4.1 排序
4.1.1 选择排序
4.1.2 插入排序
4.1.3 排序与sort函数的应用
sort函数参数
sort(首元素地址,尾元素的下一个元素的地址,比较函数(cmp,非必填))
如果不写比较函数,那默认对给定区间进行递增排序
如何实现比较函数
从基本数据类型、结构体类型、STL容器进行自定排序
(1)基本数据类型
如果不指定cmp函数则默认从小到大排序
#include<cstdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[5]={3,1,4,2};
sort(a,a+4);
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++){
printf("%d",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
如果逆序则>,正序<
#include<cstdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a,int b){
return a>b;//如果a>b把a放b前面
}
int main(){
int a[5]={3,1,4,2};
sort(a,a+4,cmp);
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++){
printf("%d",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
(2)结构体数组
在 C++ 中,如果你想对一个结构体数组进行排序,并且需要自定义排序逻辑,你可以通过定义一个比较函数 cmp 来实现。这个比较函数将基于结构体的一个或多个属性来决定排序的顺序。下面是一个示例,展示如何对一个包含某些属性的结构体数组进行排序。
定义结构体
首先,我们定义一个简单的结构体,比如一个描述人的结构体,包含姓名和年龄:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
struct Person {
std::string name;
int age;
};
自定义比较函数
接下来,我们定义一个比较函数,这个函数可以基于年龄进行排序:
bool cmp(const Person &a, const Person &b) {
return a.age < b.age; // 升序排序
}
或者,如果你想要根据姓名的字典顺序进行降序排序,可以这样写:
bool cmp(const Person &a, const Person &b) {
return a.name > b.name; // 姓名的降序排序
}
使用 sort 函数
最后,你可以创建一个 Person 类型的数组或向量,并使用 sort 函数与自定义比较函数来排序:
int main() {
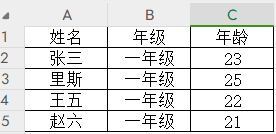
std::vector<Person> people = {
{"Alice", 30},
{"Bob", 25},
{"Charlie", 35}
};
// 根据年龄升序排序
std::sort(people.begin(), people.end(), cmp);
// 输出排序后的结果
for (const auto &person : people) {
std::cout << person.name << " is " << person.age << " years old.\n";
}
return 0;
}
(3)综合应用
1.定义相关结构体
struct student{
char name[10];
char id[10];
int score;
int r;//排名
}stu[100000];
2.cmp函数的编写
解释
按分数排序:如果两个学生的分数不同 (
a.score != b.score),函数将根据分数的降序来比较学生。这意味着分数较高的学生将排在分数较低的学生之前。按名字排序:如果两个学生的分数相同,那么
cmp函数使用strcmp函数来比较他们的名字。strcmp函数返回一个整数来表示两个字符串的比较结果:- 如果返回值小于 0,表示第一个字符串在字典序中位于第二个字符串之前。
- 如果返回值等于 0,表示两个字符串相等。
- 如果返回值大于 0,表示第一个字符串在字典序中位于第二个字符串之后。
因此,strcmp(a.name, b.name) < 0 表示如果 a.name 在字典序中早于 b.name,则应该返回 true,即 a 应该在 b 前面。
bool cmp(Student a,Student b){
if(a.score!=b.score) return a.score>b.score;
else return strcmp(a.name,b.name)<0;
}
3.排名的实现
int r = 1;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
if(i>0&&stu[i].score!=stu[i-1].score){
r = i+1;
}
stu[i].r = r;
}

![Vue3[黑马笔记]<span style='color:red;'>未</span><span style='color:red;'>完</span><span style='color:red;'>待续</span>](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d9313ece4ce04452886d12fa6d63dccf.png#pic_center)

















![[python]pyscipopt安装后测试代码](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/424cd785e291423dae5c80301456d11d.png)