目录
声明:本文所有题目均摘自leetcode
一、链表的中间节点
1.1 题目
给你单链表的头结点
head,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
1.2 题解
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* slow=head;
struct ListNode* fast=head;
while(fast!=NULL&&fast->next!=NULL)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}1.3 收获
- 快慢指针的用法:
- 链表长度为奇数: 当快指针走到尾节点时,慢指针正好走到中间节点。
- 链表长度为偶数: 当快指针走到NULL时,慢指针正好走到第二个中间节点。
二、移除链表元素
2.1 题目
给你一个链表的头节点
head和一个整数val,请你删除链表中所有满足Node.val == val的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
2.2 题解
//创建虚拟节点法
struct ListNode* removeElements1(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* dummyHead = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
dummyHead->next = head;
struct ListNode* temp = dummyHead;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
if (temp->next->val == val) {
temp->next = temp->next->next;
}
else {
temp = temp->next;
}
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
//创建新链表法
struct ListNode* removeElements3(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* phead = NULL;
struct ListNode* ptail = NULL;
struct ListNode* pcur = head;
while (pcur) {
if (pcur->val != val) {
if (phead == NULL) {
phead = ptail = pcur;
}
else {
ptail->next = pcur;
ptail = ptail->next;
}
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
if (phead) {
ptail->next = NULL;
}
return phead;
}
//双指针法
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
while (NULL != head && head->val == val) {
head = head->next;
}
struct ListNode* pcur = head;
struct ListNode* prev = head;
while (pcur)
{
if (pcur->val != val)
{
prev = pcur;
}
else
{
prev->next = pcur->next;
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
return head;
}
//递归做法
struct ListNode* removeElements2(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
if (head == NULL) {
return head;
}
head->next = removeElements(head->next, val);
if (head->val == val)
{
return head->next;
}
else
{
return head;
}
}2.3 收获
- 创建虚拟头节点:好处是可以只维护一个指针
- 创建新链表法:思路简单:仅仅为挑选符合条件的数据复制即可
- 双指针法:保存前一个链表的指针
2.4递归详解
- 停止条件:当遍历链表的指针为空时。
- 如何递归:判断节点值是否等于给定值,并决定是否要删除。
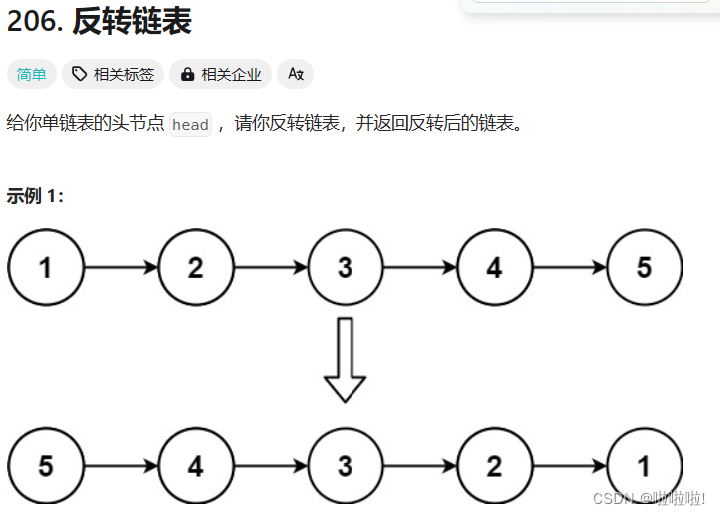
三、反转链表
3.1 题目
给你单链表的头节点
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
3.2 题解
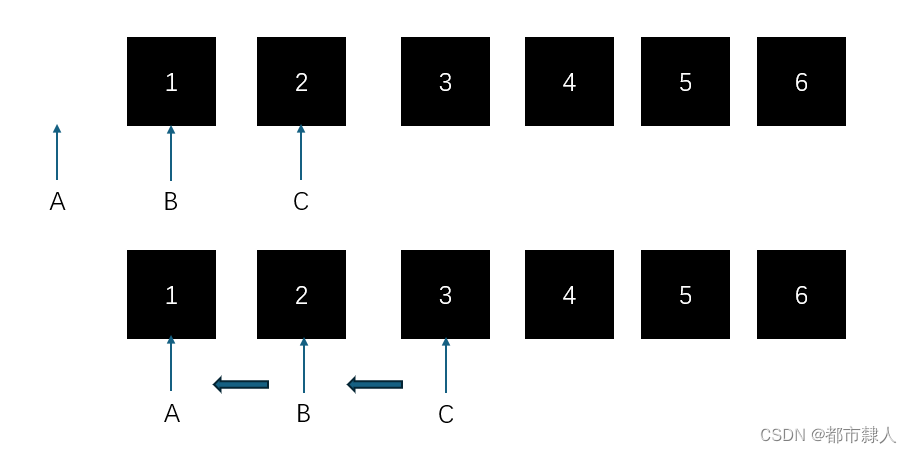
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL) {
return head;
}
struct ListNode* a = NULL;
struct ListNode* b = head;
struct ListNode* c = head->next;
while (b) {
b->next = a;
a = b;
b = c;
if (c) {
c = c->next;
}
}
return a;
}3.3 解释
三指针法:循环保留三个指针,修改朝向即可;
四、合并两个有序列表
4.1 题目
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
4.2 题解
//创建新链表法
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
if (list1 == NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if (list2 == NULL)
{
return list1;
}
if (list1 == NULL && list2 == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* l1 = list1;
struct ListNode* l2 = list2;
struct ListNode* newhead;
struct ListNode* newtail;
newhead = newtail = NULL;
while (l1 && l2)
{
if (l1->val < l2->val)
{
if (newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = l1;
}
else
{
newtail->next = l1;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
if (newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = l2;
}
else
{
newtail->next = l2;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if (l1 == NULL && l2 != NULL)
{
newtail->next = l2;
while (l2->next)
{
l2 = l2->next;
}
newtail = l2;
}
if (l2 == NULL && l1 != NULL)
{
newtail->next = l1;
while (l1->next)
{
l1 = l1->next;
}
newtail = l1;
}
return newhead;
}
//递归
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
struct ListNode* l1 = list1;
struct ListNode* l2 = list2;
if (l1 == NULL) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == NULL) {
return l1;
}
if (list1 == NULL && list2 == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (l1->val <= l2->val) {
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}4.3 递归详解
- 停止条件:当两个链表都为空时。
- 如何递归:我们判断两个头结点哪个更小,然后较小结点的 next 指针指向其余结点。