目录
拷贝构造函数是否可以修改?/是否可以去掉const关键字和&?
面向过程与面向对象
面向过程:通过一个一个过程的推动导致状态发生变化
面向对象:N个对象之间的交互导致其状态发生变化
在面向对象的世界里,要抽象出对象的类(class,类似于结构体),即对象的共同特征,例如人这种对象,就可以抽象出身份证号,性别,年龄,身高,体重等等
访问权限:
某些数据不希望被其他类所看到,那就需要设置不同的权限,用不同的访问修饰符进行修饰
public:公有成员,可以直接访问
protected:保护成员,专门交给派生类直接访问
private:私有成员,只能再本类内部访问
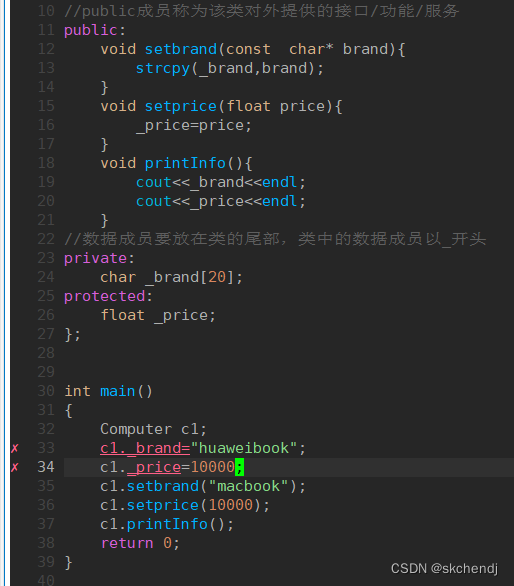
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string.h>
3 using std::cout;
4 using std::endl;
5
6 //c++命名规范:自定义类型首字母大写,
7 //如果有多个单词组成,那么写成驼峰式
8 class Computer
9 {
10 //public成员称为该类对外提供的接口/功能/服务
11 public:
12 void setbrand(const char* brand){
13 strcpy(_brand,brand);
14 }
15 void setprice(float price){
16 _price=price;
17 }
18 void printInfo(){
19 cout<<_brand<<endl;
20 cout<<_price<<endl;
21 }
22 //数据成员要放在类的尾部,类中的数据成员以_开头
23 private:
24 char _brand[20];
25 protected:
26 float _price;
27 };
28
29
30 int main()
31 {
32 Computer c1;
33 //私有成员和保护成员不允许再类外部直接访问
34 /* c1._brand="huaweibook"; */
35 /* c1._price=10000; */
36 c1.setbrand("macbook");
37 c1.setprice(10000);
38 c1.printInfo();
39 return 0;
40 }
运行结果

struct结构体和class的区别
struct的默认访问权限是public,而class的默认访问权限是private
成员函数的定义形式
1.在类内部定义
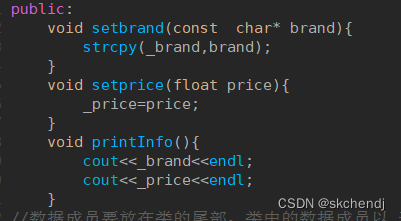
2.在类外部定义(必须加上类作用域)
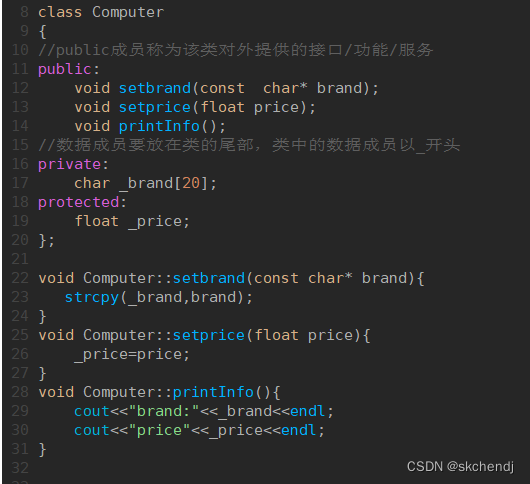
运行结果与在类内部定义成员函数一样

构造函数
对象的创建需要使用构造函数,其形式比较特别:名字与类名相同,不需要返回值
构造函数的作用:初始化对象
有关构造函数的一些情况
1.当在类内部没有定义构造函数时,系统会自动提供一个默认(无参)构造函数
1 #include <iostream>
2 using std::cout;
3 using std::endl;
4
5 class Point
6 {
7 public:
8 //1.当没有定义任何构造函数时,系统会自动提供一个默认
9 //(无参)构造函数
10 void printPoint(){
11 cout<<"("<<_ix<<","<<_iy<<")"<<endl;
12 }
13 private:
14 int _ix;
15 int _iy;
16
17 };
18 void test0(){
19 Point pt;
20 pt.printPoint();
21 }
22 int main()
23 {
24 test0();
25 std::cout << "Hello world" << std::endl;
26 return 0;
27 }
运行结果(x,y)被赋予了一个初值,说明调用了构造函数
![]()
2.当类内部提供了有参构造函数时,系统就不会再提供默认构造函数
1 #include <iostream>
2 using std::cout;
3 using std::endl;
4
5 class Point
6 {
7 public:
8 //2.当类中提供了有参构造函数时,系统就不会在提供默认
9 //构造函数
10 Point(){
11 _ix=0;
12 _iy=0;
13 cout<<"Point()"<<endl;
14 }
15 void printPoint(){
16 cout<<"("<<_ix<<","<<_iy<<")"<<endl;
17 }
18 private:
19 int _ix;
20 int _iy;
21
22 };
23 void test0(){
24 Point pt;
25 pt.printPoint();
26 }
27 int main()
28 {
29 test0();
30 return 0;
31 }
3.构造函数可以重载
1 #include <iostream>
2 using std::cout;
3 using std::endl;
4
5 class Point
6 {
7 public:
8 //3.构造函数现在有2个 说明构造函数可以重载
9 Point(){
10 _ix=0;
11 _iy=0;
12 cout<<"Point()"<<endl;
13 }
14 Point(int ix,int iy){
15 _ix=ix;
16 _iy=iy;
17 cout<<"Point()--"<<endl;
18 }
19 void printPoint(){
20 cout<<"("<<_ix<<","<<_iy<<")"<<endl;
21 }
22 private:
23 int _ix;
24 int _iy;
25
26 };
27 void test0(){
28 Point pt(1,1);
29 pt.printPoint();
30 }
31 int main()
32 {
33 test0();
34 return 0;
35 }
运行结果(根据传入参数判断调用哪一个析构函数)

初始化列表
为了简化初始化列表的使用,可以直接采用default关键字
Point()=default;在构造函数中,有一个初始化列表,用它来完成数据成员的初始化操作
位置在构造函数的形参列表之后,大括号之前,用冒号表示,多个数据之间用逗号进行分割
注意:数据初始化的顺序不是其在初始化列表中的顺序决定的
1 #include <iostream>
2 using std::cout;
3 using std::endl;
4
5 class Point
6 {
7 public:
8 //3.构造函数现在有2个 说明构造函数可以重载
9 Point(int ix,int iy)
10 :_ix(ix)
11 ,_iy(iy)
12 {
13 cout<<"Point()"<<endl;
14 }
15 void printPoint(){
16 cout<<"("<<_ix<<","<<_iy<<")"<<endl;
17 }
18 private:
19 int _ix;
20 int _iy;
21
22 };
23 void test0(){
24 Point pt(1,1);
25 pt.printPoint();
26 }
27 int main()
28 {
29 test0();
30 return 0;
31 }
运行结果

析构函数
对象在销毁时,会自动调用析构函数,也是一个比较特殊的函数
形式:函数名和类名相同,但在其前面要加上一个~,没有参数
作用:用来清理类中申请的资源
1 #include <iostream>
2 using std::cout;
3 using std::endl;
4
5 class Point
6 {
7 public:
8 Point()=default;
9 //3.构造函数现在有2个 说明构造函数可以重载
10 Point(int ix,int iy)
11 {
12 _ix=ix;
13 _iy=iy;
14 cout<<"Point()"<<endl;
15 }
16 void printPoint(){
17 cout<<"("<<_ix<<","<<_iy<<")"<<endl;
18 }
19
20 ~Point(){
21 cout<<"~Point()"<<endl;
22 }
23 private:
24 int _ix;
25 int _iy;
26
27 };
28 void test0(){
29 Point pt(1,1);
30 pt.printPoint();
31 }
32 int main()
33 {
34 test0();
35 return 0;
36 }
析构函数执行

未提供析构函数的情况下开辟堆空间会发生内存泄漏,因为默认自带的析构函数不会释放堆空间
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string.h>
3 using std::cout;
4 using std::endl;
5
6 class Computer
7 {
8 public:
9 //不提供析构函数
10 Computer(const char* brand,float price)
11 :_brand(new char[strlen(brand)+1])
12 ,_price(price)
13 {
14 strcpy(_brand,brand);
15 cout<<"Computer()"<<endl;
16 }
17 void setprice(float price);
18 void printInfo();
19 private:
20 char *_brand;
21 protected:
22 float _price;
23 };
24
25 int main()
26 {
27 Computer c1("macbook",9999);
28 return 0;
29 }
发生内存泄漏

析构函数的调用时机
1.栈对象销毁时,会自动调用析构函数
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string.h>
3 using std::cout;
4 using std::endl;
5
6 class Computer
7 {
8 public:
9 //不提供析构函数
10 Computer(const char* brand,float price)
11 :_brand(new char[strlen(brand)+1])
12 ,_price(price)
13 {
14 strcpy(_brand,brand);
15 cout<<"Computer()"<<endl;
16 }
17
18 ~Computer(){
19 delete [] _brand;
20 _brand =nullptr;
21 cout<<"~Computer"<<endl;
22 }
23 private:
24 char *_brand;
25 protected:
26 float _price;
27 };
28
29 void test0()
30 {
31 Computer c1("华为matebook",9999);
32 //test0运行结束 销毁c1 自动调用析构函数
33
34 }
35
36 int main()
37 {
38 Computer c1("macbook",9999);
39 return 0;
40 }
运行结果:

2.堆对象被销毁时(执行delete表达式时),也会自动调用析构函数
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string.h>
3 using std::cout;
4 using std::endl;
5
6 class Computer
7 {
8 public:
9 //不提供析构函数
10 Computer(const char* brand,float price)
11 :_brand(new char[strlen(brand)+1])
12 ,_price(price)
13 {
14 strcpy(_brand,brand);
15 cout<<"Computer()"<<endl;
16 }
17
18 ~Computer(){
19 delete [] _brand;
20 _brand =nullptr;
21 cout<<"~Computer"<<endl;
22 }
23 private:
24 char *_brand;
25 protected:
26 float _price;
27 };
28
29 void test0()
30 {
31 /* Computer c1("华为matebook",9999); */
32 //test0运行结束 销毁c1 自动调用析构函数
33 Computer* c2 = new Computer("macbook",7777);
34 delete c2;
35 cout<<"执行析构函数"<<endl;
36 /* c2("macbook",7777); */
37 }
39 int main()
40 {
41 test0();
42 return 0;
43 }
3.全局(静态)对象被销毁时(main函数退出时),也会自动调用析构函数
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string.h>
3 using std::cout;
4 using std::endl;
5
6 class Computer
7 {
8 public:
9 //不提供析构函数
10 Computer() = default;
11 Computer(const char* brand,float price)
12 :_brand(new char[strlen(brand)+1])
13 ,_price(price)
14 {
15 strcpy(_brand,brand);
16 cout<<"Computer()"<<endl;
17 }
18
19 ~Computer(){
20 delete [] _brand;
21 _brand =nullptr;
22 cout<<"~Computer"<<endl;
23 }
24 private:
25 char *_brand;
26 protected:
27 float _price;
28 };
29 static Computer c1;
30
31
32 int main()
33 {
34 return 0;
35 } 运行结果

对象的复制
实现类似
int a=10;
int b=a;这样的功能,对象也可以进行复制,需要使用到拷贝构造函数
拷贝构造函数的形式:类名(const 类名 &)
1 #include <iostream>
2 using std::cout;
3 using std::endl;
4
5 class Point
6 {
7 public:
8 Point() = default;
9 Point(int ix=0,int iy=0)
10 {
11 _ix=ix;
12 _iy=iy;
13 }
14
15 void printPoint(){
16 cout<<"("<<_ix<<","<<_iy<<")"<<endl;
17 }
18
19 //拷贝构造函数
20 Point(const Point & rhs)
21 :_ix(rhs._ix)
22 ,_iy(rhs._iy)
23 {
24 cout<<"拷贝构造函数调用"<<endl;
25 }
26 private:
27 int _ix;
28 int _iy;
29
30 };
31 void test0(){
32 Point pt(1,1);
33 Point pt2=pt;
34 }
35 int main()
36 {
37 test0();
38 return 0;
39 }
浅拷贝
只复制了内容,但是使两个指针指向同一片堆空间,会在函数销毁调用析构函数的时候出现问题,即同一片空间被释放了两次
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string.h>
3 using std::cout;
4 using std::endl;
5
6 class Computer
7 {
8 public:
9 Computer()=default;
10 Computer(const char * brand,float price)
11 :_brand(new char[strlen(brand)+1])
12 ,_price(price)
13 {
14 cout<<"构造函数调用"<<endl;
15 }
16 //拷贝构造函数 浅拷贝
17 Computer(const Computer &rhs)
18 :_brand(rhs._brand)
19 ,_price(rhs._price)
20 {
21 cout<<"拷贝构造函数调用,浅拷贝"<<endl;
22 }
23 ~Computer(){
24 delete [] _brand;
25 _brand=nullptr;
26 }
27
28 private:
29 char *_brand;
30 float _price;
31 };
32
33
34 int main()
35 {
36 Computer c1("macbook",9999);
37 Computer c2(c1);
38 return 0;
39 }
运行结果

深拷贝
先开辟空间,在复制内容,相当于开辟了一个新的堆空间,把其他空间的内容复制到新开辟的堆空间中,再释放的时候也是分别释放的两个指针所指的堆空间
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string.h>
3 using std::cout;
4 using std::endl;
5
6 class Computer
7 {
8 public:
9 Computer()=default;
10 Computer(const char * brand,float price)
11 :_brand(new char[strlen(brand)+1])
12 ,_price(price)
13 {
14 cout<<"构造函数调用"<<endl;
15 }
16 //拷贝构造函数 深拷贝
17 Computer(const Computer &rhs)
18 :_brand(new char[strlen(rhs._brand)+1]())
19 ,_price(rhs._price)
20 {
21 strcpy(_brand,rhs._brand);
22 cout<<"拷贝构造函数调用,深拷贝"<<endl;
23 }
24 ~Computer(){
25 if(_brand){
26 delete [] _brand;
27 _brand=nullptr;
28
29 }
30 cout<<"~Computer()"<<endl;
31 }
32
33 private:
34 char *_brand;
35 float _price;
36 };
37
38
39 int main()
40 {
41 Computer c1("macbook",9999);
42 Computer c2(c1);
43 return 0;
44 }
没有发生内存泄漏
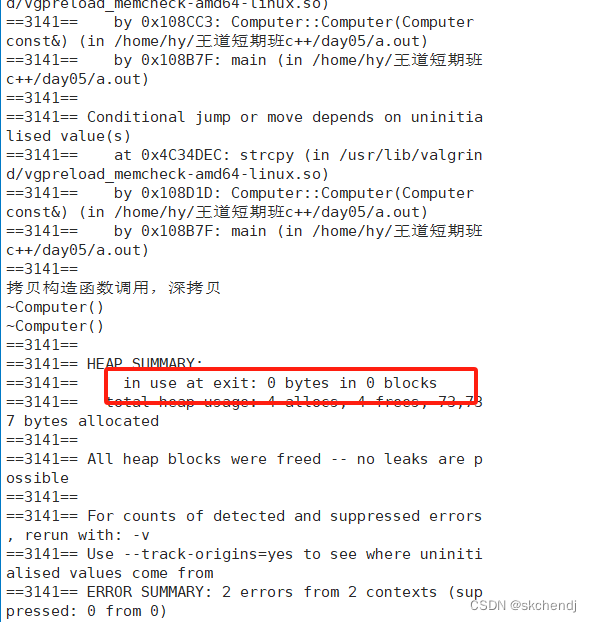
拷贝构造函数是否可以修改?/是否可以去掉const关键字和&?
1.不可以去掉const关键字,否则当传递过来的参数是一个右值时,无法完成对对象的拷贝
右值和左值:c++左值和右值
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <string.h>
3 using std::cout;
4 using std::endl;
5
6 class Computer
7 {
8 public:
9 Computer()=default;
10 Computer(const char * brand,float price)
11 :_brand(new char[strlen(brand)+1])
12 ,_price(price)
13 {
14 cout<<"构造函数调用"<<endl;
15 }
16 //拷贝构造函数 深拷贝
17 Computer(Computer &rhs)
18 :_brand(new char[strlen(rhs._brand)+1]())
19 ,_price(rhs._price)
20 {
21 strcpy(_brand,rhs._brand);
22 cout<<"拷贝构造函数调用,深拷贝"<<endl;
23 }
24 ~Computer(){
25 if(_brand){
26 delete [] _brand;
27 _brand=nullptr;
28
29 }
30 cout<<"~Computer()"<<endl;
31 }
32
33 private:
34 char *_brand;
35 float _price;
36 };
37
38 void test0(){
39 Computer c1=Computer("macbook",9999);
40
41 }
42
43 int main()
44 {
45 test0();
46 return 0;
47 }
当传递过来的值是右值时无法完成拷贝
2.不可以去掉&
去掉&符号之后,每一次只能调用拷贝构造函数,就会初始化形参,在初始化形参时,又会继续调用拷贝构造函数,导致拷贝构造函数的无穷递归调用,没有函数出口,知道栈溢出,程序崩溃
拷贝构造函数的调用时机
1.用一个已经存在的对象初始化另一个新对象
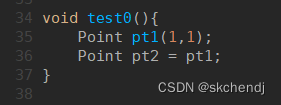
2.当形参是对象,完成形参与实参的结合时(值传递->进行复制)
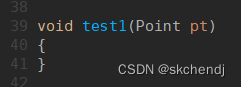
3.当函数的返回值是对象时,执行return语句时

运行结果