手动实现哈希表
哈希表的定义
哈希表的定义:
- 哈希函数:将任意长度的输入(一般是字符串)映射到一个固定长度的输出(一般是整数)上,这个映射函数称为哈希函数。
- 哈希表:是一种数据结构,它以某种方式将键(key)映射到值(value)上。
- 哈希表的特点:
- 哈希表的存储空间是有限的,当元素的数量超过了存储空间时,就会出现哈希冲突。
- 哈希表的查找、插入、删除操作的时间复杂度都为O(1)。
手动实现哈希表
手动实现哈希表的步骤如下:
- 定义哈希表的结构,包括哈希表的大小,以及哈希表的数组。
- 定义哈希函数,将键映射到数组的索引上。
- 定义节点的结构,包括节点的键和值,以及指向下一个节点的指针。
- 定义插入、查找、删除操作。
- 测试哈希表。
下面是实现的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 手动实现哈希表
// 哈希表长定义
#define HASH_SIZE 1000001
// 哈希函数
#define HASH(x) ((x) % HASH_SIZE)
// 节点的定义
struct Node {
int key;
int value;
struct Node *next;
};
// 哈希表的结构
struct HashTable {
struct Node *table[HASH_SIZE];
};
// 创建哈希表
struct HashTable *createHashTable() {
struct HashTable *ht = (struct HashTable *)malloc(sizeof(struct HashTable));
memset(ht->table, 0, sizeof(ht->table));
return ht;
}
// 插入元素
void insert(struct HashTable *ht, int key, int value) {
// 先查找是否存在该元素
int index = HASH(key);
// 遍历链表
struct Node *p = ht->table[index];
while (p) {
if (p->key == key) {
p->value = value;
return;
}
p = p->next;
}
// 元素不存在,插入到链表头
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->key = key;
newNode->value = value;
newNode->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = newNode;
}
// 查找元素
int search(struct HashTable *ht, int key) {
int index = HASH(key);
struct Node *p = ht->table[index];
while (p) {
if (p->key == key) {
return p->value;
}
p = p->next;
}
return -1;
}
// 删除元素
void delete(struct HashTable *ht, int key) {
int index = HASH(key);
struct Node *p = ht->table[index];
struct Node *q = NULL;
while (p) {
if (p->key == key) {
if (q) {
q->next = p->next;
} else {
ht->table[index] = p->next;
}
free(p);
return;
}
q = p;
p = p->next;
}
}
// 测试代码
int main() {
// 测试哈希表
struct HashTable *ht = createHashTable();
// 插入元素
insert(ht, 1, 10);
insert(ht, 2, 20);
insert(ht, 3, 30);
// 查找元素
printf("%d\n", search(ht, 2)); // 20
// 删除元素
delete(ht, 2);
// 查找元素
printf("%d\n", search(ht, 2)); // -1
return 0;
}
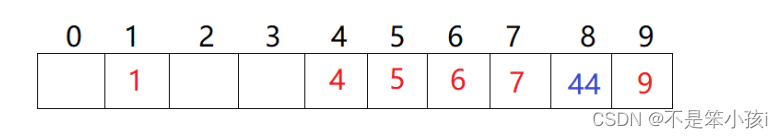
哈希冲突
当多个元素映射到同一个索引时,称为哈希冲突。常见的哈希冲突解决方法有开放寻址法、链表法、再散列法。
开放寻址法
开放寻址法是指当发生哈希冲突时,重新探测一个空闲位置,直到找到一个空闲位置为止。
void insert(struct HashTable *ht, int key, int value) {
int index = HASH(key);
int i = 0;
while (ht->table[index] != NULL) {
// 探测下一个位置
index = (index + i) % HASH_SIZE;
i++;
}
// 找到空闲位置
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->key = key;
newNode->value = value;
newNode->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = newNode;
}
链表法
链表法是指将哈希表的数组元素指向链表,每个链表中存储同一哈希值的所有元素。
struct Node {
int key;
int value;
struct Node *next;
};
struct HashTable {
struct Node **table;
};
void insert(struct HashTable *ht, int key, int value) {
int index = HASH(key);
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->key = key;
newNode->value = value;
newNode->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = newNode;
}
int search(struct HashTable *ht, int key) {
int index = HASH(key);
struct Node *p = ht->table[index];
while (p) {
if (p->key == key) {
return p->value;
}
p = p->next;
}
return -1;
}
void delete(struct HashTable *ht, int key) {
int index = HASH(key);
struct Node *p = ht->table[index];
struct Node *q = NULL;
while (p) {
if (p->key == key) {
if (q) {
q->next = p->next;
} else {
ht->table[index] = p->next;
}
free(p);
return;
}
q = p;
p = p->next;
}
}
struct HashTable *createHashTable() {
struct HashTable *ht = (struct HashTable *)malloc(sizeof(struct HashTable));
ht->table = (struct Node **)malloc(sizeof(struct Node *) * HASH_SIZE);
memset(ht->table, 0, sizeof(ht->table));
return ht;
}
再散列法
再散列法是指当发生哈希冲突时,重新计算哈希值,直到找到一个空闲位置为止。
void insert(struct HashTable *ht, int key, int value) {
int index = HASH(key);
while (ht->table[index] != NULL) {
// 重新计算哈希值
key = (key + 1) % HASH_SIZE;
index = HASH(key);
}
// 找到空闲位置
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->key = key;
newNode->value = value;
newNode->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = newNode;
}
哈希表的应用
- 字符串查找(涉及到字符串哈希):字符串查找是哈希表的典型应用。
- 缓存:缓存是哈希表的另一个典型应用。
- 数据库索引:数据库索引也是哈希表的一种应用。
- 哈希函数的设计:哈希函数的设计可以影响哈希表的性能。
- 哈希表的扩展:哈希表的扩展可以实现动态哈希表。
参考
每一个不曾起舞的日子,都是对生命的辜负。



![详解—[<span style='color:red;'>C</span>++<span style='color:red;'>数据</span>结构]—<span style='color:red;'>哈</span><span style='color:red;'>希</span> <<span style='color:red;'>哈</span><span style='color:red;'>希</span><span style='color:red;'>表</span>&&<span style='color:red;'>哈</span><span style='color:red;'>希</span>桶>](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ce1c8ac6b2ef48f4be66c884135b22ef.png)