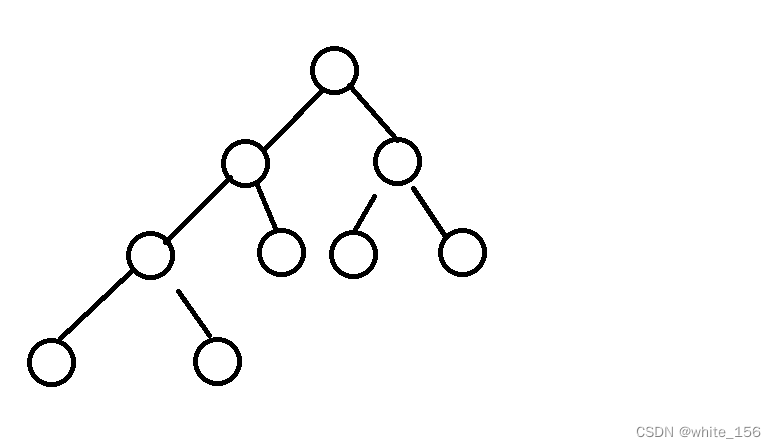
F. Andrey's Tree:
题目描述:


思路解析:
我们假设删除任意一个结点后,我们会将整个树切分为k个联通块,那么可以明确的知道我们只需要连接(k-1)条边就可以将这k个联通块重新连为一棵树。
那么最小代价是啥呢? 图解分析
第一种情况,有至少一个联通块即拥有小于删除点的数,又有大于删除的数,此时代价就是要增加的边数
第二种情况,没有上诉的联通块。
我们可以发现我们还是可以将整个联通块连接为 (1,x-1) 和 (x+1,n)的两个联通块,花费为k-2,此时还需要2个花费,将整个联通块连接为(1,n)的联通块,总花费为删除结点后,联通块的个数。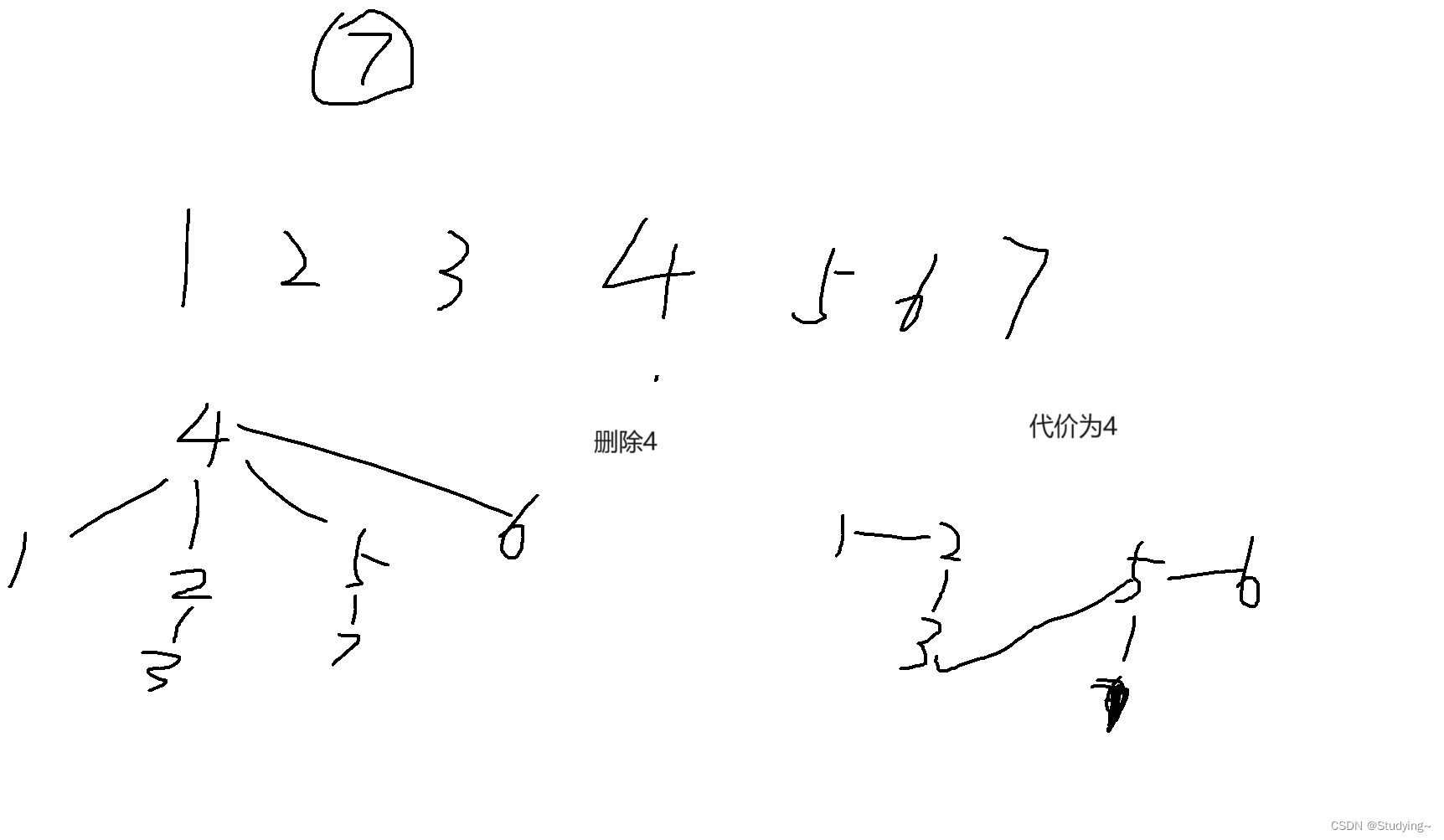
经过此时分析,我们可以发现我们其实已知需要连多少条边,需要多少代价,这是固定的。花费只由是否有一个联通块中既有小于x的值和大于x的值决定。 因为初始是一棵树,那么假如有一条边为2-7,可以发现后面的边无论怎么样,对于删除3,4,6,来说,一定有个联通块含有(2和7)满足上诉要求,则此时可以通过前缀和来实现。
根据前两个图发现,只要两种连接情况 (x,x+1) (x,x-1)(y,y+2), 且x为联通块的最小值或者最大值,y=删除值-1,那么我们只要维护每个联通块的最小值和最大值即可,并且维护删除结点后,有哪些联通块即可。
代码实现:
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
import static java.util.Collections.*;
public class Main {
static int inf = (int) 1e9;
static int mod = 998244353;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int t = f.nextInt();
while (t > 0) {
solve();
t--;
}
w.flush();
w.close();
br.close();
}
static int[] maxIn;
static int[] maxOut;
static int[] minIn;
static int[] minOut;
static int[] p;
static Vector<Integer>[] g;
static int n;
public static void solve() {
n = f.nextInt();
g = new Vector[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
g[i] = new Vector<>();
}
int[] d = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int u = f.nextInt() - 1;
int v = f.nextInt() - 1;
g[u].add(v);
g[v].add(u);
if (u > v) {
int tmp = u;
u = v;
v = tmp;
}
d[u + 1]++;
d[v]--;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
d[i] += d[i - 1];
}
d[0] = d[n - 1] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
d[i] = d[i] >= 1 ? 1 : 0;
}
maxIn = new int[n];
minIn = new int[n];
maxOut = new int[n];
minOut = new int[n];
p = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(minOut, n);
dfs1(0);
dfs2(0);
for (int x = 0; x < n; x++) {
int res = g[x].size() - d[x];
w.println(res + " " + (g[x].size() - 1));
ArrayList<int[]> q = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < g[x].size(); i++) {
int y = g[x].get(i);
if (y == p[x]){
q.add(new int[] {minOut[x], maxOut[x]});
}else {
q.add(new int[]{minIn[y], maxIn[y]});
}
}
int lst = -1;
q.sort(new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[0] - o2[0];
}
});
for (int[] a : q) {
if (a[0] >= x) break;
if (lst != - 1) w.println(a[0] + 1 + " " + a[0]);
lst = a[0];
}
lst = -1;
q.sort(new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o2[1] - o1[1];
}
});
int c = 0;
for (int[] a : q) {
if (a[1] <= x) break;
if (lst != - 1 && (c == 0 || a[0] > x)) w.println(a[1] + 2 + " " + (a[1] + 1));
lst = a[0];
c |= (a[0] < x ? 1 : 0);
}
if (c == 0 && x > 0 && x + 1 < n) w.println(x + " " + (x + 2));
w.println();
}
}
static void dfs1(int x) {
minIn[x] = x;
maxIn[x] = x;
for (int i = 0; i < g[x].size(); i++) {
int y = g[x].get(i);
if (y == p[x]) continue;
p[y] = x;
dfs1(y);
minIn[x] = Math.min(minIn[y], minIn[x]);
maxIn[x] = Math.max(maxIn[y], maxIn[x]);
}
}
static void dfs2(int x) {
int[] mx = new int[2];
int[] mn = new int[2];
mn[0] = mn[1] = n;
for (int i = 0; i < g[x].size(); i++) {
int y = g[x].get(i);
if (y == p[x]) continue;
int a = minIn[y];
int b = maxIn[y];
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
if (a < mn[j]){
int tmp = mn[j];
mn[j] = a;
a = tmp;
}
if (b > mx[j]){
int tmp = mx[j];
mx[j] = b;
b = tmp;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < g[x].size(); i++) {
int y = g[x].get(i);
if (y == p[x]) continue;
int a = mx[mx[0] == maxIn[y] ? 1 : 0];
int b = mn[mn[0] == minIn[y] ? 1 : 0];
maxOut[y] = Math.max(maxOut[x], Math.max(a, x));
minOut[y] = Math.min(minOut[x], Math.min(b, x));
dfs2(y);
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
try {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() {
String str = null;
try {
str = reader.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() {
return new BigInteger(next());
}
}
}