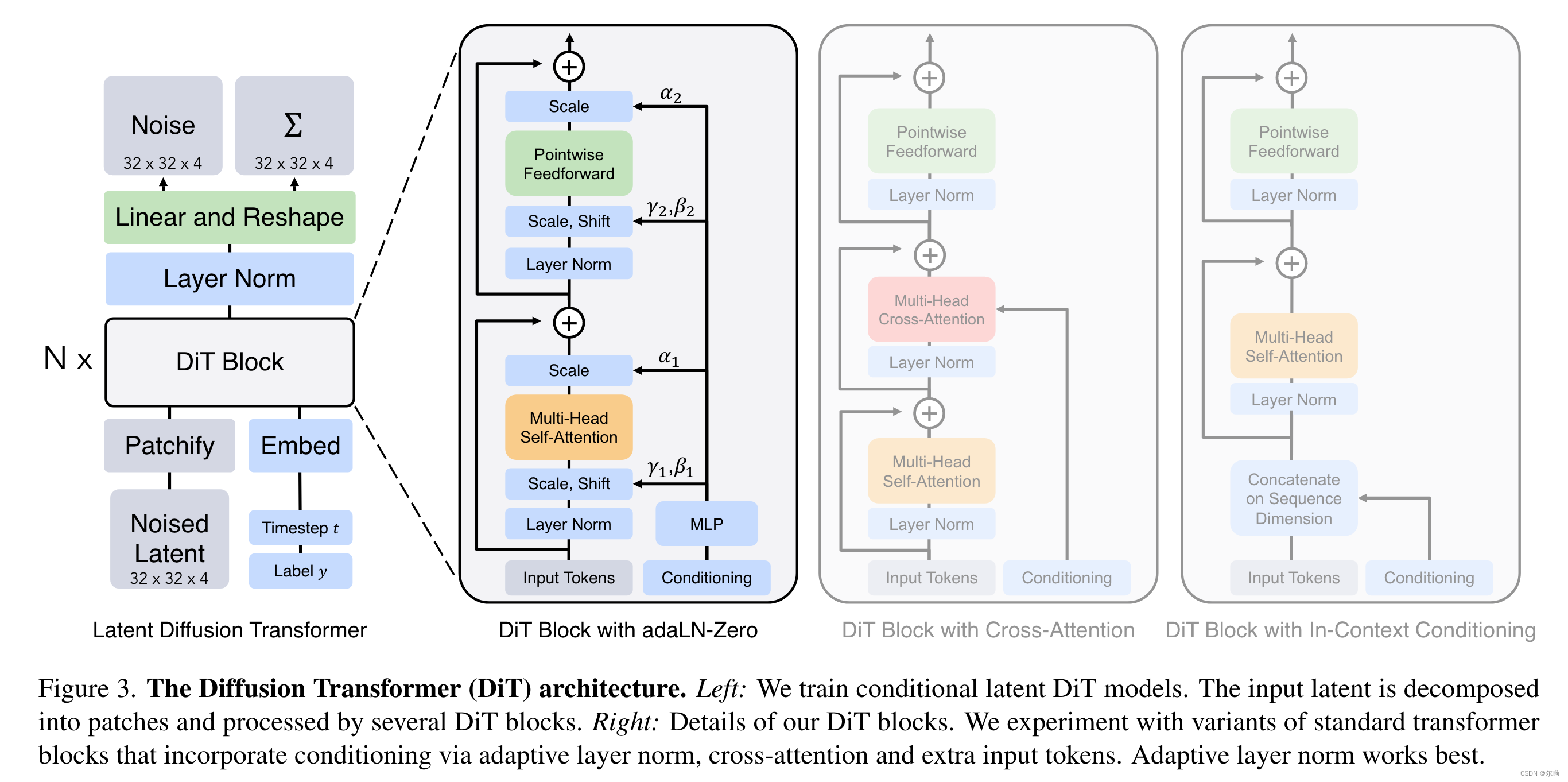
目录
- 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊 | 接辅导、项目定制
1、序言
这篇博客,主要是讲的是彩色图片分类,数据集为:cifar10。
和以往的流程一样:
① 判断是否在GPU上运行
② 导入cifar10数据集
③ 归一化(将像素的值标准化至0-1的区间内)
④ 可视化数据集里的数据(展示了2行,共20张图片)
⑤ 搭建神经网络
⑥ 编译
⑦ 训练模型
⑧ 预测并显示预测的图片
⑨ 模型评估
2、主要代码
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import datasets, layers, models
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 1、设置GPU
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')
if gpus:
gpu0 = gpus[0] # 如果有多个GPU,仅使用第0个GPU
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu0,True) # 设置GPU显存用量按需使用
tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpu0], "GPU")
# 2、导入数据
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = datasets.cifar10.load_data()
# 3、归一化
# 将像素的值标准化至0到1的区间内。
train_images, test_images = train_images / 255.0, test_images / 255.0
print(train_images.shape,test_images.shape,train_labels.shape,test_labels.shape)
# (50000, 32, 32, 3) (10000, 32, 32, 3) (50000, 1) (10000, 1)
# 4、可视化
class_names = ['airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer','dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck']
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
for i in range(20):
plt.subplot(5,10,i+1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i][0]])
plt.show()
# 二、搭建神经网络
model = models.Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(32, 32, 3)), # 卷积层1,卷积核3*3
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)), # 池化层1,2*2采样
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'), # 卷积层2,卷积核3*3
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)), # 池化层2,2*2采样
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'), # 卷积层3,卷积核3*3
layers.Flatten(), # Flatten层,连接卷积层与全连接层
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'), # 全连接层,特征进一步提取
layers.Dense(10) # 输出层,输出预期结果
])
# model.summary() # 打印网络结构
# 三、编译
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
# 四、训练模型
history = model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10,
validation_data=(test_images, test_labels))
# 五、预测
plt.imshow(test_images[1])
plt.show()
pre = model.predict(test_images)
print(class_names[np.argmax(pre[1])])
# 六、模型评估
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='accuracy')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='val_accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.ylim([0.5, 1])
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2)
print("test_loss:", test_loss, "---------test_acc:", test_acc)
3、运行结果展示
(1)展示cifar10里面的20张图片

(2)预测的图片

遗憾,我的结果预测错误,预测的是:automobile
(3)模型评估
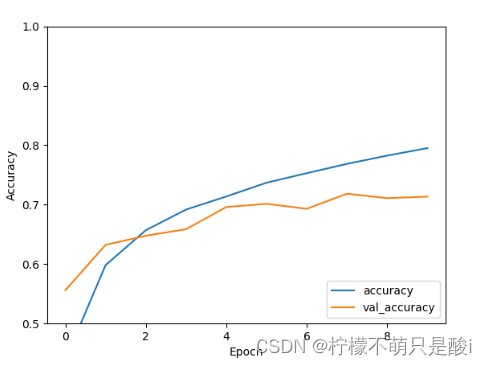
上图可以看到,测试精确度达到70%左右。

























![[数据概念]大模型时代演进的DIKW模型【2】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9be5b5a12c1c765b31f87b0bbab6ff2d.png)