C++ 23种设计模式
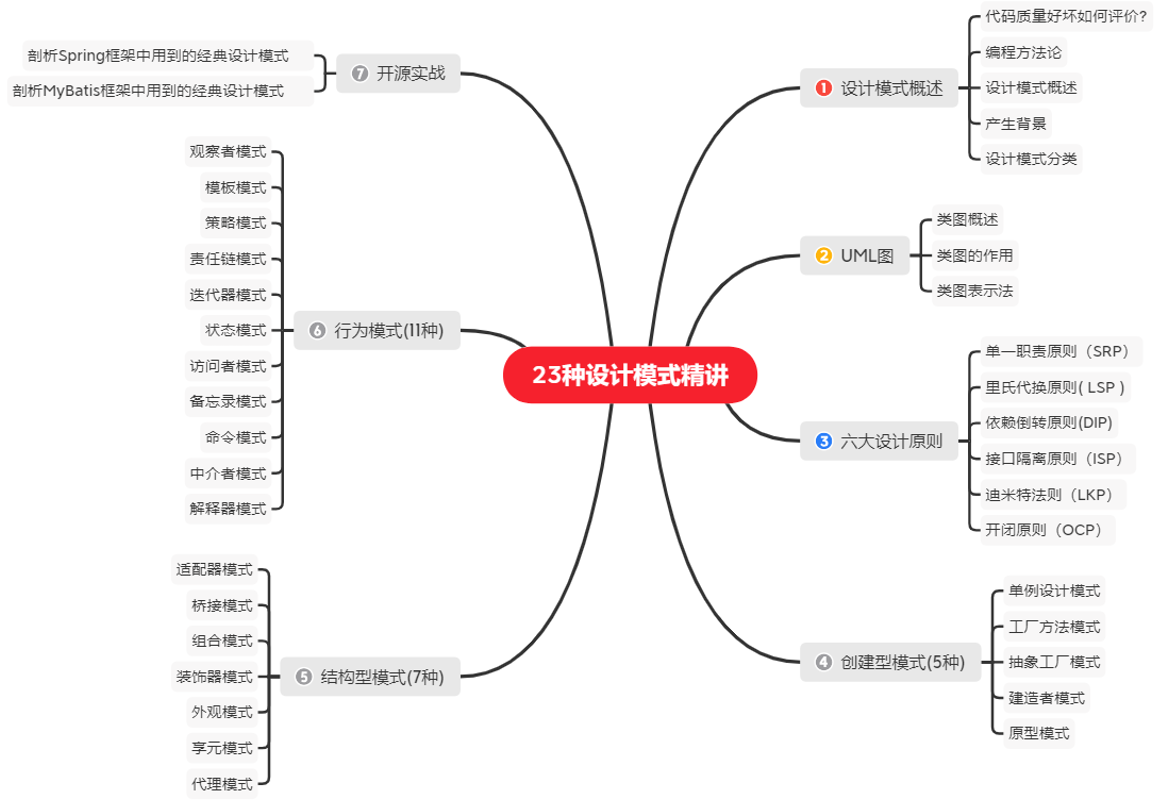
■ 创建型模式(5种)
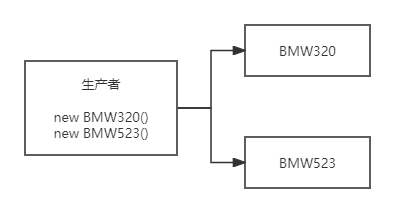
■ 工厂模式
示例一:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
enum CTYPE{COREA,COREB};
//定义一个基类单核
class SingleCore
{
public:
virtual void show() = 0;
};
//单核A
class SingleCoreA:public SingleCore
{
public:
void show() {
cout << "SingleCore A" << endl;
}
};
//单核B
class SingleCoreB:public SingleCore
{
public:
void show() {
cout << "SingleCore B" << endl;
}
};
//唯一的工厂,可以生成A、B两种处理器核,在内部判断
class Factory {
public:
//基类的对象指针指向子类的对象,也就是多态
SingleCore* CreateSingleCore(CTYPE ctype)
{
//工厂内部判断
if (ctype == COREA)
{
//生产核A
return new SingleCoreA();
}
else if (ctype == COREB)
{
//生产核B
return new SingleCoreB();
}
else {
return NULL;
}
}
};
int main()
{
Factory* factor = new Factory();
factor->CreateSingleCore(COREA)->show();
getchar();
return 0;
}
■ 抽象工厂模式
■ 原型模式
■ 单例模式
■ 第一种:单线程(懒汉)
//单线程解法
//这种解法在多线程的情况下,可能创建多个实例。
class Singleton1
{
private:
static Singleton1* m_pInstance1;//需要的时候才创建,懒汉
//利用static关键字的特性,不属于任何类,整个类只有一个
Singleton1();
public:
static Singleton1* GetInstance1();
static void DestroyInstance1();
};
Singleton1::Singleton1()
{
cout << "创建单例" << endl;
}
Singleton1* Singleton1::GetInstance1()
{
return m_pInstance1;
}
void Singleton1::DestroyInstance1()
{
if (m_pInstance1 != nullptr)
{
delete m_pInstance1;
m_pInstance1 = nullptr;
}
}
//初始化一个对象
Singleton1* Singleton1::m_pInstance1 = new Singleton1();
//单线程下多次获取实例
void test1()
{
Singleton1* singletoObj1 = Singleton1::GetInstance1();
cout << singletoObj1 << endl;
Singleton1* singletoObj2 = Singleton1::GetInstance1();
cout << singletoObj2 << endl;
//上面的两个对象会指向同一个地址
Singleton1::DestroyInstance1();
}
■ 第二种:多线程(互斥量实现锁+懒汉)
//多线程+加锁(互斥量)
class Singleton2
{
private:
Singleton2();
static Singleton2* m_pInstance2;
static mutex m_mutex;//互斥量
public:
static Singleton2* GetInstance2();
static void DestroyInstance2();
};
Singleton2::Singleton2()
{
cout << "创建单例2" << endl;
}
Singleton2* Singleton2::GetInstance2()
{
if (m_pInstance2 == nullptr)
{
cout << "加锁中" << endl;
m_mutex.lock();
if (m_pInstance2 == nullptr)
{
m_pInstance2 = new Singleton2();
}
cout << "解锁中" << endl;
m_mutex.unlock();
}
return m_pInstance2;
}
void Singleton2::DestroyInstance2()
{
if (m_pInstance2 != nullptr)
{
delete m_pInstance2;
m_pInstance2 = nullptr;
}
}
//静态成员变量的定义
Singleton2* Singleton2::m_pInstance2 = nullptr;//懒汉式的写法
mutex Singleton2::m_mutex;
//常见一个实例对象,给下面的多线程调用
void print_singleton_instance()
{
Singleton2* singletonObj2 = Singleton2::GetInstance2();
cout << "新的一个实例对象" << singletonObj2 << endl;
}
void test2()
{
vector<thread> threads;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
//十个线程都指向同一个静态变量的地址
threads.push_back(thread(print_singleton_instance));
}
for (auto& thr : threads)
{
thr.join();
}
}
■ 第三种:多线程(const static+饿汉)(还要继续了解)
//方案三:使用const特性,来替换方案二的加锁操作
class Singleton3
{
private:
Singleton3(){}
static const Singleton3* m_pInstance3;
public:
static Singleton3* GetInstance3();
static void DestroyInstance3();
};
Singleton3* Singleton3::GetInstance3()
{
//这个函数的返回值如果变化曾const static属性,就不用进行const_cast
return const_cast<Singleton3*> (m_pInstance3);
}
void Singleton3::DestroyInstance3()
{
if (m_pInstance3 != nullptr)
{
delete m_pInstance3;
m_pInstance3 = nullptr;
}
}
//静态成员变量的定义
const Singleton3* Singleton3::m_pInstance3 = new Singleton3();//饿汉式的写法
//常见一个实例对象,给下面的多线程调用
void print_singleton_instance3()
{
Singleton3* singletonObj3 = Singleton3::GetInstance3();
cout << "新的一个实例对象" << singletonObj3 << endl;
}
void test3()
{
vector<thread> threads;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
//十个线程都指向同一个静态变量的地址
threads.push_back(thread(print_singleton_instance3));
}
for (auto& thr : threads)
{
thr.join();
}
}