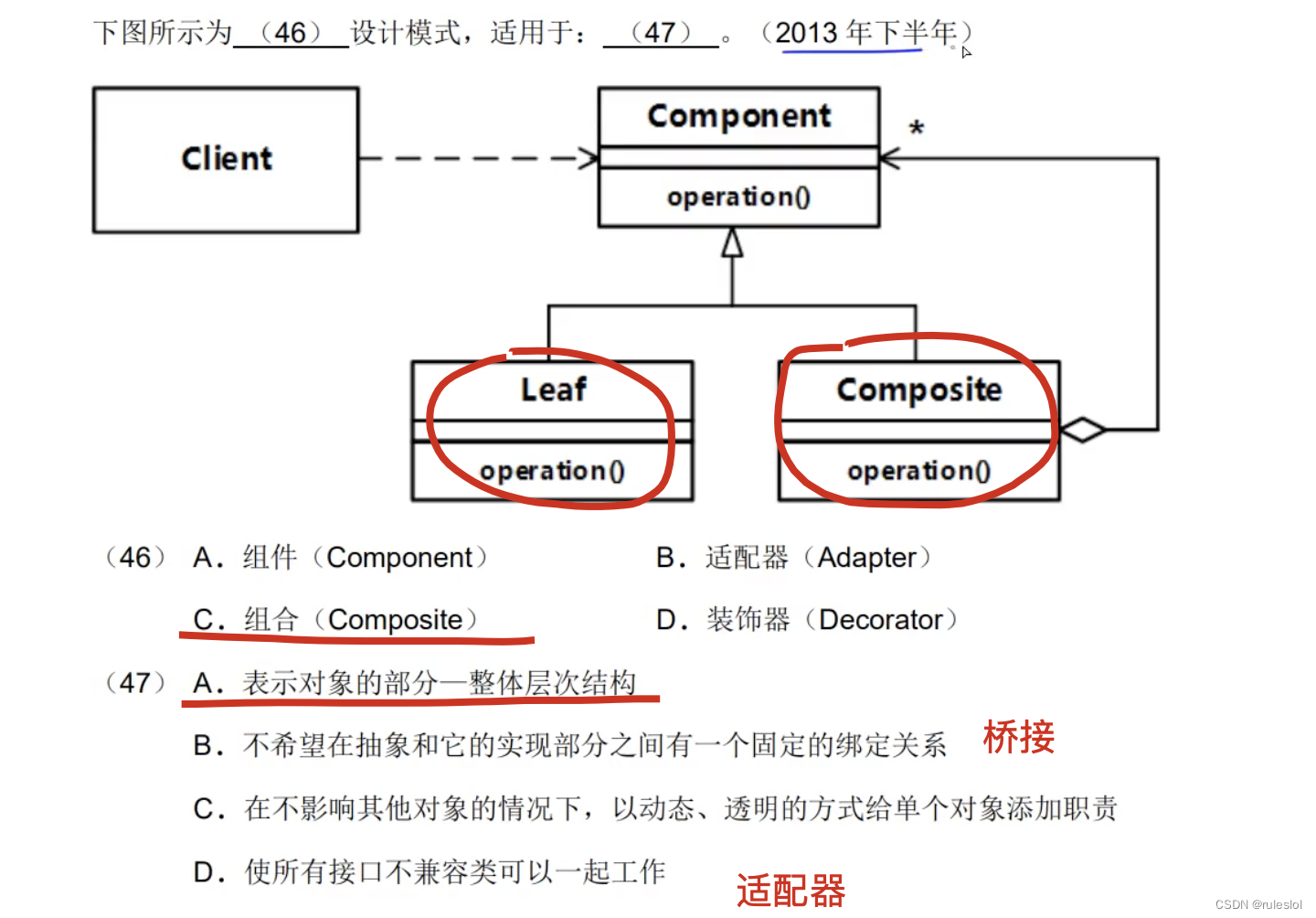
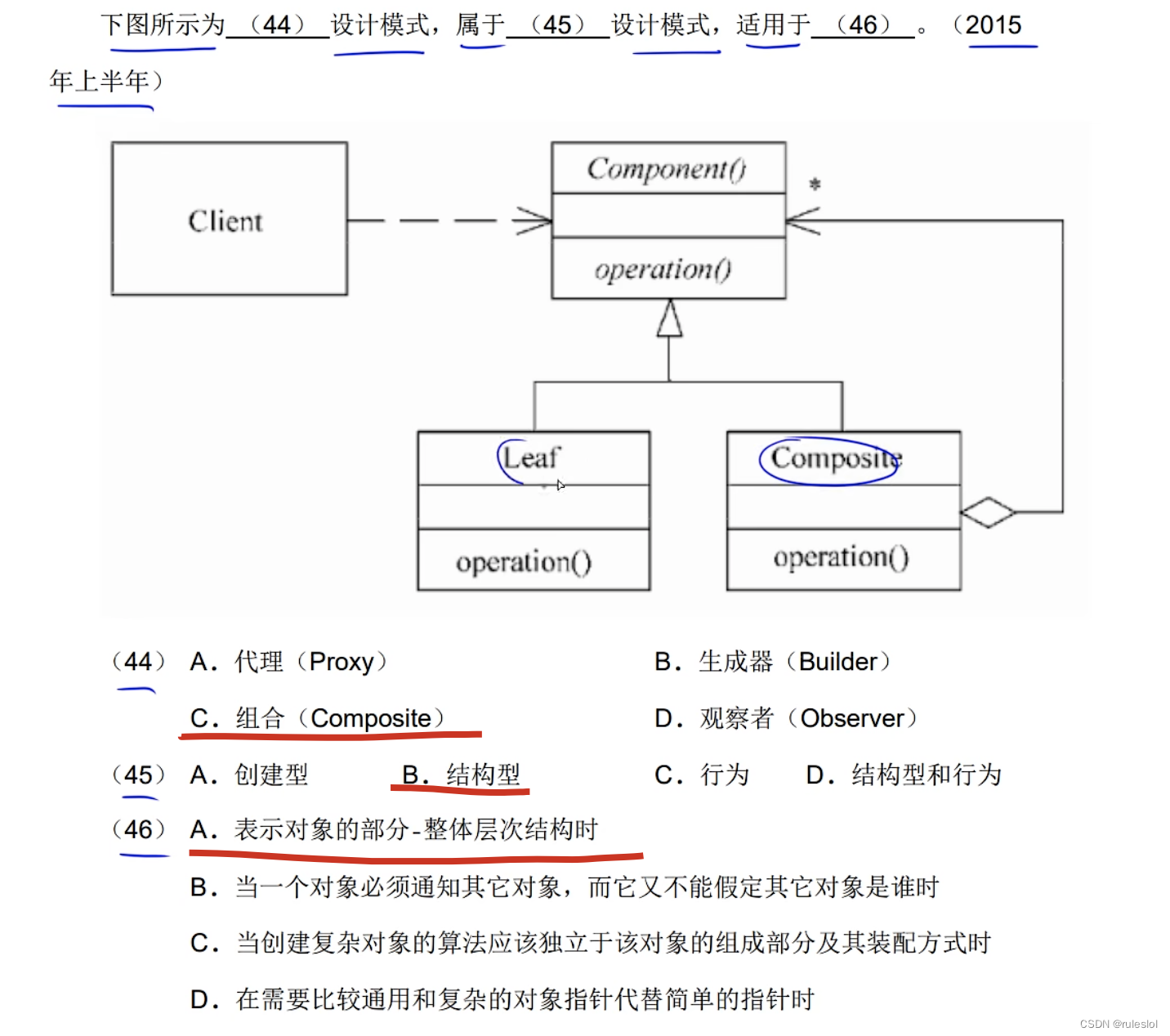
- 想表示对象的部分-整体层次结构。
- 希望用户忽略组合对象与单个对象的不同,用户将统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象。
1-5、真题
真题1:
真题2:
真题3:
二、装饰模式
2-1、意图
动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。
就增加功能而言,Decorator 模式比生成子类更加灵活。
2-2、结构
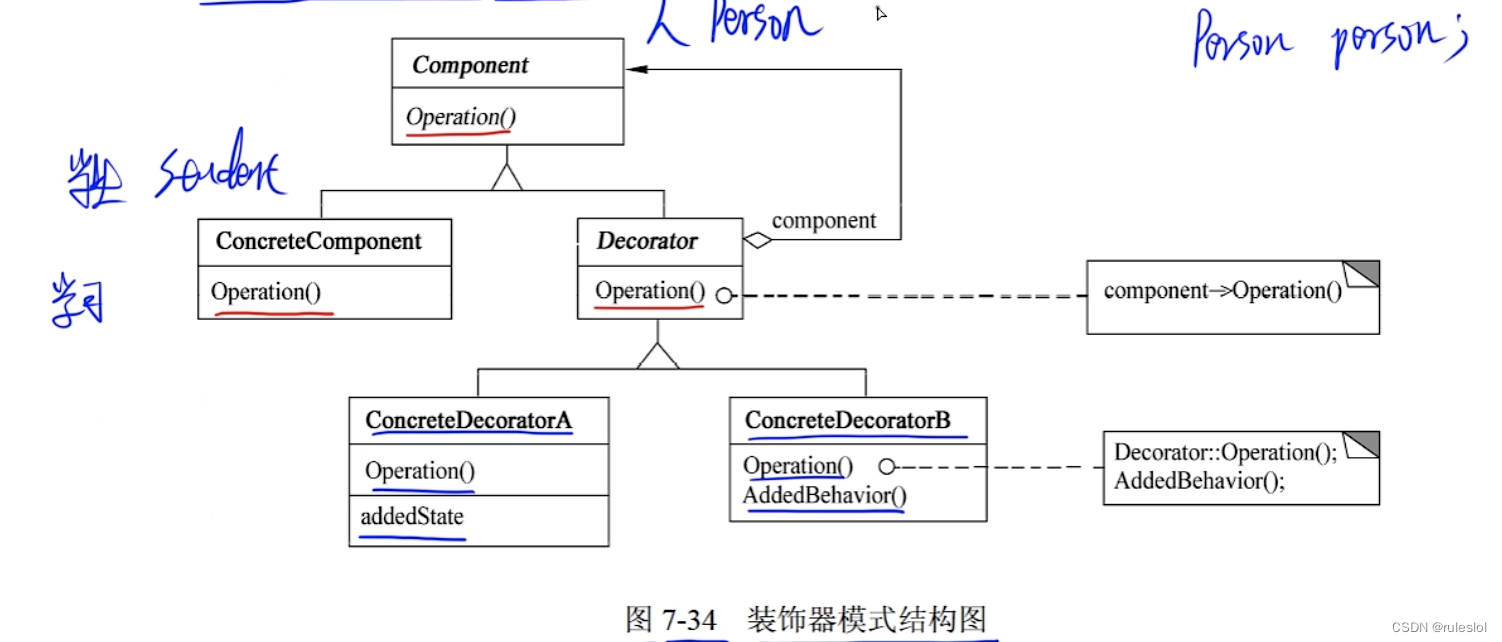
- Component 定义一个对象接口,可以给这些对象动态地添加职责;
- ConcreteComponent 定义一个对象,可以给这个对象添加一些职责;
- Decorator 维持一个指向 Component 对象的指针,并定义一个与 Component 接口一致的接口。
- ConcreteDecorator 向组件添加职责。
2-3、代码实现
abstract class Person {
protected String name;
// 职责
public abstract void Operation();
}public class Student extends Person{
public Student(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void Operation() {
System.out.print(name + "的职责:学习 ");
}
}// 装饰器
abstract class Decorator extends Person{
// Decorator 维持一个指向 Component 对象的指针
protected Person person;
}
public class DecoratorA extends Decorator{
public DecoratorA(Person person){
this.person = person;
}
@Override
public void Operation() {
// 原本的职责
person.Operation();
// 新的职责
System.out.print("写作业 ");
}
}public class DecoratorB extends Decorator{
public DecoratorB(Person person){
this.person = person;
}
@Override
public void Operation() {
// 原本的职责
person.Operation();
// 新的职责
System.out.print("考试 ");
}
}// 客户端
public class DecoratorPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person zhangSan = new Student("张三");
zhangSan.Operation();// 张三的职责:学习
System.out.println();
zhangSan = new DecoratorA(zhangSan);
zhangSan.Operation();// 张三的职责:学习 写作业
System.out.println();
zhangSan = new DecoratorB(zhangSan);// 张三的职责:学习 写作业 考试
zhangSan.Operation();
System.out.println("=============");
// 对象链
Person lili = new DecoratorB(new DecoratorA(new Student("丽丽")));
lili.Operation();// 丽丽的职责:学习 写作业 考试
}
}2-4、适用性
- 在不影响其他对象的情况下,以动态、透明的方式给单个对象添加职责。
- 处理那些可以撤销的职责。
- 当不能采用生成子类的方式进行扩充时。一种情况是,可能有大量独立的扩展,为支持每一种组合将产生大量的子类,使得子类数目呈爆炸性增长。另一种情况可能是,由于类定义被隐藏,或类定义不能用于生成子类。
2-5、真题
真题1:


























![XCTF:level0[WriteUP]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/701fbf1e774a481f9fe77f2699b97619.png)