文章目录
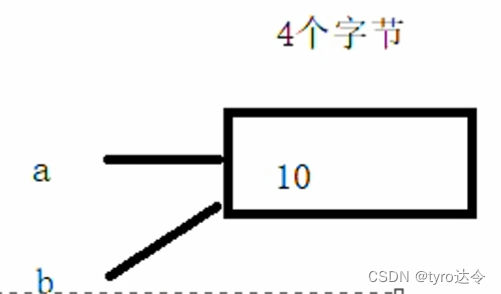
如果一个变量被声明为引用,那它就成了一个已有变量的别名。一个变量可以通过在声明的时候加
& 而成为引用。
此外,还可以将引用变量定义为一种类型,它可以作为另一个变量的引用。& 用于表示变量或任何内存的地址。与引用变量关联的变量,既可以通过变量名访问,也可以通过与之关联的引用变量访问。
语法:
data_type &ref = variable;
例子:
// C++ Program to demonstrate
// use of references
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 10;
// ref is a reference to x.
int& ref = x;
// Value of x is now changed to 20
ref = 20;
cout << "x = " << x << '\n';
// Value of x is now changed to 30
x = 30;
cout << "ref = " << ref << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
x = 20
ref = 30
C++ 引用的应用
C++中的引用有很多的应用,如下是其中的一些:
- 修改函数中传递的参数;
- 避免复制大型结构;
- for 循环中修改所有对象;
- for 循环中避免复制对象;
1. 修改函数中传递的参数
如果一个函数接收到了一个变量的引用,它可以修改这个变量的值。如下程序变量是使用引用交换的。
// C++ Program to demonstrate
// Passing of references as parameters
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function having parameters as
// references
void swap(int& first, int& second)
{
int temp = first;
first = second;
second = temp;
}
// Driver function
int main()
{
// Variables declared
int a = 2, b = 3;
// function called
swap(a, b);
// changes can be seen
// printing both variables
cout << a << " " << b;
return 0;
}
输出:
3 2
2. 避免复制大型结构
想象一下,一个函数必须接收一个大对象。如果我们没有使用引用来传递,那么它的一个新副本就会被创建,这回导致CPU时间和内存的浪费。可以使用引用来避免这种情况。
struct Student {
string name;
string address;
int rollNo;
}
// If we remove & in below function, a new
// copy of the student object is created.
// We use const to avoid accidental updates
// in the function as the purpose of the function
// is to print s only.
void print(const Student &s)
{
cout << s.name << " " << s.address << " " << s.rollNo
<< '\n';
}
3. for 循环中修改所有对象
我们可以在每个循环中使用引用来修改所有元素。
// C++ Program for changing the
// values of elements while traversing
// using references
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector<int> vect{
10, 20, 30, 40 };
// We can modify elements if we
// use reference
for (int& x : vect) {
x = x + 5;
}
// Printing elements
for (int x : vect) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
15 25 35 45
4. for 循环中避免复制对象
我们可以在每个循环中使用引用,以避免在对象很大时复制单个对象。
// C++ Program to use references
// For Each Loop to avoid the
// copy of objects
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Declaring vector
vector<string> vect{
"geeksforgeeks practice",
"geeksforgeeks write",
"geeksforgeeks ide" };
// We avoid copy of the whole string
// object by using reference.
for (const auto& x : vect) {
cout << x << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
输出
geeksforgeeks practice
geeksforgeeks write
geeksforgeeks ide
References vs Pointers
引用和指针都可以用于在一个函数中修改另一个函数的局部变量。当作为参数传递给函数或从函数返回时,它们都可以用来避免复制大对象,从而提高效率。尽管有上述相似之处,引用和指针之间还是有以下区别。
- 指针可以被声明为
void,但引用不可以int a = 10; void* aa = &a; // it is valid void& ar = a; // it is not valid - 指针变量有n层/多层的间接,即单指针、双指针、三指针。然而,引用变量只有一个间接层次。下面的代码揭示了上述几点:
输出:// C++ Program to demonstrate // references and pointers #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Driver Code int main() { // simple or ordinary variable. int i = 10; // single pointer int* p = &i; // double pointer int** pt = &p; // triple pointer int*** ptr = &pt; // All the above pointers differ in the value they store // or point to. cout << "i = " << i << "\t" << "p = " << p << "\t" << "pt = " << pt << "\t" << "ptr = " << ptr << '\n'; // simple or ordinary variable int a = 5; int& S = a; int& S0 = S; int& S1 = S0; // All the references do not differ in their // values as they all refer to the same variable. cout << "a = " << a << "\t" << "S = " << S << "\t" << "S0 = " << S0 << "\t" << "S1 = " << S1 << '\n'; return 0; }i = 10 p = 0x7ffecfe7c07c pt = 0x7ffecfe7c080 ptr = 0x7ffecfe7c088 a = 5 S = 5 S0 = 5 S1 = 5 - 引用变量不能更新;
- 引用变量是一个内部指针;
- 引用变量的声明前面有
&符号(但不要将其读作“address of”)。
引用的限制
- 一个引用一旦被创建,它就不能再引用另一个对象;它不能被重置。这通常使用指针完成。
- 引用不能是NULL。指针经常用 NULL 来表示它没有指向任何有效的东西。
- 引用必须在声明的时候初始化,而指针没有该限制。
由于上面的限制,C++中的引用不能用于实现如链表、树等数据结构。Java 中,引用没有上述限制,可以用于实现所有的数据结构。Java不需要指针的主要原因是引用功能更强大。
使用引用的优点
- 更安全:由于引用必须初始化,所以像野指针这样的野引用不太可能存在。但仍然有可能存在不指向有效位置的引用(见下面练习中的第5和6题)
- 使用更方便:引用不需要解引用运算符来访问值。它们可以像普通变量一样使用。
&运算符只有在声明的时候需要。此外,对象引用的成员可以通过点运算符(.) 访问,而不像指针,需要箭头运算符(->) 才能访问成员。
除了上述原因,还有一些地方如拷贝构造函数不能使用指针。在拷贝构造函数中必须使用引用传递实参,类似地,重载某些运算符如++时必须使用引用。
练习
Quesition 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int& fun()
{
static int x = 10;
return x;
}
int main()
{
fun() = 30;
cout << fun();
return 0;
}
输出:
30
Question 2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fun(int& x) {
return x; }
int main()
{
cout << fun(10);
return 0;
}
输出:
./3337ee98-ae6e-4792-8128-7c879288221f.cpp: In function 'int main()':
./3337ee98-ae6e-4792-8128-7c879288221f.cpp:8:19: error: invalid initialization of non-const reference of type 'int&' from an rvalue of type 'int'
cout << fun(10);
^
./3337ee98-ae6e-4792-8128-7c879288221f.cpp:4:5: note: in passing argument 1 of 'int fun(int&)'
int fun(int& x) {
return x; }
Question 3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(char*& str1, char*& str2)
{
char* temp = str1;
str1 = str2;
str2 = temp;
}
int main()
{
char* str1 = "GEEKS";
char* str2 = "FOR GEEKS";
swap(str1, str2);
cout << "str1 is " << str1 << '\n';
cout << "str2 is " << str2 << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
str1 is FOR GEEKS
str2 is GEEKS
Question 4
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 10;
int* ptr = &x;
int&* ptr1 = ptr;
}
输出:
./18074365-ebdc-4b13-81f2-cfc42bb4b035.cpp: In function 'int main()':
./18074365-ebdc-4b13-81f2-cfc42bb4b035.cpp:8:11: error: cannot declare pointer to 'int&'
int&* ptr1 = ptr;
Question 5
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int* ptr = NULL;
int& ref = *ptr;
cout << ref << '\n';
}
输出:
timeout: the monitored command dumped core
/bin/bash: line 1: 34 Segmentation fault timeout 15s ./372da97e-346c-4594-990f-14edda1f5021 < 372da97e-346c-4594-990f-14edda1f5021.in
Question 6
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int& fun()
{
int x = 10;
return x;
}
int main()
{
fun() = 30;
cout << fun();
return 0;
}
输出:
0