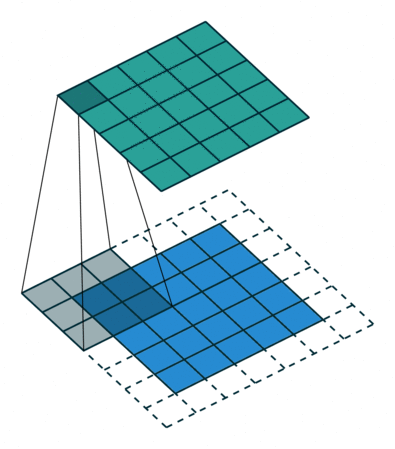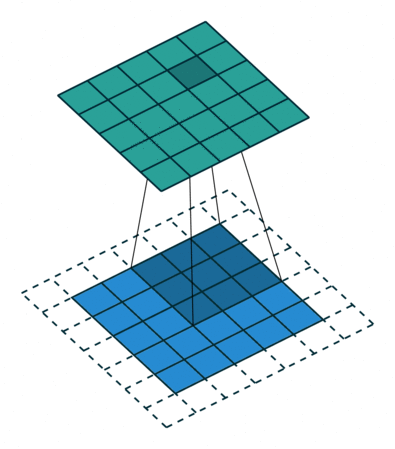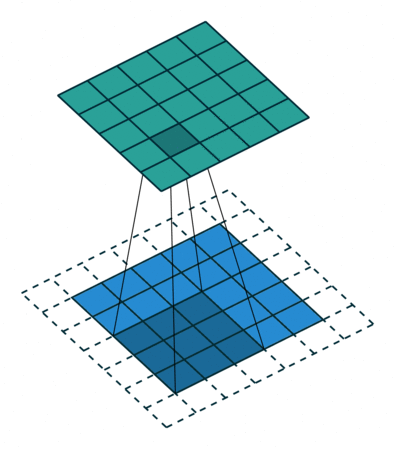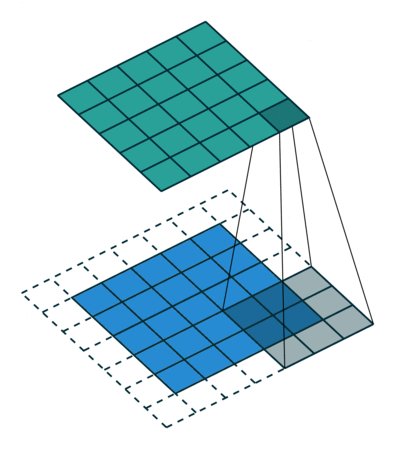
1. 2D 卷积操作
import numpy as np
def conv2d(image, kernel, stride=1, padding=0):
"""
应用2D卷积操作到输入图像上。
参数:
- image: 输入图像,2D数组。
- kernel: 卷积核,2D数组。
- stride: 卷积步幅。
- padding: 图像周围的零填充数量。
返回值:
- output: 卷积操作的结果。
"""
# 对输入图像添加零填充
if padding > 0:
image = np.pad(image, ((padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode='constant')
kernel_height, kernel_width = kernel.shape
image_height, image_width = image.shape
# 计算输出的尺寸
output_height = (image_height - kernel_height) // stride + 1
output_width = (image_width - kernel_width) // stride + 1
output = np.zeros((output_height, output_width))
for i in range(0, output_height):
for j in range(0, output_width):
start_i = i * stride
start_j = j * stride
end_i = start_i + kernel_height
end_j = start_j + kernel_width
output[i, j] = np.sum(image[start_i:end_i, start_j:end_j] * kernel)
return output
# 示例用法
image = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15, 16]])
kernel = np.array([[1, 0],
[0, -1]])
conv_result = conv2d(image, kernel, stride=1, padding=1)
print("卷积结果:\n", conv_result)
2. 2D 最大池化操作
def max_pool2d(image, pool_size=2, stride=2, padding=0):
"""
应用2D最大池化操作到输入图像上。
参数:
- image: 输入图像,2D数组。
- pool_size: 池化窗口的大小。
- stride: 池化步幅。
- padding: 图像周围的零填充数量。
返回值:
- output: 最大池化操作的结果。
"""
# 对输入图像添加零填充
if padding > 0:
image = np.pad(image, ((padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode='constant')
image_height, image_width = image.shape
# 计算输出的尺寸
output_height = (image_height - pool_size) // stride + 1
output_width = (image_width - pool_size) // stride + 1
output = np.zeros((output_height, output_width))
for i in range(0, output_height):
for j in range(0, output_width):
start_i = i * stride
start_j = j * stride
end_i = start_i + pool_size
end_j = start_j + pool_size
output[i, j] = np.max(image[start_i:end_i, start_j:end_j])
return output
# 示例用法
pool_result = max_pool2d(conv_result, pool_size=2, stride=2, padding=0)
print("最大池化结果:\n", pool_result)
3. Dropout 操作
def dropout(X, drop_prob):
"""
对输入应用dropout。
参数:
- X: 输入数组。
- drop_prob: 丢弃神经元的概率 (0 <= drop_prob < 1)。
返回值:
- output: 应用dropout后的结果。
"""
if drop_prob < 0.0 or drop_prob >= 1.0:
raise ValueError("drop_prob必须在范围[0.0, 1.0)内。")
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
mask = np.random.rand(*X.shape) < keep_prob
return X * mask / keep_prob
# 示例用法
np.random.seed(0) # 为了结果的可重复性
X = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
dropout_result = dropout(X, drop_prob=0.5)
print("Dropout结果:\n", dropout_result)
更多示例和代码请参考我的 GitHub 项目:Machine_DLearning_With_NP,欢迎 star
水平有限,有问题随时交流~

























![AR和AP重分类(Regroup)[FAGLF101/OBBU/OBBV]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/a65c6fd9dc7743ee903c9e4acf3504cc.png)