目录
引言
栈(stack),可以用数组实现,也可以用链表实现。用数组实现的栈叫顺序栈,用链表实现的栈叫链式栈,本文讲解的是顺序栈。栈,作为一种特殊的数据结构,在一些方面有着重要用途,例如,快速排序的非递归实现就需要借助栈来完成。
栈的性质
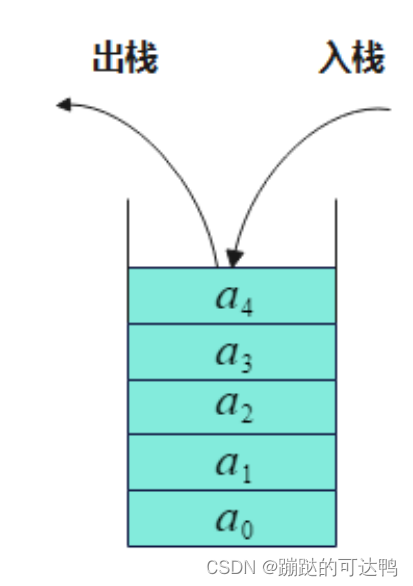
栈是限定仅在栈顶进行插入或删除操作的线性表。它是遵循“后进先出”的原则的,队列正好与之相反。

顺序栈
底层用数组实现,当数组空间不够用时就扩容。这些操作和用数组来实现通讯录如出一辙,想必大家已轻车熟路,这里就点到为止了。

栈的基本操作
因为顺序栈的底层是用数组实现,所以本质上还是在操作数组。
初始化
初始化操作一般有两种,第一种,在初始化时就给数组分配一定的空间,第二种,初始化时不给分配空间,第一次插入数据时才个数组分配空间。这两种方法用哪一种都无可厚非,按自己喜好来就好,这里呢我就偏爱第二种方法。
代码:
typedef int StackDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
StackDataType* a;
int capacity;//容量
int top;
}Stack;void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;//容量
pst->top = 0;
}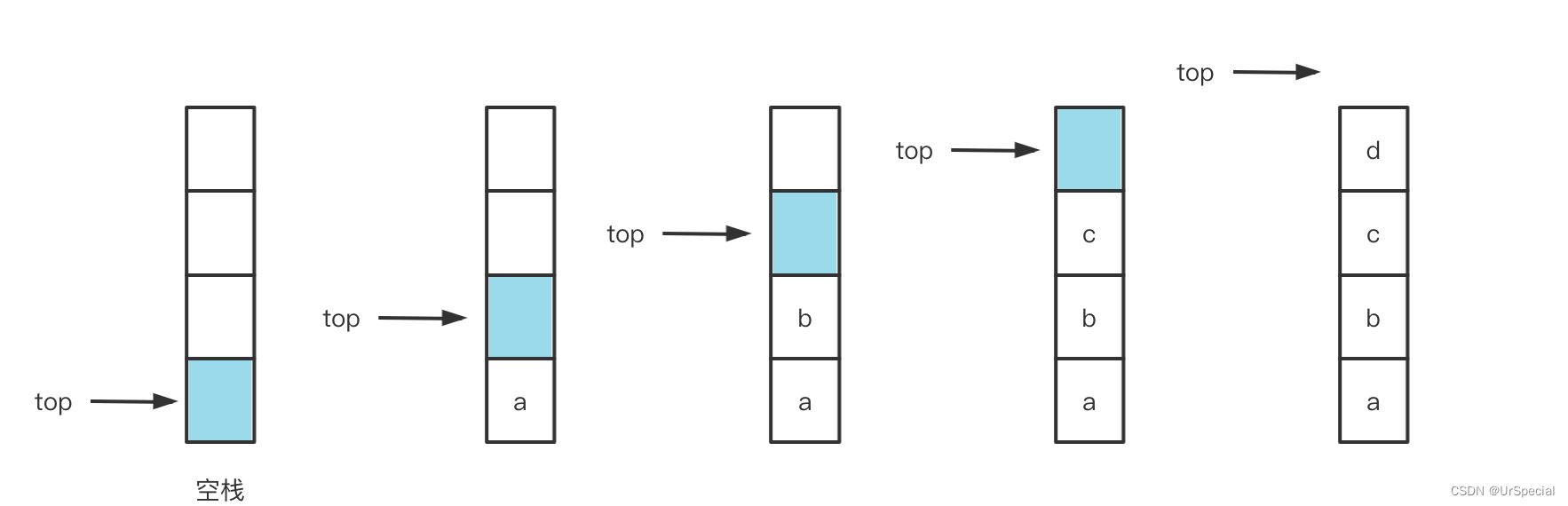 需要注意的一个细节是,top指向的是栈顶元素的下一个,以防返回栈顶元素时出现错误。细心观察也会发现,top的值就是栈中的元素个数,这样,返回栈的大小就简单了。
需要注意的一个细节是,top指向的是栈顶元素的下一个,以防返回栈顶元素时出现错误。细心观察也会发现,top的值就是栈中的元素个数,这样,返回栈的大小就简单了。
销毁
因为底层使用数组实现,所以要释放数组空间只需要free一把就行了。
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->top = 0;
free(pst->a);
}插入
底层用数组实现,那么在插入时就有可能面临着空间不够的问题,所以在插入之前,需要判断数组是否已满。
代码:
void StackPush(Stack* pst, StackDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->capacity == pst->top)
{
int newCapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
StackDataType* tmp = (StackDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(StackDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
删除
顺序栈的删除实际上就是数组最后一个元素的删除,不需要挪动数据,top--即可,这样即使数组中还存在该元素,但是已经访问不到了。
代码:
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->top--;
}判空
空的特征是:top为0,所以只需要判断top是否为0即可。
代码:
bool StackEmtpy(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}取栈顶元素
栈顶元素的下标为top-1,返回该下标对应的值即可。
代码:
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}虽然简单,但请不要写成pst->a[pst->top--]. 后置--是有副作用的,也就是说会改变top的值,但这里不需要改变top的值。当然,这种错误是极小概率事件,只是顺便提一提。
栈的大小
top的值就是栈的大小,所以返回top即可。
代码:
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}完整代码:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int StackDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
StackDataType* a;
int capacity;//容量
int top;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* pst);
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst);
void StackPush(Stack* pst, StackDataType x);
void StackPop(Stack* pst);
bool StackEmtpy(Stack* pst);
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
int StackSize(Stack* pst);
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->top = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->top = 0;
free(pst->a);
}
void StackPush(Stack* pst, StackDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->capacity == pst->top)
{
int newCapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
StackDataType* tmp = (StackDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(StackDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->top--;
}
bool StackEmtpy(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}