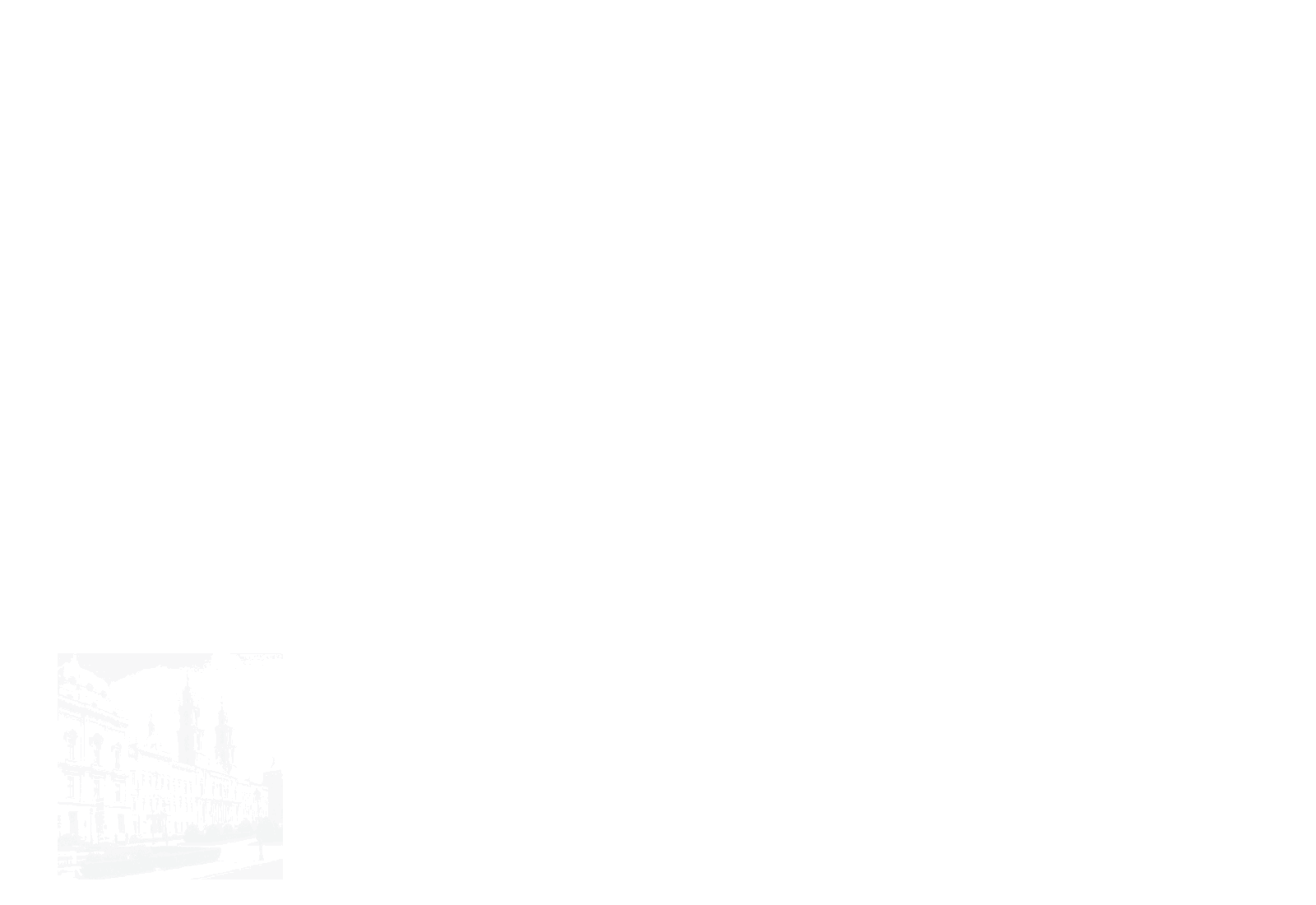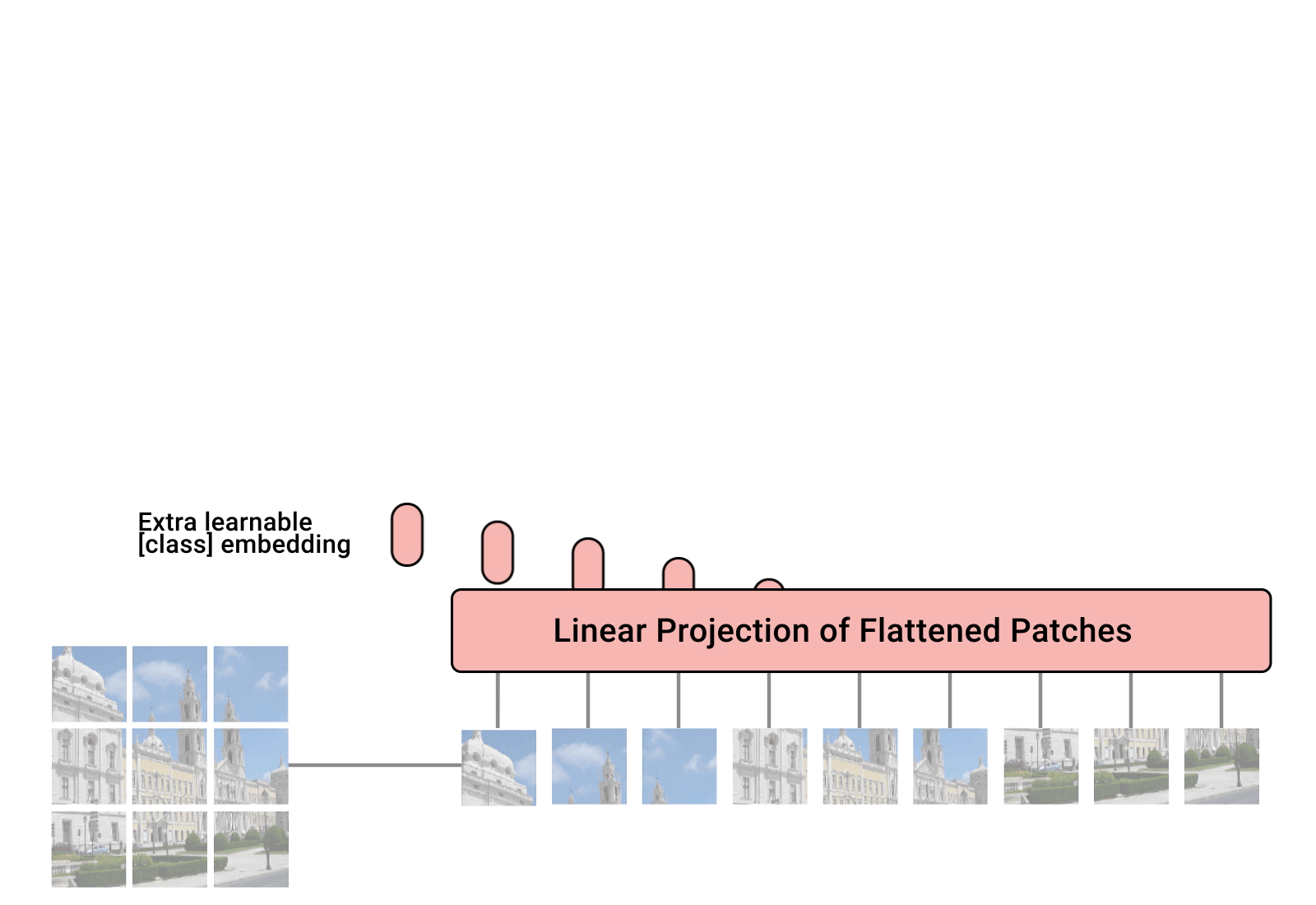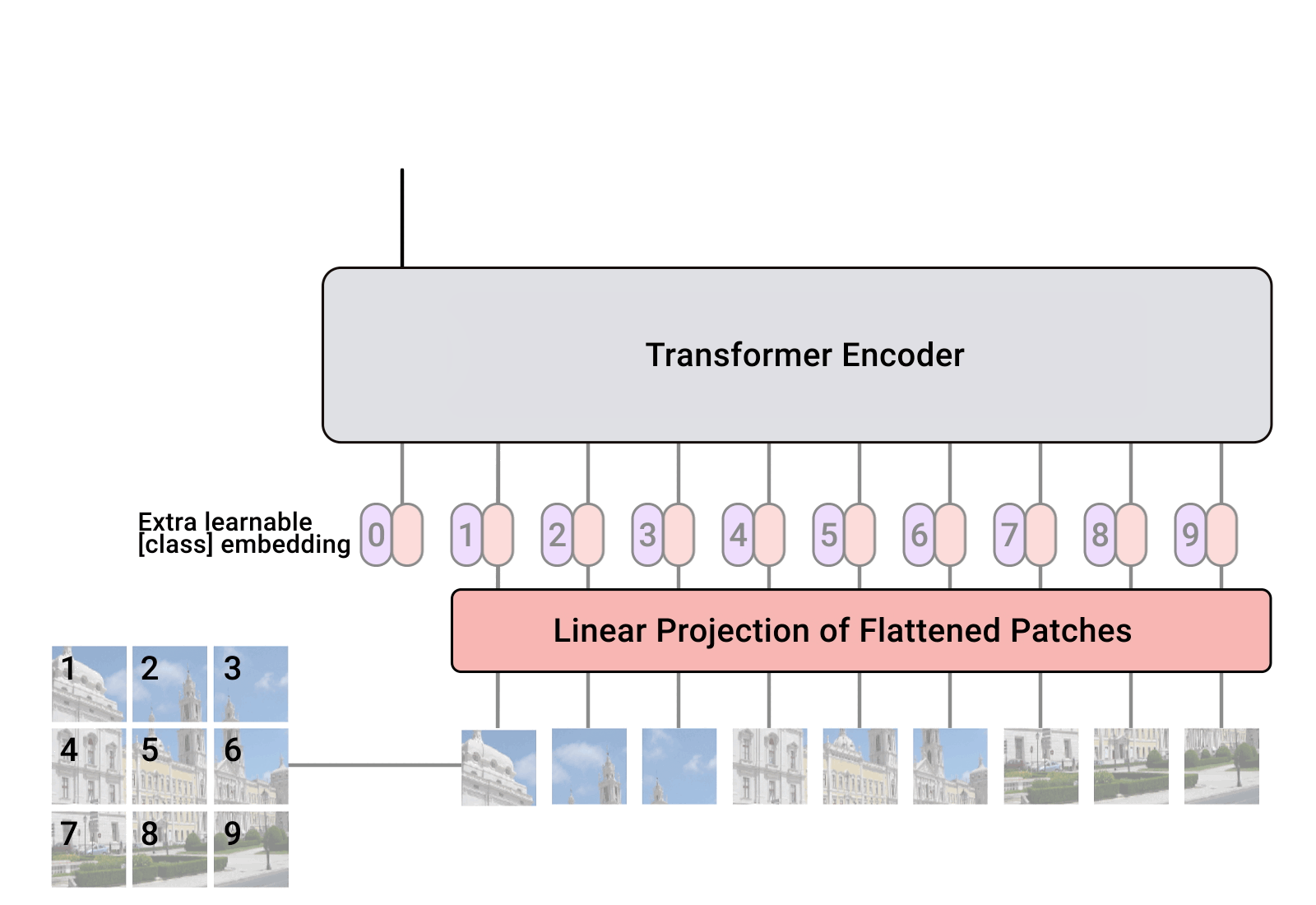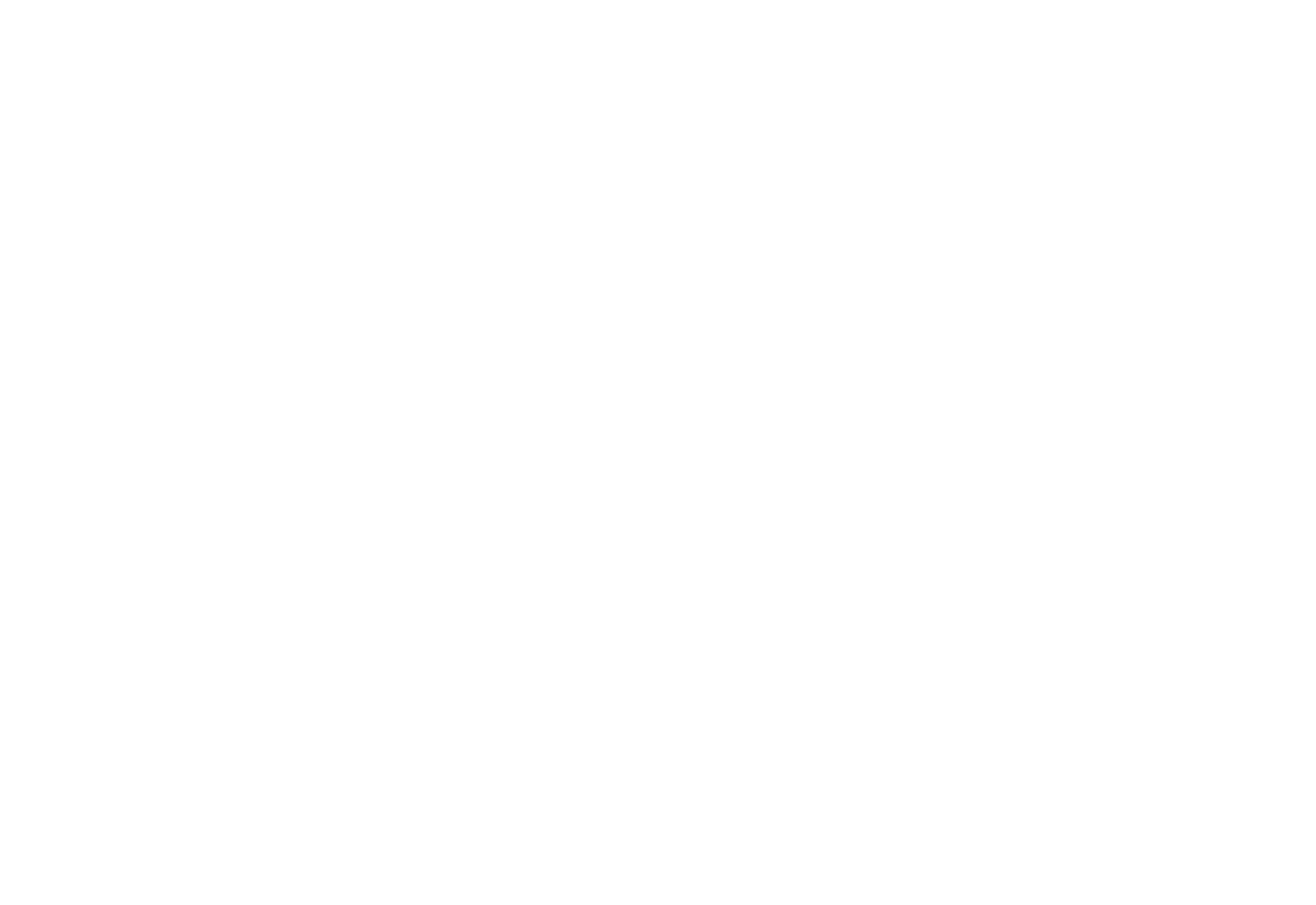Tensorflow 的核心就是注意力机制,在之前详细的介绍过,具体可以看这个:Python深度学习基于Tensorflow(9)注意力机制_tensorflow的各种注意力机制python代码-CSDN博客
基础数据清洗
如果有其他数据可以忽略这一步,这里的数据效果出乎意料的差;
书中不知道是哪里来的数据集,并没有介绍,对话数据放在两个文件中,一个文件路径 ./data/movie_lines.txt,另一个文件路径 ./data/movie_conversations.txt
import os
def base_process(max_nums=50000, return_lines=False):
"""max_nums 用来限制 conversation pair 个数、 return_lines 用来构建词表"""
## 生成 id 与 line 的字典
id2line = {}
with open('./data/movie_lines.txt', errors='ignore') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
parts = line.replace('\n', '').split(' +++$+++ ')
id2line[parts[0]] = parts[4]
## 利用 id2line 查找 conversation ,并将 conversation 依次遍历生成 line_pair
X, y = [], []
with open('./data/movie_conversations.txt', 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
for line in lines:
parts = line.replace('\n', '').split(' +++$+++ ')
conversation = [line[1:-1] for line in parts[3][1:-1].split(', ')]
for ix in range(len(conversation)-1):
X.append(id2line[conversation[ix]].replace('-', ''))
y.append(id2line[conversation[ix+1]].replace('-', ''))
if len(X) > max_nums:
break
if return_lines == True:
return X, y, list(id2line.values())
else:
return X, y
# return_lines 用来构建词表
X, y, lines = base_process(return_lines=True)
# 数据展示
for i in range(5):
print(f'inputs: {X[i]} \noutputs: {y[i]} \n')
得到数据展示,简直了,牛头不对马嘴…
inputs: Can we make this quick? Roxanne Korrine and Andrew Barrett are having an incredibly horrendous public break up on the quad. Again.
outputs: Well, I thought we'd start with pronunciation, if that's okay with you.
inputs: Well, I thought we'd start with pronunciation, if that's okay with you.
outputs: Not the hacking and gagging and spitting part. Please.
inputs: Not the hacking and gagging and spitting part. Please.
outputs: Okay... then how 'bout we try out some French cuisine. Saturday? Night?
inputs: You're asking me out. That's so cute. What's your name again?
outputs: Forget it.
inputs: No, no, it's my fault we didn't have a proper introduction
outputs: Cameron.
数据生成词汇表
代码如下
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_text as tf_text
from tensorflow_text.tools.wordpiece_vocab import bert_vocab_from_dataset as bert_vocab
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X, y))
lines_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((lines))
## 构建词表,这一步耗时较久 大概时间为2min 21s
bert_vocab_args = dict(
vocab_size = 8000, # The target vocabulary size
reserved_tokens = ["[PAD]", "[UNK]", "[START]", "[END]"], # Reserved tokens that must be included in the vocabulary
bert_tokenizer_params=dict(lower_case=True), # Arguments for `text.BertTokenizer`
learn_params={}, # Arguments for `wordpiece_vocab.wordpiece_tokenizer_learner_lib.learn`
)
vocab = bert_vocab.bert_vocab_from_dataset(dataset=lines_dataset, **bert_vocab_args)
# print(vocab[: 5], len(vocab))
# ['[PAD]', '[UNK]', '[START]', '[END]', '!'] 7881
得到 vocab 后,定义函数将 vocab 写入文件
def write_vocab_file(filepath, vocab):
with open(filepath, 'w') as f:
for token in vocab:
print(token, file=f)
## 保存 vocab 到文件 vocab.txt
write_vocab_file('vocab.txt', vocab)
得到词汇表,vocab.txt
定义分词器并制作数据集
分词器定义可以看这篇:Tokenizing with TF Text | TensorFlow (google.cn);执行代码如下
@tf.function
def process_batch_strings(inputs, outputs, left_pad=tf.constant([2], dtype=tf.int64), right_pad=tf.constant([3], dtype=tf.int64)):
""" 这里 left_pad 添加 [START] 其 ids 默认为 2 同样的 [END] 其 ids 默认为3 """
inputs = tokenizer.tokenize(inputs).merge_dims(-2, -1) # 对 RaggedTensor 操作 flat_values 等价于 .merge_dims(-2, -1).merge_dims(-2, -1)
# 在 sequence 开头和结尾添加东西 如 tf.constant([0], dtype=tf.int64)
inputs = tf_text.pad_along_dimension(inputs, axis=-1, left_pad=left_pad, right_pad=right_pad)
inputs = tf_text.pad_model_inputs(inputs, max_seq_length=128, pad_value=0)
outputs = tokenizer.tokenize(outputs).merge_dims(-2, -1) # 对 RaggedTensor 操作 flat_values 等价于 .merge_dims(-2, -1).merge_dims(-2, -1)
# 在 sequence 开头和结尾添加东西 如 tf.constant([0], dtype=tf.int64)
outputs = tf_text.pad_along_dimension(outputs, axis=-1, left_pad=left_pad, right_pad=right_pad)
outputs = tf_text.pad_model_inputs(outputs, max_seq_length=128, pad_value=0)
# inputs 和 outputs 由 ids 和 mask 组成,由于 embedding 有 mask_zero优化 这里只提取出 ids
return (inputs[0], outputs[0][:, :-1]), outputs[0][:, 1:]
# tokenizer 定义分词器
tokenizer = tf_text.BertTokenizer('vocab.txt', **dict(lower_case=True))
# 处理数据集
dataset = dataset.batch(128).map(process_batch_strings)
# dataset.take(1).get_single_element()
# ((<tf.Tensor: shape=(16, 128), dtype=int64, numpy=
# array([[ 2, 276, 259, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 2, 306, 14, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 2, 274, 250, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# ...,
# [ 2, 253, 10, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 2, 297, 260, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 2, 286, 16, ..., 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int64)>,
# <tf.Tensor: shape=(16, 127), dtype=int64, numpy=
# array([[ 2, 306, 14, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 2, 274, 250, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 2, 351, 16, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# ...,
# [ 2, 599, 1322, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 2, 306, 14, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 2, 322, 33, ..., 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int64)>),
# <tf.Tensor: shape=(16, 127), dtype=int64, numpy=
# array([[ 306, 14, 47, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 274, 250, 5477, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 351, 16, 16, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# ...,
# [ 599, 1322, 16, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 306, 14, 286, ..., 0, 0, 0],
# [ 322, 33, 3, ..., 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int64)>)
构建Transformer模型并训练
这里使用三角绝对位置编码,采取旋转位置编码的方式进行构建模型,由于 tensorflow 没有旋转位置编码的类,这里定义一个 RotaryEmbedding ;
class RotaryEmbedding(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__( self, max_wavelength=10000, scaling_factor=1.0, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.max_wavelength = max_wavelength
self.scaling_factor = scaling_factor
self.built = True
def call(self, inputs, start_index=0, positions=None):
cos_emb, sin_emb = self._compute_cos_sin_embedding(inputs, start_index, positions)
output = self._apply_rotary_pos_emb(inputs, cos_emb, sin_emb)
return output
def _apply_rotary_pos_emb(self, tensor, cos_emb, sin_emb):
x1, x2 = tf.split(tensor, 2, axis=-1)
half_rot_tensor = tf.stack((-x2, x1), axis=-2)
half_rot_tensor = tf.reshape(half_rot_tensor, tf.shape(tensor))
return (tensor * cos_emb) + (half_rot_tensor * sin_emb)
def _compute_positions(self, inputs, start_index=0):
seq_len = tf.shape(inputs)[1]
positions = tf.range(seq_len, dtype="float32")
return positions + tf.cast(start_index, dtype="float32")
def _compute_cos_sin_embedding(self, inputs, start_index=0, positions=None):
feature_axis = len(inputs.shape) - 1
sequence_axis = 1
rotary_dim = tf.shape(inputs)[feature_axis]
inverse_freq = self._get_inverse_freq(rotary_dim)
if positions is None:
positions = self._compute_positions(inputs, start_index)
else:
positions = tf.cast(positions, "float32")
positions = positions / tf.cast(self.scaling_factor, "float32")
freq = tf.einsum("i,j->ij", positions, inverse_freq)
embedding = tf.stack((freq, freq), axis=-2)
# 这里 *tf.shape(freq)[:-1] 使用 model.fit 的话无法计算
# embedding = tf.reshape(embedding, (*tf.shape(freq)[:-1], tf.shape(freq)[-1] * 2))
embedding = tf.reshape(embedding, (tf.shape(freq)[0], tf.shape(freq)[-1] * 2))
if feature_axis < sequence_axis:
embedding = tf.transpose(embedding)
for axis in range(len(inputs.shape)):
if axis != sequence_axis and axis != feature_axis:
embedding = tf.expand_dims(embedding, axis)
cos_emb = tf.cast(tf.cos(embedding), self.compute_dtype)
sin_emb = tf.cast(tf.sin(embedding), self.compute_dtype)
return cos_emb, sin_emb
def _get_inverse_freq(self, rotary_dim):
freq_range = tf.divide(tf.range(0, rotary_dim, 2, dtype="float32"),tf.cast(rotary_dim, "float32"))
inverse_freq = 1.0 / (self.max_wavelength**freq_range)
return inverse_freq
在注意力机制中融合 RotaryEmbedding 得到 MultiHeadAttention ;
class MultiHeadAttention(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_heads, d_model, with_rotary=True):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.d_model = d_model
self.with_rotary = with_rotary
## 判断能否被整除
assert self.d_model % self.num_heads == 0
## 定义需要用到的 layer
self.query_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model)
self.key_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model)
self.value_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model)
self.output_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model)
self.rotary_query = RotaryEmbedding()
self.rotary_key = RotaryEmbedding()
# self.rotary_query = keras_nlp.layers.RotaryEmbedding()
# self.rotary_key = keras_nlp.layers.RotaryEmbedding()
def call(self, x_query, x_key, x_value, use_casual_mask=False):
if self.with_rotary:
query = self._split_heads(self.rotary_query(self.query_dense(x_query)))
key = self._split_heads(self.rotary_key(self.key_dense(x_key)))
else:
query = self._split_heads(self.query_dense(x_query))
key = self._split_heads(self.key_dense(x_key))
value = self._split_heads(self.value_dense(x_value))
output, attention_weights = self._scaled_dot_product_attention(query, key, value, use_casual_mask)
output = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda output: tf.transpose(output, perm=[0, 2, 1, 3]))(output)
output = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda output: tf.reshape(output, [tf.shape(output)[0], -1, self.d_model]))(output)
output = self.output_dense(output)
return output
def _split_heads(self, x):
# x = tf.reshape(x, [tf.shape(x)[0], -1, self.num_heads, self.d_model / self.num_heads])
# x = tf.transpose(x, perm=[0, 2, 1, 3])
x = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.reshape(x, [tf.shape(x)[0], -1, self.num_heads, self.d_model // self.num_heads]))(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.transpose(x, perm=[0, 2, 1, 3]))(x)
return x
def _scaled_dot_product_attention(self, query, key, value, use_casual_mask):
dk = tf.cast(tf.shape(key)[-1], tf.float32)
scaled_attention_logits = tf.matmul(query, key, transpose_b=True) / tf.math.sqrt(dk)
if use_casual_mask:
casual_mask = 1 - tf.linalg.band_part(tf.ones_like(scaled_attention_logits), -1, 0)
scaled_attention_logits += casual_mask * -1e9
attention_weights = tf.nn.softmax(scaled_attention_logits, axis=-1)
output = tf.matmul(attention_weights, value)
return output, attention_weights
定义前馈神经网络层 FeedForward;
class FeedForward(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, d_model):
super(FeedForward, self).__init__()
self.dense_1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(4 * 2 * d_model // 3)
self.dense_2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(d_model)
self.dense_3 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(4 * 2 * d_model // 3)
def call(self, x):
x = self.dense_2(tf.nn.silu(self.dense_1(x)) * self.dense_3(x))
return x
再定义 RMSNorm 代替 LayerNorm 加快计算速度;
class RMSNorm(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, d_model, eps=1e-6):
super(RMSNorm, self).__init__()
self.eps = eps
self.gamma = self.add_weight(shape=d_model, initializer='ones', trainable=True)
def call(self, x):
x = self._norm(x)
output = x * self.gamma
return output
def _norm(self, x):
return x * tf.math.rsqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(x, 2), axis=-1, keepdims=True) + self.eps)
构建 EncoderLayer 和 Encoder ;
class EncoderLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_heads, d_model):
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.mha = MultiHeadAttention(num_heads, d_model, with_rotary=True)
self.ffn = FeedForward(d_model)
self.rms_mha = RMSNorm(d_model)
self.rms_ffn = RMSNorm(d_model)
def call(self, x):
## attention 层计算
x = self.rms_mha(x)
x = x + self.mha(x, x, x, use_casual_mask=False)
## feedforward 层计算
x = self.rms_ffn(x)
x = x + self.ffn(x)
return x
class Encoder(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, encoder_layer_nums, vocabulary_size, num_heads, d_model):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocabulary_size, d_model, mask_zero=True)
self.encoder_layers = [EncoderLayer(num_heads, d_model) for _ in range(encoder_layer_nums)]
def call(self, x):
x = self.embedding(x)
for encoder_layer in self.encoder_layers:
x = encoder_layer(x)
return x
同样的,DecoderLayer 和 Decoder ;
class DecoderLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_heads, d_model):
super(DecoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.mha_1 = MultiHeadAttention(num_heads, d_model, with_rotary=True)
self.mha_2 = MultiHeadAttention(num_heads, d_model, with_rotary=True)
self.ffn = FeedForward(d_model)
self.rms_mha_1 = RMSNorm(d_model)
self.rms_mha_2 = RMSNorm(d_model)
self.rms_ffn = RMSNorm(d_model)
def call(self, x, encoder_output):
## mask attention 层计算
x = self.rms_mha_1(x)
x = x + self.mha_1(x, x, x, use_casual_mask=True)
## attention 层计算
x = self.rms_mha_2(x)
x = x + self.mha_2(x, encoder_output, encoder_output, use_casual_mask=False)
## feedforward 层计算
x = self.rms_ffn(x)
x = x + self.ffn(x)
return x
class Decoder(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, decoder_layer_nums, vocabulary_size, num_heads, d_model):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocabulary_size, d_model, mask_zero=True)
self.decoder_layers = [DecoderLayer(num_heads, d_model) for _ in range(decoder_layer_nums)]
def call(self, x, encoder_output):
x = self.embedding(x)
for decoder_layer in self.decoder_layers:
x = decoder_layer(x, encoder_output)
return x
建立 Transformer 模型
class Transformer(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, decoder_layer_nums, encoder_layer_nums, vocabulary_size, num_heads, d_model):
super(Transformer, self).__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(encoder_layer_nums, vocabulary_size, num_heads, d_model)
self.decoder = Decoder(decoder_layer_nums, vocabulary_size, num_heads, d_model)
self.final_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(vocabulary_size, activation='softmax')
def call(self, x):
x1, x2 = x[0], x[1]
x1 = self.encoder(x1)
x2 = self.decoder(x2, x1)
output = self.final_dense(x2)
return output
定义调度器类,使用 warmup
class CustomSchedule(tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule):
def __init__(self, d_model, warmup_steps=4000):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.d_model = tf.cast(self.d_model, tf.float32)
self.warmup_steps = warmup_steps
def __call__(self, step):
step = tf.cast(step, dtype=tf.float32)
arg1 = tf.math.rsqrt(step)
arg2 = step * (self.warmup_steps ** -1.5)
return tf.math.rsqrt(self.d_model) * tf.math.minimum(arg1, arg2)
定义模型并开始学习
decoder_layer_nums=2
encoder_layer_nums=2
vocabulary_size=len(vocab)
num_heads=8
d_model=256
learning_rate = CustomSchedule(d_model)
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.98, epsilon=1e-9)
model = Transformer(decoder_layer_nums, encoder_layer_nums, vocabulary_size, num_heads, d_model)
model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy']
)
## 开始训练
history = model.fit(dataset, epochs=10)
# Epoch 1/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 43s 94ms/step - loss: 2.3794 - accuracy: 0.8041
# Epoch 2/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 37s 94ms/step - loss: 0.6215 - accuracy: 0.9024
# Epoch 3/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 37s 95ms/step - loss: 0.5656 - accuracy: 0.9060
# Epoch 4/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 37s 95ms/step - loss: 0.5365 - accuracy: 0.9077
# Epoch 5/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 37s 95ms/step - loss: 0.5097 - accuracy: 0.9095
# Epoch 6/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 37s 96ms/step - loss: 0.4812 - accuracy: 0.9119
# Epoch 7/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 37s 95ms/step - loss: 0.4549 - accuracy: 0.9145
# Epoch 8/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 37s 94ms/step - loss: 0.4335 - accuracy: 0.9166
# Epoch 9/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 37s 94ms/step - loss: 0.4162 - accuracy: 0.9183
# Epoch 10/10
# 391/391 [==============================] - 37s 95ms/step - loss: 0.4047 - accuracy: 0.9192
模型推理
定义推理类 Inference ;
class Inference(tf.Module):
def __init__(self, model, tokenizer):
self.model = model
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
def __call__(self, x, max_length=128):
from rich.progress import track
x = self.tokenizer.tokenize(x).flat_values
## 定义 start 和 end
start = tf.constant([2], dtype=tf.int64)
end = tf.constant([3], dtype=tf.int64)
x = tf_text.pad_along_dimension(x, axis=-1, left_pad=start, right_pad=end)[tf.newaxis, :]
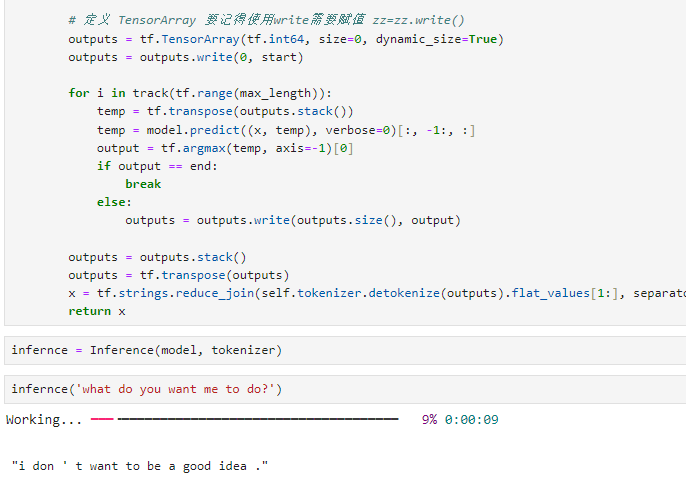
# 定义 TensorArray 要记得使用write需要赋值 zz=zz.write()
outputs = tf.TensorArray(tf.int64, size=0, dynamic_size=True)
outputs = outputs.write(0, start)
for i in track(tf.range(max_length)):
temp = tf.transpose(outputs.stack())
temp = model.predict((x, temp), verbose=0)[:, -1:, :]
output = tf.argmax(temp, axis=-1)[0]
if output == end:
break
else:
outputs = outputs.write(outputs.size(), output)
outputs = outputs.stack()
outputs = tf.transpose(outputs)
x = tf.strings.reduce_join(self.tokenizer.detokenize(outputs).flat_values[1:], separator=' ').numpy().decode('utf-8')
return x
初始化类,并开始推理
infernce = Inference(model, tokenizer)
infernce('what do you want me to do?')
# "i don ' t want to be a good idea ."
可以看到牛头不对马嘴,数据是一个原因,训练层数是一个原因