目录
背景
睡眠对人体健康很重要。监测人体的睡眠分期对于人体健康和医疗具有重要意义。
亮点
- 架构在第一层使用两个具有不同滤波器大小的 CNN 和双向 LSTM。 CNN 可以被训练来学习滤波器,以从原始单通道 EEG 中提取时不变特征,而双向 LSTM 可以被训练来将时间信息(例如睡眠阶段转换规则)编码到模型中。
- 实现了一种两步训练算法,可以通过反向传播有效地端到端训练我们的模型,同时防止模型遭受大睡眠中出现的类别不平衡问题(即学习仅对大多数睡眠阶段进行分类) 数据集。
- 在不改变模型架构和训练算法的情况下,模型可以从两个数据集的不同原始单通道脑电图自动学习睡眠阶段评分的特征,这两个数据集具有不同的属性(例如采样率)和评分标准( AASM 和 R&K)。
环境配置
- python3.5.4
- tensorflowgpu 1.15.2
数据
Sleep-EDF
MASS

方法

模型主要代码:
class MyModel(DeepFeatureNet):
def __init__(
self,
batch_size,
input_dims,
n_classes,
seq_length,
n_rnn_layers,
return_last,
is_train,
reuse_params,
use_dropout_feature,
use_dropout_sequence,
name="deepsleepnet"
):
super(self.__class__, self).__init__(
batch_size=batch_size,
input_dims=input_dims,
n_classes=n_classes,
is_train=is_train,
reuse_params=reuse_params,
use_dropout=use_dropout_feature,
name=name
)
self.seq_length = seq_length
self.n_rnn_layers = n_rnn_layers
self.return_last = return_last
self.use_dropout_sequence = use_dropout_sequence
def _build_placeholder(self):
# Input
name = "x_train" if self.is_train else "x_valid"
self.input_var = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(
tf.float32,
shape=[self.batch_size*self.seq_length, self.input_dims, 1, 1],
name=name + "_inputs"
)
# Target
self.target_var = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(
tf.int32,
shape=[self.batch_size*self.seq_length, ],
name=name + "_targets"
)
def build_model(self, input_var):
# Create a network with superclass method
network = super(self.__class__, self).build_model(
input_var=self.input_var
)
# Residual (or shortcut) connection
output_conns = []
# Fully-connected to select some part of the output to add with the output from bi-directional LSTM
name = "l{}_fc".format(self.layer_idx)
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(name) as scope:
output_tmp = fc(name="fc", input_var=network, n_hiddens=1024, bias=None, wd=0)
output_tmp = batch_norm_new(name="bn", input_var=output_tmp, is_train=self.is_train)
# output_tmp = leaky_relu(name="leaky_relu", input_var=output_tmp)
output_tmp = tf.nn.relu(output_tmp, name="relu")
self.activations.append((name, output_tmp))
self.layer_idx += 1
output_conns.append(output_tmp)
######################################################################
# Reshape the input from (batch_size * seq_length, input_dim) to
# (batch_size, seq_length, input_dim)
name = "l{}_reshape_seq".format(self.layer_idx)
input_dim = network.get_shape()[-1].value
seq_input = tf.reshape(network,
shape=[-1, self.seq_length, input_dim],
name=name)
assert self.batch_size == seq_input.get_shape()[0].value
self.activations.append((name, seq_input))
self.layer_idx += 1
# Bidirectional LSTM network
name = "l{}_bi_lstm".format(self.layer_idx)
hidden_size = 512 # will output 1024 (512 forward, 512 backward)
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(name) as scope:
def lstm_cell():
cell = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(hidden_size,
use_peepholes=True,
state_is_tuple=True,
reuse=tf.compat.v1.get_variable_scope().reuse)
if self.use_dropout_sequence:
keep_prob = 0.5 if self.is_train else 1.0
cell = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(
cell,
output_keep_prob=keep_prob
)
return cell
fw_cell = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([lstm_cell() for _ in range(self.n_rnn_layers)], state_is_tuple = True)
bw_cell = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([lstm_cell() for _ in range(self.n_rnn_layers)], state_is_tuple = True)
# Initial state of RNN
self.fw_initial_state = fw_cell.zero_state(self.batch_size, tf.float32)
self.bw_initial_state = bw_cell.zero_state(self.batch_size, tf.float32)
# Feedforward to MultiRNNCell
list_rnn_inputs = tf.unstack(seq_input, axis=1)
#outputs, fw_state, bw_state = tf.nn.bidirectional_rnn(
outputs, fw_state, bw_state = tf.compat.v1.nn.static_bidirectional_rnn(
cell_fw=fw_cell,
cell_bw=bw_cell,
inputs=list_rnn_inputs,
initial_state_fw=self.fw_initial_state,
initial_state_bw=self.bw_initial_state
)
if self.return_last:
network = outputs[-1]
else:
network = tf.reshape(tf.concat(axis=1, values=outputs), [-1, hidden_size*2],
name=name)
self.activations.append((name, network))
self.layer_idx +=1
self.fw_final_state = fw_state
self.bw_final_state = bw_state
# Append output
output_conns.append(network)
######################################################################
# Add
name = "l{}_add".format(self.layer_idx)
network = tf.add_n(output_conns, name=name)
self.activations.append((name, network))
self.layer_idx += 1
# Dropout
if self.use_dropout_sequence:
name = "l{}_dropout".format(self.layer_idx)
if self.is_train:
network = tf.nn.dropout(network, keep_prob=0.5, name=name)
else:
network = tf.nn.dropout(network, keep_prob=1.0, name=name)
self.activations.append((name, network))
self.layer_idx += 1
return network
def init_ops(self):
self._build_placeholder()
# Get loss and prediction operations
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(self.name) as scope:
# Reuse variables for validation
if self.reuse_params:
scope.reuse_variables()
# Build model
network = self.build_model(input_var=self.input_var)
# Softmax linear
name = "l{}_softmax_linear".format(self.layer_idx)
network = fc(name=name, input_var=network, n_hiddens=self.n_classes, bias=0.0, wd=0)
self.activations.append((name, network))
self.layer_idx += 1
# Outputs of softmax linear are logits
self.logits = network
######### Compute loss #########
# Weighted cross-entropy loss for a sequence of logits (per example)
loss = tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example(
[self.logits],
[self.target_var],
[tf.ones([self.batch_size * self.seq_length])],
name="sequence_loss_by_example"
)
loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss) / self.batch_size
# Regularization loss
regular_loss = tf.add_n(
tf.compat.v1.get_collection("losses", scope=scope.name + "\/"),
name="regular_loss"
)
# print " "
# print "Params to compute regularization loss:"
# for p in tf.compat.v1.get_collection("losses", scope=scope.name + "\/"):
# print p.name
# print " "
# Total loss
self.loss_op = tf.add(loss, regular_loss)
# Predictions
self.pred_op = tf.argmax(self.logits, 1)结果
睡眠分期效果图

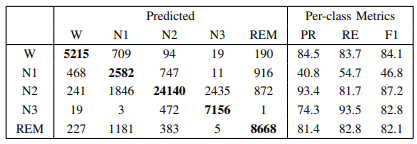
MASS数据集分类表
代码获取
后台私信 1
参考文献
K. Wulffet al., “Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disease,”Nature Reviews Neuroscience, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 589–599, 2010.
C. S. Huanget al., “Knowledge-based identification of sleep stages based on two forehead electroencephalogram channels,”Frontiers in Neuroscience, vol. 8, p. 263, 2014.
N. Srivastavaet al., “Dropout : A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting,”J. of Machine Learning Research, vol. 15, pp. 1929–1958, 2014.
B. Kempet al., “Analysis of a sleep-dependent neuronal feedback loop: The slow-wave microcontinuity of the EEG,”IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., vol. 47, no. 9, pp. 1185–1194, 2000.