1 前言
随着功能安全的推广,动态内存分配在RTOS领域的用武之地将越来越小。但heap4毕竟是为RTOS量身打造,相对简单,作为堆内存管理的入门学习,仍是很不错的选择。
1.1 标准c库动态内存函数的弊端
对于标准C库的malloc和free函数,freeRTOS官方的说法如下:
1.在嵌入式系统上并不完全通用(移植性不好);
2.占用了宝贵的代码空间(代码资源消耗大);
3.不是线程安全的(不安全);
4.执行时间不确定(实时性不好);
因此,freeRTOS在可移植层(port层)封装了类似的接口,比如pvPortMalloc和vPortFree分别用于申请和释放动态内存。
此外,FreeRTOS 提供了几种堆管理方案, 其复杂性和功能各不相同。 用户也可以提供自己的堆实现, 甚至同时使用两个堆实现。 同时使用两个堆实现 允许将任务堆栈和其他 RTOS 对象放置在 内部 RAM 中,并将应用程序数据放置在较慢的外部 RAM 中。
1.2 五种堆实现方式
- heap_1 —— 最简单,,具有确定性,从静态数组中分配内存,不允许释放内存,不会导致内存碎片化,一锤子买卖,不算真正的动态内存分配;
- heap_2—— 非确定性,允许释放内存,但不会合并相邻的空闲块,也就是说没有内存碎片优化措施;
- heap_3 —— 简单包装了标准 malloc() 和 free(),以保证线程安全,借壳上市,需要连接器设置堆空间分布,且需要编译器库提供malloc和free函数的实现,可能回增加RTOS内核大小;
- heap_4 —— 非确定性,使用第一适应算法(first fit,FF),支持合并相邻的空闲块以避免碎片化,允许将堆放置在内存中的特定地址,官方称比大多数标准 C 库 malloc 的实现要快;
- heap_5—— 如同 heap_4,但能够跨越多个不相邻内存区域的堆,且使用动态内存分配前,必须调用 vPortDefineHeapRegions() 进行初始化。
目前来说,heap_4的使用最为广泛,也是下面分析的重点。
2. 源码分析
2.1 堆内存池
/* The application writer has already defined the array used for the RTOS
* heap - probably so it can be placed in a special segment or address. */
extern uint8_t ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ];
#else
PRIVILEGED_DATA static uint8_t ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ];
#endif /* configAPPLICATION_ALLOCATED_HEAP */显然,从上述代码中可以看出:
①传说中的内存池采用了最简单的线性数组结构,字节大小由configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE定义;
②通过配置configAPPLICATION_ALLOCATED_HEAP可以由应用层自定义内存池ucHeap[ configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE ],即可以由应用划分堆位于特定内存段,而RTOS引用该内存池;
2.2 内存块链表结构
首先看链表的数据结构:
typedef struct A_BLOCK_LINK
{
struct A_BLOCK_LINK * pxNextFreeBlock; /*<< The next free block in the list. */
size_t xBlockSize; /*<< The size of the free block. */
} BlockLink_t;
/* Create a couple of list links to mark the start and end of the list. */
PRIVILEGED_DATA static BlockLink_t xStart, * pxEnd = NULL;显然,该链表记录了空闲内存块的信息(姑且称为内存块头),包括内存块大小和指向下一个内存块头的指针,并由两个静态链表元素指针xStart和pxEnd标识开头和结尾。从该链表元素构成可以看出,每次申请动态内存,堆中至少需要多划分处8个字节的空间来存放内存块头,随后就是应用层申请的动态内存空间。可以想象,在释放内存时,根据动态内存的起始地址,向前偏移sizeof(BlockLink_t)字节的位置,就是该内存块头的位置,在32位的ARM V7下,该偏移量为8字节。
在堆内存池进行初始化后,由于整个内存池由一个线性数组提供,还没有划分过内存块出去,空闲空间还是一块连续的大内存,链表的状态如图1所示:
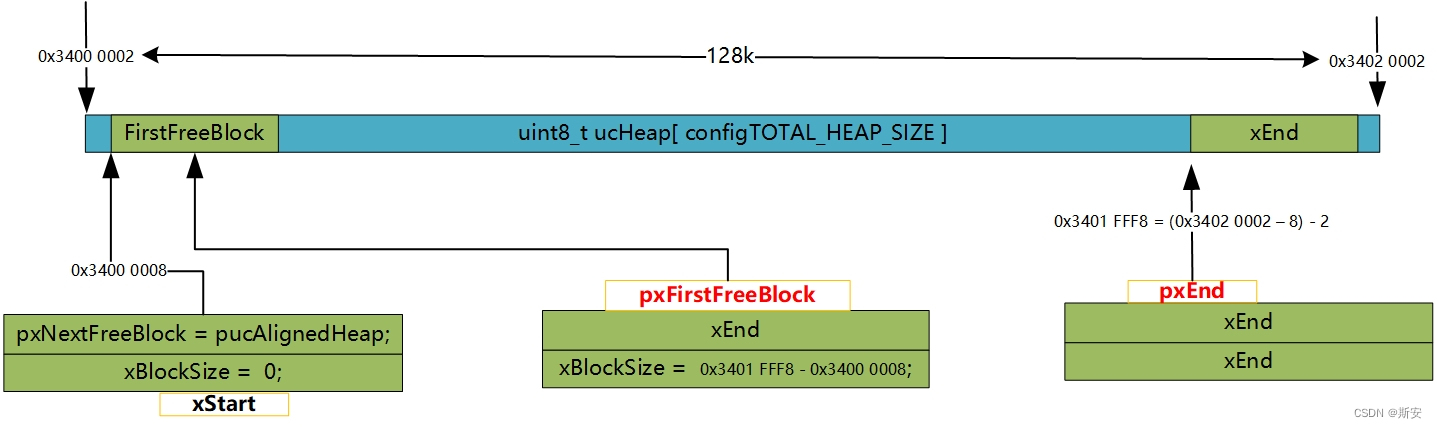
图1 堆初始化后内存块链表示意图
其中,图1中假设了ucHeap的起始地址为0x3400 0002(为了更好的演示8字节对齐的情况,通常最好使用已对齐地址),configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE为128k,除了xStart外,其余内存控制块的实体都是在内存池中,只是以指针的形式来访问。至于为什么要8字节对齐呢?据说,是AAPCS (Procedure Call Standard for the ARM Architecture)规范的要求,本质还是为了兼容64位对齐访存吧。
/* Block sizes must not get too small. */
#define heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE ( ( size_t ) ( xHeapStructSize << 1 ) )此外,heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE限制了最小内存块的大小,在32位CPU的情况下,该值位16字节。当内存碎片化到小于此值时,heap_4 就不再维护并使用该内存碎片了。
2.3 堆状态字
再来点直观的,用户可以通过vPortGetHeapStats函数来获取当前的堆状态,主要包含以下内容:
typedef struct xHeapStats
{
size_t xAvailableHeapSpaceInBytes; /* The total heap size currently available - this is the sum of all the free blocks, not the largest block that can be allocated. */
size_t xSizeOfLargestFreeBlockInBytes; /* The maximum size, in bytes, of all the free blocks within the heap at the time vPortGetHeapStats() is called. */
size_t xSizeOfSmallestFreeBlockInBytes; /* The minimum size, in bytes, of all the free blocks within the heap at the time vPortGetHeapStats() is called. */
size_t xNumberOfFreeBlocks; /* The number of free memory blocks within the heap at the time vPortGetHeapStats() is called. */
size_t xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining; /* The minimum amount of total free memory (sum of all free blocks) there has been in the heap since the system booted. */
size_t xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations; /* The number of calls to pvPortMalloc() that have returned a valid memory block. */
size_t xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees; /* The number of calls to vPortFree() that has successfully freed a block of memory. */
} HeapStats_t;其中:
①xAvailableHeapSpaceInBytes记录了当前堆空间中所有剩余的内存大小,单位为字节,在prvHeapInit的时候,该值达到人生巅峰,随后,每次pvPortMalloc时,都会自裁掉分配出去的空间;每次vPortFree的时候,又会加回来回收的内存空间,总之它记录了整个堆内存池中所有的可分配内存大小,这些内存有可能时连续的,也可能是分布在不连续的块中;在此基础上,xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining则是记录了xAvailableHeapSpaceInBytes的历史最小值,类似watermark的概念,可以用来评估堆内存空间大小是否够用;
②xSizeOfLargestFreeBlockInBytes,xSizeOfSmallestFreeBlockInBytes和xNumberOfFreeBlocks分别表示堆内存池中,最大空闲内存块的的大小、最小空闲内存块的大小和空闲内存块的大小,这两个极值和空闲内存块总数量主要是通过遍历所有空闲内存块链表来获取的;
③xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations和xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees则比较酱油,主要记录了成功pvPortMalloc和vPortFree的次数;
可以预想的是,heap_4维护了一些静态变量来记录堆内存的状态变量,尤其是对于①和③,果不其然:
PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xFreeBytesRemaining = 0U;
PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = 0U;
PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations = 0;
PRIVILEGED_DATA static size_t xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees = 0;这些静态变量贯穿整个heap_4所有的API实现,记录了堆内存池的实时状态,再接下来的源码分析中,随处可见。
2.4 vPortGetHeapStats
下面,是vPortGetHeapStats的源码:
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
void vPortGetHeapStats( HeapStats_t * pxHeapStats )
{
BlockLink_t * pxBlock;
size_t xBlocks = 0, xMaxSize = 0, xMinSize = portMAX_DELAY; /* portMAX_DELAY used as a portable way of getting the maximum value. */
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
pxBlock = xStart.pxNextFreeBlock;
/* pxBlock will be NULL if the heap has not been initialised. The heap
* is initialised automatically when the first allocation is made. */
if( pxBlock != NULL )
{
do
{
/* Increment the number of blocks and record the largest block seen
* so far. */
xBlocks++;
if( pxBlock->xBlockSize > xMaxSize )
{
xMaxSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize;
}
if( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xMinSize )
{
xMinSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize;
}
/* Move to the next block in the chain until the last block is
* reached. */
pxBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock;
} while( pxBlock != pxEnd );
}
}
( void ) xTaskResumeAll();
pxHeapStats->xSizeOfLargestFreeBlockInBytes = xMaxSize;
pxHeapStats->xSizeOfSmallestFreeBlockInBytes = xMinSize;
pxHeapStats->xNumberOfFreeBlocks = xBlocks;
taskENTER_CRITICAL();
{
pxHeapStats->xAvailableHeapSpaceInBytes = xFreeBytesRemaining;
pxHeapStats->xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations = xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations;
pxHeapStats->xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees = xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees;
pxHeapStats->xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining;
}
taskEXIT_CRITICAL();
}整个函数很简单,主要是遍历内存块链表获取总的内存块数、最大空闲内存块和最小空闲内存块大小,并从前文所说的静态状态字变量获取实时的内存池空闲空间大小、历史最小空闲空间大小、成功申请和释放内存的次数等。
2.5 prvHeapInit
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
static void prvHeapInit( void ) /* PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION */
{
BlockLink_t * pxFirstFreeBlock;
uint8_t * pucAlignedHeap;
size_t uxAddress;
size_t xTotalHeapSize = configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE;
/* Ensure the heap starts on a correctly aligned boundary. */
uxAddress = ( size_t ) ucHeap;
if( ( uxAddress & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0 )
{
uxAddress += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 );
uxAddress &= ~( ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK );
xTotalHeapSize -= uxAddress - ( size_t ) ucHeap;
}
pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) uxAddress;
/* xStart is used to hold a pointer to the first item in the list of free
* blocks. The void cast is used to prevent compiler warnings. */
xStart.pxNextFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap;
xStart.xBlockSize = ( size_t ) 0;
/* pxEnd is used to mark the end of the list of free blocks and is inserted
* at the end of the heap space. */
uxAddress = ( ( size_t ) pucAlignedHeap ) + xTotalHeapSize;
uxAddress -= xHeapStructSize;
uxAddress &= ~( ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK );
pxEnd = ( void * ) uxAddress;
pxEnd->xBlockSize = 0;
pxEnd->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL;
/* To start with there is a single free block that is sized to take up the
* entire heap space, minus the space taken by pxEnd. */
pxFirstFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap;
pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize = uxAddress - ( size_t ) pxFirstFreeBlock;
pxFirstFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxEnd;
/* Only one block exists - and it covers the entire usable heap space. */
xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize;
xFreeBytesRemaining = pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize;
/* Work out the position of the top bit in a size_t variable. */
xBlockAllocatedBit = ( ( size_t ) 1 ) << ( ( sizeof( size_t ) * heapBITS_PER_BYTE ) - 1 );
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/该初始化函数主要完成了内存块链表的初始化,具体见2.2章节,值得注意的是:
①初始化完成后,xStart.pxNextFreeBlock指向了内存池对齐后的首地址,pxEnd指针则指向了内存池末尾倒数第二个对齐的位置(即不再是空指针),也就是说,除了掐头去尾的对齐外(如有必要),内存池完成初始化后,还要缩水8字节用于存放pxEnd指向的内存头,用于标识内存之的末尾;
②在初始化函数的结尾,初始化了一个静态变量,该变量本质上是一个只有最高位是1、其余位为0的无符号的long,可以理解为是一个用于标识内存块是否已经被分配的掩码,(不清楚为什么没采用宏或者const变量),这个掩码也贯穿了整个heap_4;
2.6 pvPortMalloc
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
void * pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize )
{
BlockLink_t * pxBlock, * pxPreviousBlock, * pxNewBlockLink;
void * pvReturn = NULL;
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
/* If this is the first call to malloc then the heap will require
* initialisation to setup the list of free blocks. */
if( pxEnd == NULL )
{
prvHeapInit();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* Check the requested block size is not so large that the top bit is
* set. The top bit of the block size member of the BlockLink_t structure
* is used to determine who owns the block - the application or the
* kernel, so it must be free. */
if( ( xWantedSize & xBlockAllocatedBit ) == 0 )
{
/* The wanted size must be increased so it can contain a BlockLink_t
* structure in addition to the requested amount of bytes. */
if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) &&
( ( xWantedSize + xHeapStructSize ) > xWantedSize ) ) /* Overflow check */
{
xWantedSize += xHeapStructSize;
/* Ensure that blocks are always aligned. */
if( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0x00 )
{
/* Byte alignment required. Check for overflow. */
if( ( xWantedSize + ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) )
> xWantedSize )
{
xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) );
configASSERT( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 );
}
else
{
xWantedSize = 0;
}
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
else
{
xWantedSize = 0;
}
if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( xWantedSize <= xFreeBytesRemaining ) )
{
/* Traverse the list from the start (lowest address) block until
* one of adequate size is found. */
pxPreviousBlock = &xStart;
pxBlock = xStart.pxNextFreeBlock;
while( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xWantedSize ) && ( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock != NULL ) )
{
pxPreviousBlock = pxBlock;
pxBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock;
}
/* If the end marker was reached then a block of adequate size
* was not found. */
if( pxBlock != pxEnd )
{
/* Return the memory space pointed to - jumping over the
* BlockLink_t structure at its start. */
pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) + xHeapStructSize );
/* This block is being returned for use so must be taken out
* of the list of free blocks. */
pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock;
/* If the block is larger than required it can be split into
* two. */
if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE )
{
/* This block is to be split into two. Create a new
* block following the number of bytes requested. The void
* cast is used to prevent byte alignment warnings from the
* compiler. */
pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize );
configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pxNewBlockLink ) & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 );
/* Calculate the sizes of two blocks split from the
* single block. */
pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize;
pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize;
/* Insert the new block into the list of free blocks. */
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( pxNewBlockLink );
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize;
if( xFreeBytesRemaining < xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining )
{
xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xFreeBytesRemaining;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* The block is being returned - it is allocated and owned
* by the application and has no "next" block. */
pxBlock->xBlockSize |= xBlockAllocatedBit;
pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL;
xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations++;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize );
}
( void ) xTaskResumeAll();
#if ( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 )
{
if( pvReturn == NULL )
{
extern void vApplicationMallocFailedHook( void );
vApplicationMallocFailedHook();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif /* if ( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 ) */
configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pvReturn ) & ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 );
return pvReturn;
}其中:
①首次调用pvPortMalloc分配内存时,由于pxEnd还没初始化,所以会调用prvHeapInit对内存链表进行初始化;
②应用申请的内存大小为xWantedSize,该大小有上限,在32位CPU上,long为4字节,所以该上限为0x7FFFFFFF,嵌入式环境下也很少有这么大的内存池吧;
③由于需要额外的内存块头八字节的开销,xWantedSize会在应用申请的大小上自增八字节,这里的溢出校验在32位环境下显得没那么必要;
④随后,会对xWantedSize进行圆整,即向上八字节对齐;
⑤如果xWantedSize小于xFreeBytesRemaining(内存池空余的总内存大小,能分配的不充分必要条件),就从xStart开始遍历各空闲内存块,从内存块头上读取该内存块大小是否足够分配xWantedSize个字节;
⑥如果找到了足够大小的内存块,则将该空闲内存块头后的内存地址返回给应用,并将该内存块从内存块链表中剔除;在此基础上,如果该内存块剩余的空间大于heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE(32位上为8*2字节),则在此移植上建立新的内存块,并将该内存块头插入内存块链表中;
⑦如果内存分配成功,更新xFreeBytesRemaining,即减去xWantedSize(包含应用所需内存大小和内存头大小以及可能存在的对齐开销),并更新xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining(如果内存池剩余量创历史新低)和xNumberOfSuccessfulAllocations,并将返回给用户的该内存块头打上已分配的标记,即pxBlock->xBlockSize的最高位置1,同时将pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock置为空指针;
⑧如果分配失败,且应用层注册了对应的钩子函数,则运行该函数;
整体来看,动态内存对于的内存池的消耗,是要大于应用层申请的内存大小的,包括内存块头和对齐产生的内存开销,所以其优势还是在于灵活性。另一方面,内存块头中记录的pxBlock->xBlockSize的值包含了内存块BlockLink_t本身的大小,该内存块中可用的大小是pxBlock->xBlockSize - sizeof(BlockLink_t),缩水的这部分就是内存块头占用内存池的内存大小,这对于后边内存块链表操作的理解很重要。
2.7 prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
static void prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( BlockLink_t * pxBlockToInsert ) /* PRIVILEGED_FUNCTION */
{
BlockLink_t * pxIterator;
uint8_t * puc;
/* Iterate through the list until a block is found that has a higher address
* than the block being inserted. */
for( pxIterator = &xStart; pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock < pxBlockToInsert; pxIterator = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock )
{
/* Nothing to do here, just iterate to the right position. */
}
/* Do the block being inserted, and the block it is being inserted after
* make a contiguous block of memory? */
puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxIterator;
if( ( puc + pxIterator->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert )
{
pxIterator->xBlockSize += pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize;
pxBlockToInsert = pxIterator;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* Do the block being inserted, and the block it is being inserted before
* make a contiguous block of memory? */
puc = ( uint8_t * ) pxBlockToInsert;
if( ( puc + pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize ) == ( uint8_t * ) pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock )
{
if( pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock != pxEnd )
{
/* Form one big block from the two blocks. */
pxBlockToInsert->xBlockSize += pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock->xBlockSize;
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock;
}
else
{
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxEnd;
}
}
else
{
pxBlockToInsert->pxNextFreeBlock = pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock;
}
/* If the block being inserted plugged a gab, so was merged with the block
* before and the block after, then it's pxNextFreeBlock pointer will have
* already been set, and should not be set here as that would make it point
* to itself. */
if( pxIterator != pxBlockToInsert )
{
pxIterator->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlockToInsert;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/由于内存池是一片线性连续的内存,且其起始地址由xStart标识,且其起始地址是低地址,而后链表中的各内存块头记录的内存块起始地址必定是一山更比一山高的。所以,当一个内存块需要插入该链表时,其插入位置必定是在xStart标识的位置之后,且可以从链表中各内存块头标识的起始地址定位到插入位置。
因此,在prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList函数中:
①首先从xStart标识的位置开始遍历链表中各空闲内存块头,找到一个位置,该位置前面的链表元素的地址比插入元素(pxBlockToInsert指针指向的元素,记为BlockToInsert)的地址低,而后面的链表元素地址比插入元素的地址高,此处即是插入位置;
②既然找到了插入位置,则比较BlockToInsert的首尾地址与前后链表元素标识的地址是否可以衔接起来,即边界处是否相等,如果可以衔接起来,则将其合并成一个大的内存块;
所以说,heap_4所谓的内存碎片合并只能合并相邻的内存碎片,这归功于内存池的线性连续性,其碎片合并也反过来受制于整个线性连续上。反过来说,如果我们要使用heap_4的动态内存,对于那些上电后不释放的一类内存,要尽量集中在初始化时申请,对于那些需要反复申请并释放,甚至每次大小都不同的动态内存,则尽量在初始化完成后再开始使用。
2.8 vPortFree
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
void vPortFree( void * pv )
{
uint8_t * puc = ( uint8_t * ) pv;
BlockLink_t * pxLink;
if( pv != NULL )
{
/* The memory being freed will have an BlockLink_t structure immediately
* before it. */
puc -= xHeapStructSize;
/* This casting is to keep the compiler from issuing warnings. */
pxLink = ( void * ) puc;
/* Check the block is actually allocated. */
configASSERT( ( pxLink->xBlockSize & xBlockAllocatedBit ) != 0 );
configASSERT( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL );
if( ( pxLink->xBlockSize & xBlockAllocatedBit ) != 0 )
{
if( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL )
{
/* The block is being returned to the heap - it is no longer
* allocated. */
pxLink->xBlockSize &= ~xBlockAllocatedBit;
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
/* Add this block to the list of free blocks. */
xFreeBytesRemaining += pxLink->xBlockSize;
traceFREE( pv, pxLink->xBlockSize );
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( ( BlockLink_t * ) pxLink ) );
xNumberOfSuccessfulFrees++;
}
( void ) xTaskResumeAll();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/其中:
①通过申请释放的内存地址pv前移xHeapStructSize个字节找到内存块头的位置,即pxLink指向的位置;
②将内存块头中xBlockSize的最高位中已分配的标识清除;
③关调度,将该内存块插入空闲内存块链表,并将其大小增加到xFreeBytesRemaining变量中去,完成后打开调度;
3.总结
回过头来看:
①heap_4的内存是完全是建立在一片线性连续的内存上的,heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE的定义可以抑制过度的内存碎片化;
②而在申请和释放内存时,必然要有查询空闲块链表的操作,其所谓的不确定性也主要存在这里,即链表的查询时间;
③另外,除了链表的首个元素xStart外,其余链表元素(内存块头)都是占用内存池的空间,这也在一定程度上导致了可分配内存的缩水;
④如果需要且允许使用动态内存,heap_4支持指定内存池的起始地址,需要注意内存池是否与其他内存空间隔离开,防止内存踩踏。