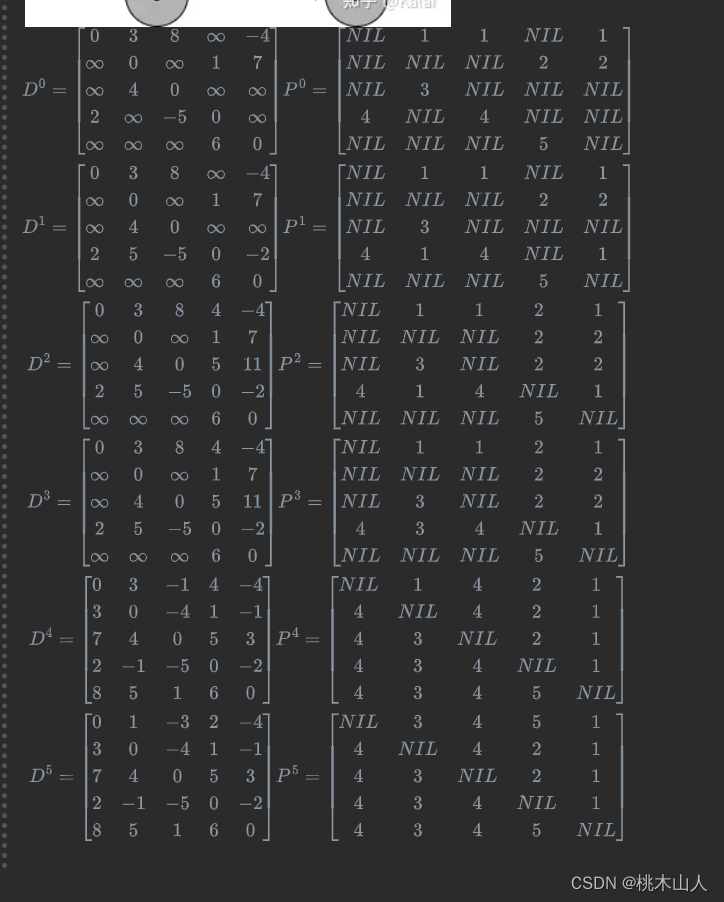
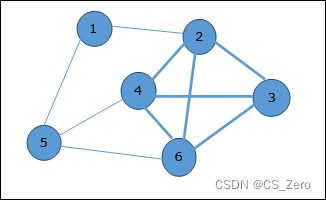
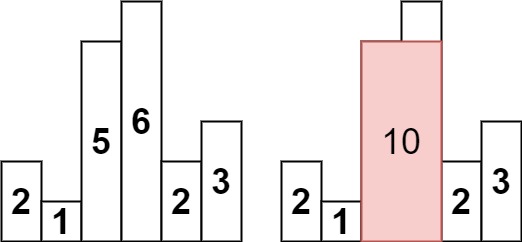
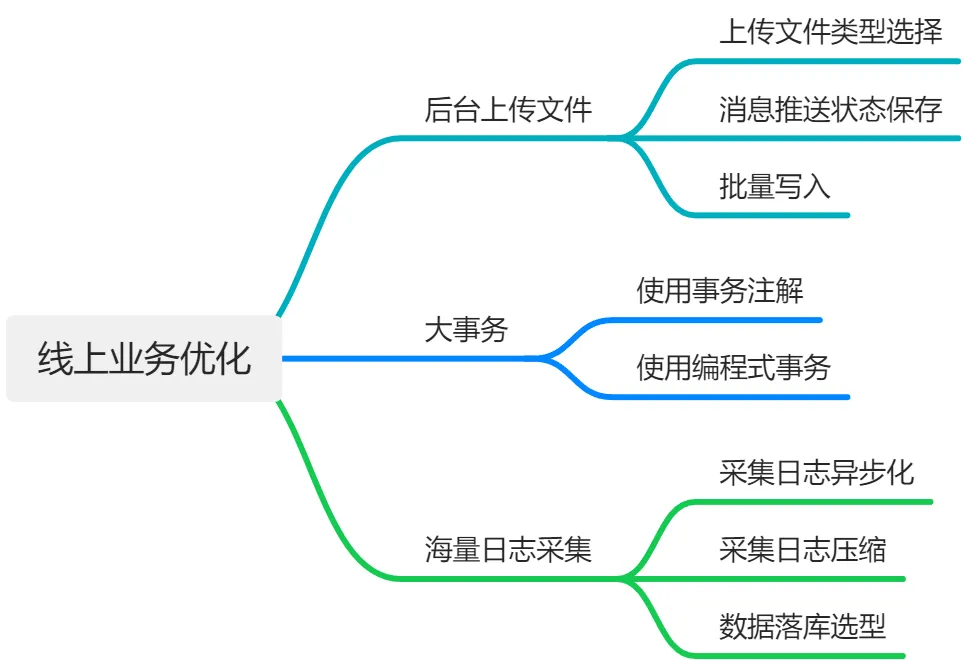
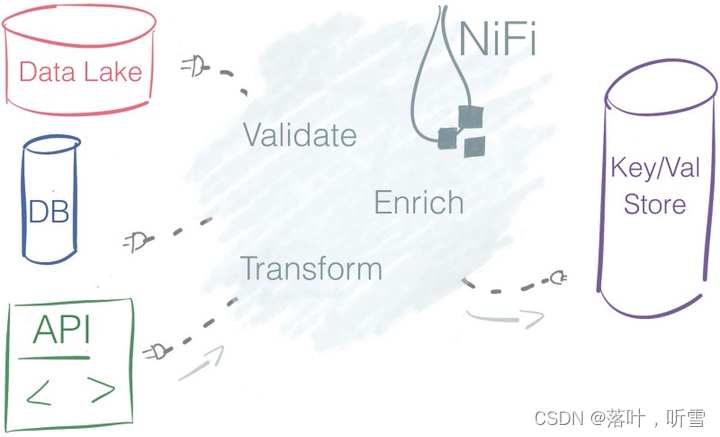
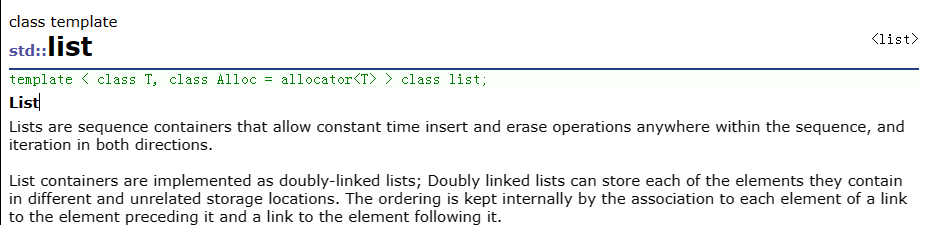
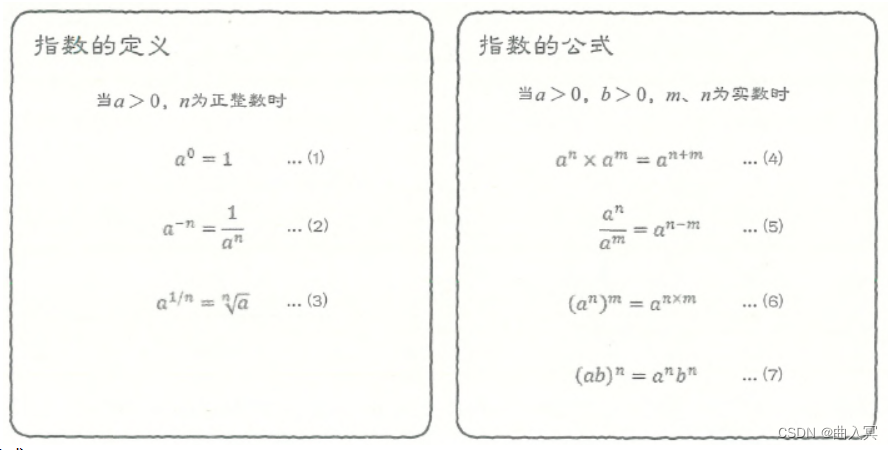
1 文本格式
// C++ implementation of Dinic's Algorithm
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A structure to represent a edge between
// two vertex
struct Edge
{
int v; // Vertex v (or "to" vertex)
// of a directed edge u-v. "From"
// vertex u can be obtained using
// index in adjacent array.
int flow; // flow of data in edge
int C; // capacity
int rev; // To store index of reverse
// edge in adjacency list so that
// we can quickly find it.
};
// Residual Graph
class Graph
{
int V; // number of vertex
int* level; // stores level of a node
vector< Edge >* adj;
public:
Graph(int V)
{
adj = new vector<Edge>[V];
this->V = V;
level = new int[V];
}
// add edge to the graph
void addEdge(int u, int v, int C)
{
// Forward edge : 0 flow and C capacity
Edge a{ v, 0, C, adj[v].size() };
// Back edge : 0 flow and 0 capacity
Edge b{ u, 0, 0, adj[u].size() };
adj[u].push_back(a);
adj[v].push_back(b); // reverse edge
}
bool BFS(int s, int t);
int sendFlow(int s, int flow, int t, int ptr[]);
int DinicMaxflow(int s, int t);
};
// Finds if more flow can be sent from s to t.
// Also assigns levels to nodes.
bool Graph::BFS(int s, int t)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
level[i] = -1;
level[s] = 0; // Level of source vertex
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex
// and mark source vertex as visited here
// level[] array works as visited array also.
list< int > q;
q.push_back(s);
vector<Edge>::iterator i;
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();
q.pop_front();
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); i++)
{
Edge& e = *i;
if (level[e.v] < 0 && e.flow < e.C)
{
// Level of current vertex is,
// level of parent + 1
level[e.v] = level[u] + 1;
q.push_back(e.v);
}
}
}
// IF we can not reach to the sink we
// return false else true
return level[t] < 0 ? false : true;
}
// A DFS based function to send flow after BFS has
// figured out that there is a possible flow and
// constructed levels. This function called multiple
// times for a single call of BFS.
// flow : Current flow send by parent function call
// start[] : To keep track of next edge to be explored.
// start[i] stores count of edges explored
// from i.
// u : Current vertex
// t : Sink
int Graph::sendFlow(int u, int flow, int t, int start[])
{
// Sink reached
if (u == t)
return flow;
// Traverse all adjacent edges one -by - one.
for (; start[u] < adj[u].size(); start[u]++)
{
// Pick next edge from adjacency list of u
Edge& e = adj[u][start[u]];
if (level[e.v] == level[u] + 1 && e.flow < e.C)
{
// find minimum flow from u to t
int curr_flow = min(flow, e.C - e.flow);
int temp_flow = sendFlow(e.v, curr_flow, t, start);
// flow is greater than zero
if (temp_flow > 0)
{
// add flow to current edge
e.flow += temp_flow;
// subtract flow from reverse edge
// of current edge
adj[e.v][e.rev].flow -= temp_flow;
return temp_flow;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// Returns maximum flow in graph
int Graph::DinicMaxflow(int s, int t)
{
// Corner case
if (s == t)
return -1;
int total = 0; // Initialize result
// Augment the flow while there is path
// from source to sink
while (BFS(s, t) == true)
{
// store how many edges are visited
// from V { 0 to V }
int* start = new int[V + 1];
// while flow is not zero in graph from S to D
while (int flow = sendFlow(s, INT_MAX, t, start))
// Add path flow to overall flow
total += flow;
}
// return maximum flow
return total;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
Graph g(6);
g.addEdge(0, 1, 16);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 13);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 10);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 12);
g.addEdge(2, 1, 4);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 14);
g.addEdge(3, 2, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 20);
g.addEdge(4, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 4);
// next exmp
/*g.addEdge(0, 1, 3 );
g.addEdge(0, 2, 7 ) ;
g.addEdge(1, 3, 9);
g.addEdge(1, 4, 9 );
g.addEdge(2, 1, 9 );
g.addEdge(2, 4, 9);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 3);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 7 );
g.addEdge(0, 4, 10);
// next exp
g.addEdge(0, 1, 10);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 10);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 4 );
g.addEdge(1, 4, 8 );
g.addEdge(1, 2, 2 );
g.addEdge(2, 4, 9 );
g.addEdge(3, 5, 10 );
g.addEdge(4, 3, 6 );
g.addEdge(4, 5, 10 ); */
cout << "Maximum flow " << g.DinicMaxflow(0, 5);
return 0;
}
2 代码格式
// C++ implementation of Dinic's Algorithm
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A structure to represent a edge between
// two vertex
struct Edge
{
int v; // Vertex v (or "to" vertex)
// of a directed edge u-v. "From"
// vertex u can be obtained using
// index in adjacent array.
int flow; // flow of data in edge
int C; // capacity
int rev; // To store index of reverse
// edge in adjacency list so that
// we can quickly find it.
};
// Residual Graph
class Graph
{
int V; // number of vertex
int* level; // stores level of a node
vector< Edge >* adj;
public:
Graph(int V)
{
adj = new vector<Edge>[V];
this->V = V;
level = new int[V];
}
// add edge to the graph
void addEdge(int u, int v, int C)
{
// Forward edge : 0 flow and C capacity
Edge a{ v, 0, C, adj[v].size() };
// Back edge : 0 flow and 0 capacity
Edge b{ u, 0, 0, adj[u].size() };
adj[u].push_back(a);
adj[v].push_back(b); // reverse edge
}
bool BFS(int s, int t);
int sendFlow(int s, int flow, int t, int ptr[]);
int DinicMaxflow(int s, int t);
};
// Finds if more flow can be sent from s to t.
// Also assigns levels to nodes.
bool Graph::BFS(int s, int t)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
level[i] = -1;
level[s] = 0; // Level of source vertex
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex
// and mark source vertex as visited here
// level[] array works as visited array also.
list< int > q;
q.push_back(s);
vector<Edge>::iterator i;
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();
q.pop_front();
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); i++)
{
Edge& e = *i;
if (level[e.v] < 0 && e.flow < e.C)
{
// Level of current vertex is,
// level of parent + 1
level[e.v] = level[u] + 1;
q.push_back(e.v);
}
}
}
// IF we can not reach to the sink we
// return false else true
return level[t] < 0 ? false : true;
}
// A DFS based function to send flow after BFS has
// figured out that there is a possible flow and
// constructed levels. This function called multiple
// times for a single call of BFS.
// flow : Current flow send by parent function call
// start[] : To keep track of next edge to be explored.
// start[i] stores count of edges explored
// from i.
// u : Current vertex
// t : Sink
int Graph::sendFlow(int u, int flow, int t, int start[])
{
// Sink reached
if (u == t)
return flow;
// Traverse all adjacent edges one -by - one.
for (; start[u] < adj[u].size(); start[u]++)
{
// Pick next edge from adjacency list of u
Edge& e = adj[u][start[u]];
if (level[e.v] == level[u] + 1 && e.flow < e.C)
{
// find minimum flow from u to t
int curr_flow = min(flow, e.C - e.flow);
int temp_flow = sendFlow(e.v, curr_flow, t, start);
// flow is greater than zero
if (temp_flow > 0)
{
// add flow to current edge
e.flow += temp_flow;
// subtract flow from reverse edge
// of current edge
adj[e.v][e.rev].flow -= temp_flow;
return temp_flow;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// Returns maximum flow in graph
int Graph::DinicMaxflow(int s, int t)
{
// Corner case
if (s == t)
return -1;
int total = 0; // Initialize result
// Augment the flow while there is path
// from source to sink
while (BFS(s, t) == true)
{
// store how many edges are visited
// from V { 0 to V }
int* start = new int[V + 1];
// while flow is not zero in graph from S to D
while (int flow = sendFlow(s, INT_MAX, t, start))
// Add path flow to overall flow
total += flow;
}
// return maximum flow
return total;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
Graph g(6);
g.addEdge(0, 1, 16);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 13);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 10);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 12);
g.addEdge(2, 1, 4);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 14);
g.addEdge(3, 2, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 20);
g.addEdge(4, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 4);
// next exmp
/*g.addEdge(0, 1, 3 );
g.addEdge(0, 2, 7 ) ;
g.addEdge(1, 3, 9);
g.addEdge(1, 4, 9 );
g.addEdge(2, 1, 9 );
g.addEdge(2, 4, 9);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 3);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 7 );
g.addEdge(0, 4, 10);
// next exp
g.addEdge(0, 1, 10);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 10);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 4 );
g.addEdge(1, 4, 8 );
g.addEdge(1, 2, 2 );
g.addEdge(2, 4, 9 );
g.addEdge(3, 5, 10 );
g.addEdge(4, 3, 6 );
g.addEdge(4, 5, 10 ); */
cout << "Maximum flow " << g.DinicMaxflow(0, 5);
return 0;
}