迭代器模式(Iterator)
定义
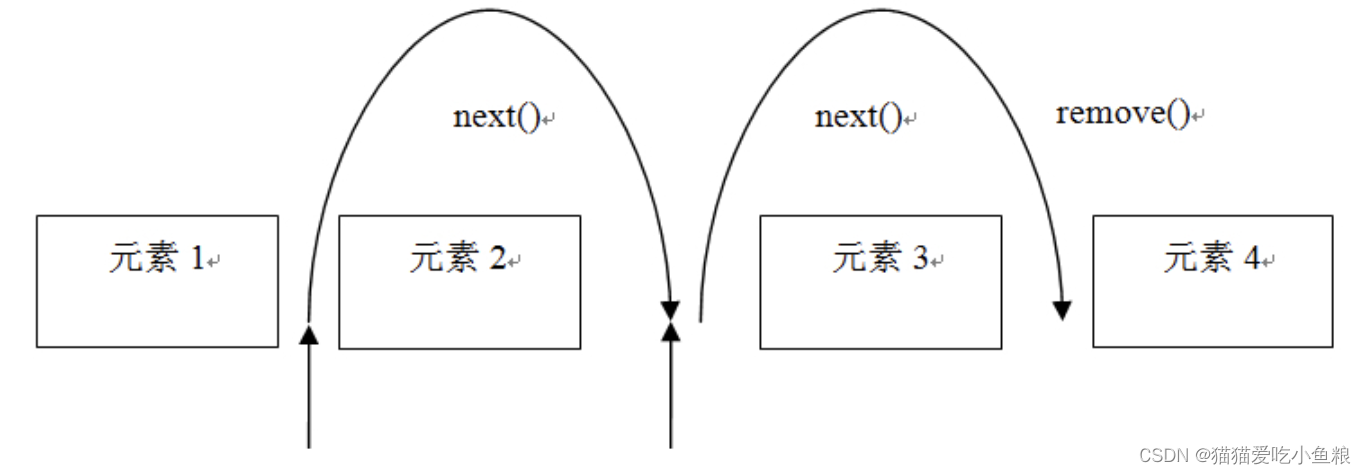
提供一种顺序访问一个聚合对象(容器)中各个元素的方法,而又不暴露其内部的表示。
使用场景
主要角色
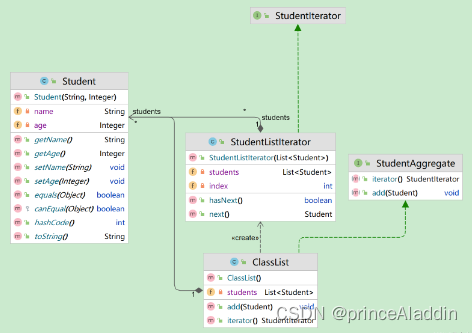
- 迭代器Iterator
- 具体的迭代器ConcreteIterator
- 聚合Aggregate
- 具体的聚合ConcreteAggregate
类图
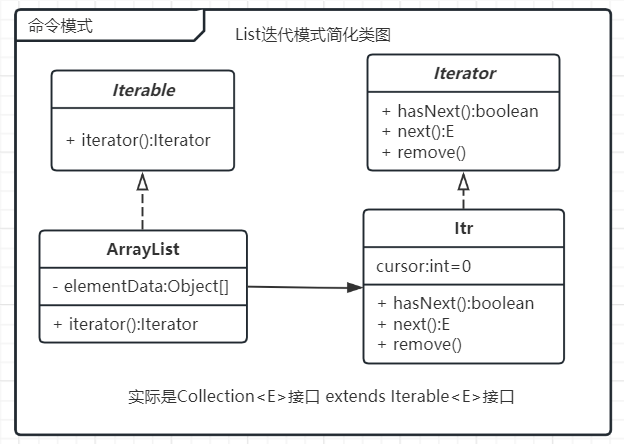
ArrayList真实的继承体系

示例代码
public interface Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext();
E next();
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");
}
default void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (hasNext())
action.accept(next());
}
}
java.util.ArrayList.Itr
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
java.util.ArrayList#iterator
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}