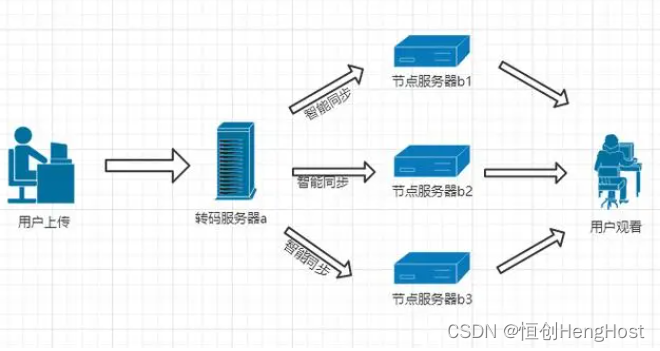
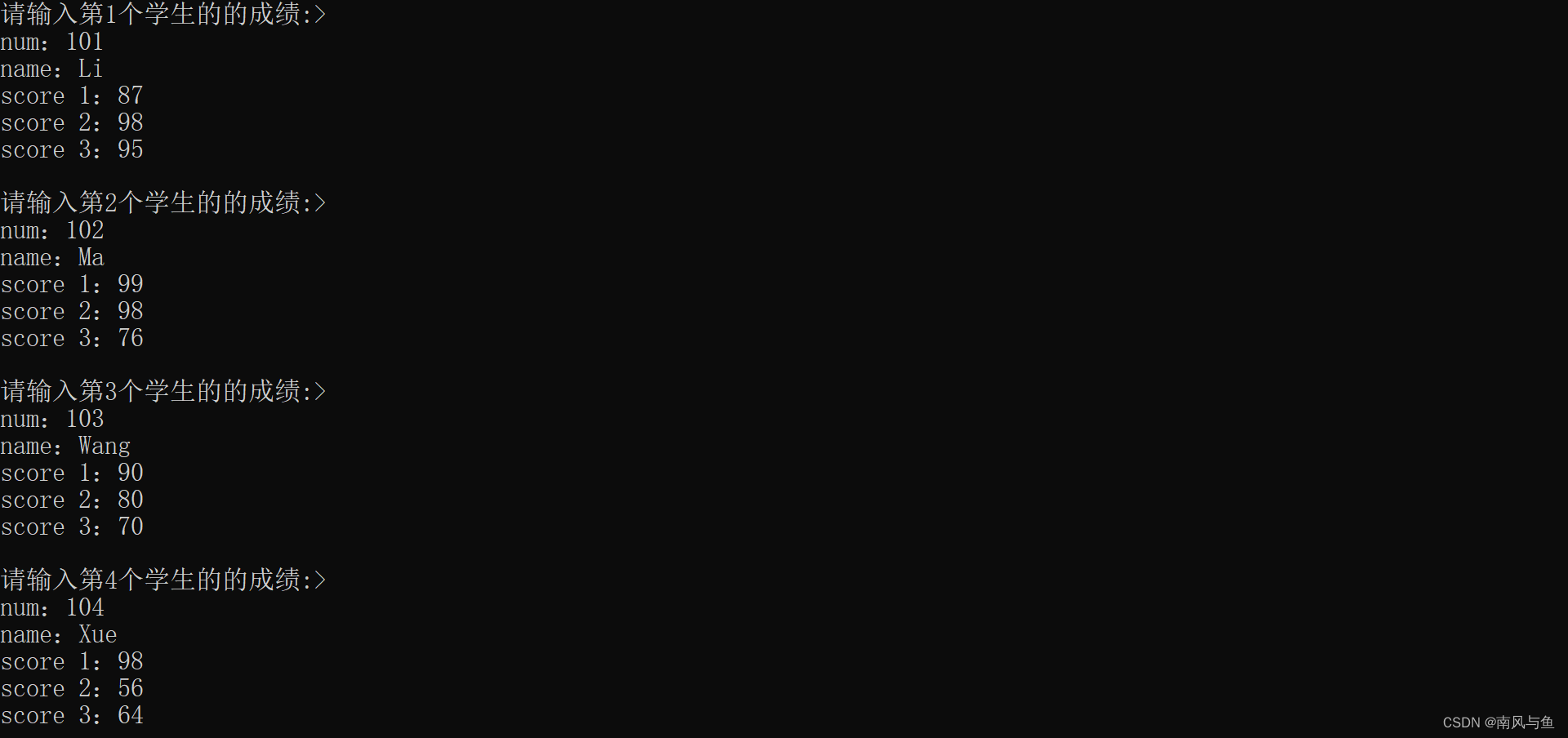
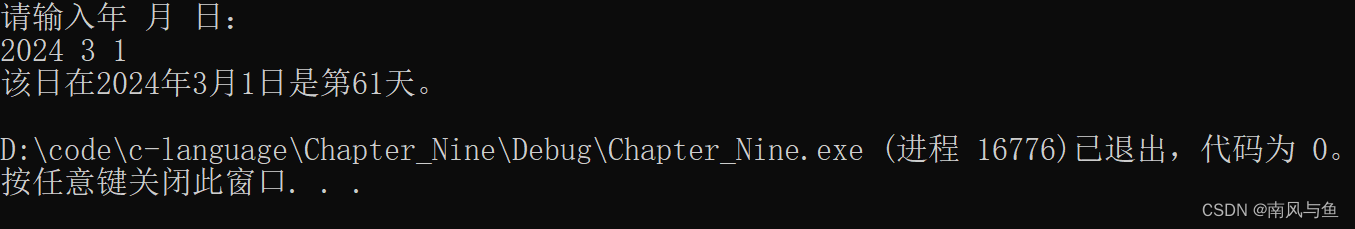
1.定义一个结构体变量(包括年、月、日)。计算该日在本年中是第几天,注意闰年问题。
#include <stdio.h> struct date { int year; int month; int day; }d; int main() { int day[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; printf("请输入年 月 日:\n"); scanf("%d%d%d", &d.year, &d.month, &d.day); int days = 0; for (int i = 1; i < d.month; i++) { days += day[i]; } days += d.day; if (d.year % 4 == 0 && d.year % 100 != 0 || d.year % 400 == 0) { if (d.month > 2) { days++; } } printf("该日在%d年%d月%d日是第%d天。\n", d.year, d.month, d.day, days); return 0; }
2.写一个函数days,实现第1题的计算。由主函数将年、月、日传递给 days函数,计算后将日子数传回主函数输出。
#include <stdio.h> struct date { int year; int month; int day; }d; int days(int year, int month, int day) { int day_tab[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; int day_sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i < d.month; i++) { day_sum += day_tab[i]; } day_sum += d.day; if (d.year % 4 == 0 && d.year % 100 != 0 || d.year % 400 == 0) { if (d.month > 2) { day_sum++; } } return day_sum; } int main() { printf("请输入年 月 日:\n"); scanf("%d%d%d", &d.year, &d.month, &d.day); int day_sum = days(d.year, d.month, d.day); printf("该日在%d年%d月%d日是第%d天。\n", d.year, d.month, d.day, day_sum); return 0; }
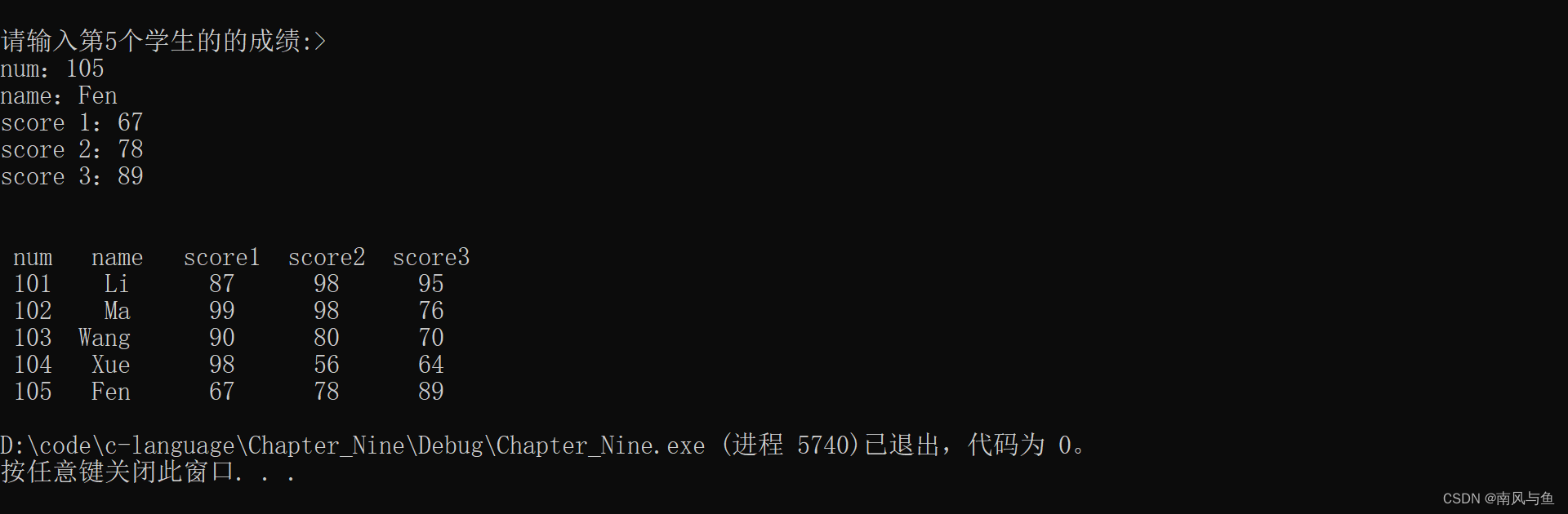
3.编写一个函数 print,打印一个学生的成绩数组,该数组中有5个学生的数据记录,每个记录包括 num, name, score[3],用主函数输入这些记录,用 print函数输出这些记录。
#include <stdio.h> #define N 5 struct student { char num[6]; char name[8]; int score[3]; }stu[N]; void print(struct student stu[6]) { printf("\n num name score1 score2 score3\n"); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { printf("%4s%6s", stu[i].num, stu[i].name); for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { printf("%8d", stu[i].score[j]); } printf("\n"); } } int main() { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { printf("请输入第%d个学生的的成绩:>\n", i + 1); printf("num:"); scanf("%s", stu[i].num); printf("name:"); scanf("%s", stu[i].name); for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { printf("score %d:", j + 1); scanf("%d", &stu[i].score[j]); } printf("\n"); } print(stu); return 0; }
4.在第3题的基础上,编写一个函数 input,用来输入5个学生的数据记录。
#include <stdio.h> #define N 5 struct student { char num[6]; char name[8]; int score[3]; }stu[N]; void print(struct student stu[6]) { printf("\n num name score1 score2 score3\n"); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { printf("%4s%6s", stu[i].num, stu[i].name); for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { printf("%8d", stu[i].score[j]); } printf("\n"); } } void input(struct student stu[]) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { printf("请输入第%d个学生的的成绩:>\n", i + 1); printf("num:"); scanf("%s", stu[i].num); printf("name:"); scanf("%s", stu[i].name); for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { printf("score %d:", j + 1); scanf("%d", &stu[i].score[j]); } printf("\n"); } } int main() { input(stu); print(stu); return 0; }
5.有10个学生,每个学生的数据包括学号、姓名、3门课程的成绩,从键盘输入10个学生数据,要求输出3门课程总平均成绩,以及最高分的学生的数据(包括学号、姓名、3门课程成绩、平均分数)。
#include <stdio.h> #define N 3 struct student { char num[6]; char name[8]; float score[3]; float avg; }stu[N]; int main() { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { printf("请输入第%d个学生的的数据:>\n", i + 1); printf("num:"); scanf("%s", stu[i].num); printf("name:"); scanf("%s", stu[i].name); for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { printf("score %d:", j + 1); scanf("%f", &stu[i].score[j]); } } //计算 float average = 0, max = 0; int maxi = 0; float sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { sum = 0; for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { sum += stu[i].score[j];//计算第i个学生总分 } stu[i].avg = sum / 3.0;//计算第i个学生平均分 average += stu[i].avg; if (sum > max)//找分数最高者 { max = sum; maxi = i;//将此学生的下标保存在maxi } } average /= N;//计算总平均分数 printf("\n num name score1 score2 score3 average\n"); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { printf("%3.2s%6.2s", stu[i].num, stu[i].name); for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { printf("%8.2f", stu[i].score[j]); } printf("%8.2f\n", stu[i].avg); } printf("\naverage=%5.2f\n", average); printf("最高成绩是:student %s, %s\n", stu[maxi].num, stu[maxi].name); printf("他的成绩是:%6.2f,%6.2f,%6.2f,average:%5.2f\n", stu[maxi].score[0], stu[maxi].score[1], stu[maxi].score[2], stu[maxi].avg); return 0; }
6.13个人围成一圈,从第1个人开始顺序报号1,2,3。凡报到3者退出圈子。找出最后留在圈子中的人原来的序号。要求用链表实现。
#include <stdio.h> #define NUM 13 //定义节点 typedef struct people { int num; struct people* next; }people; int main() { //定义包含13个人的数据 people arr[NUM]; //建立环状链表 people* head = arr; for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++) { head->num = i + 1; head->next = &arr[i + 1]; head = head->next; } //构成环状链表 arr[NUM - 1].next = arr; //开始报数 int count = NUM; //从1开始报数 int i = 1; head = arr; while (count > 1) { //1.判断是否已经退出 if (head->next == 0) { //跳过此人 head = head->next; continue; } if (i == 3) { //当前此人需要退出 printf("第%d个人退出\n", head->num); head->num = 0; count--; } //继续报号 i++; head = head->next; //判断报号是否大于3 if (i > 3) { i = 1; } } //找出编号不为0的人 while (head->num == 0) { //找下一个人 head = head->next; if (head->num != 0) { printf("没有退出的人为:%d\n", head->num); } } return 0; }
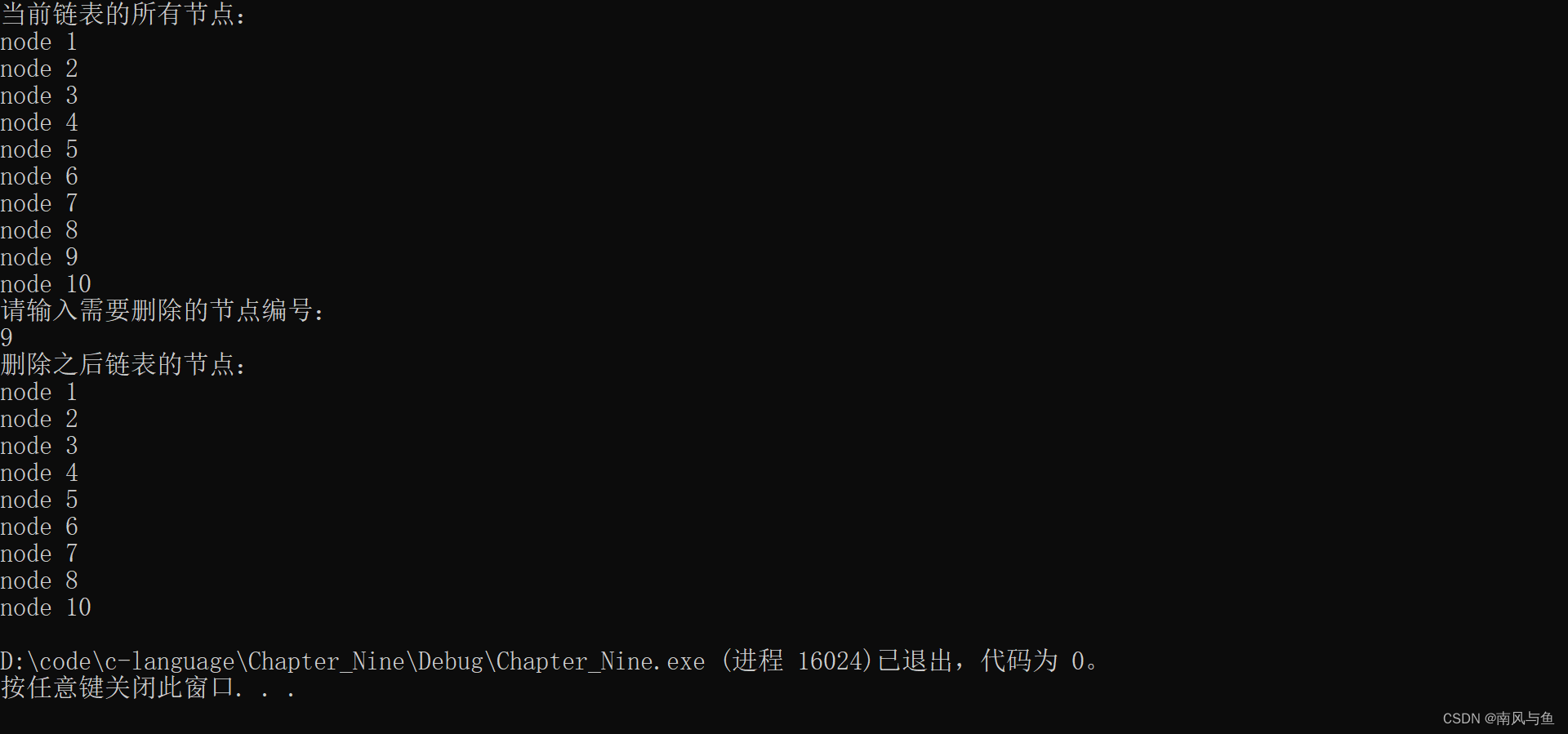
7. 在第9章例9.9和例9.10的基础上,写一个函数del,用来删除动态链表中指定的结点。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef struct node { int num; struct node* next; }node; //创建链表:创建一个含有n个节点的链表,返回头节点的指针 node* creat(int n) { //创建一个头节点 node* head = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); head->num = 0; head->next = NULL; node* p = head; //创建数据为1~n的节点 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { node* newNode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); newNode->num = i; newNode->next = NULL; p->next = newNode; p = p->next; } return head; } //打印链表数据 void printNode(node* head) { //第一个数据为head->next node* p = head->next; while (p != NULL) { printf("node %d\n", p->num); p = p->next; } } void del(node* head, int val) { node* prev = head; node* p = head; //遍历链表,找到需要删除的节点 while (p != NULL) { if (p->num == val) { prev->next = p->next; free(p); break; } else { prev = p; p = p->next; } } } int main() { node* head = creat(10); int n; printf("当前链表的所有节点:\n"); printNode(head); printf("请输入需要删除的节点编号:\n"); scanf("%d", &n); del(head, n); //删除之后链表的节点 printf("删除之后链表的节点:\n"); printNode(head); return 0; }
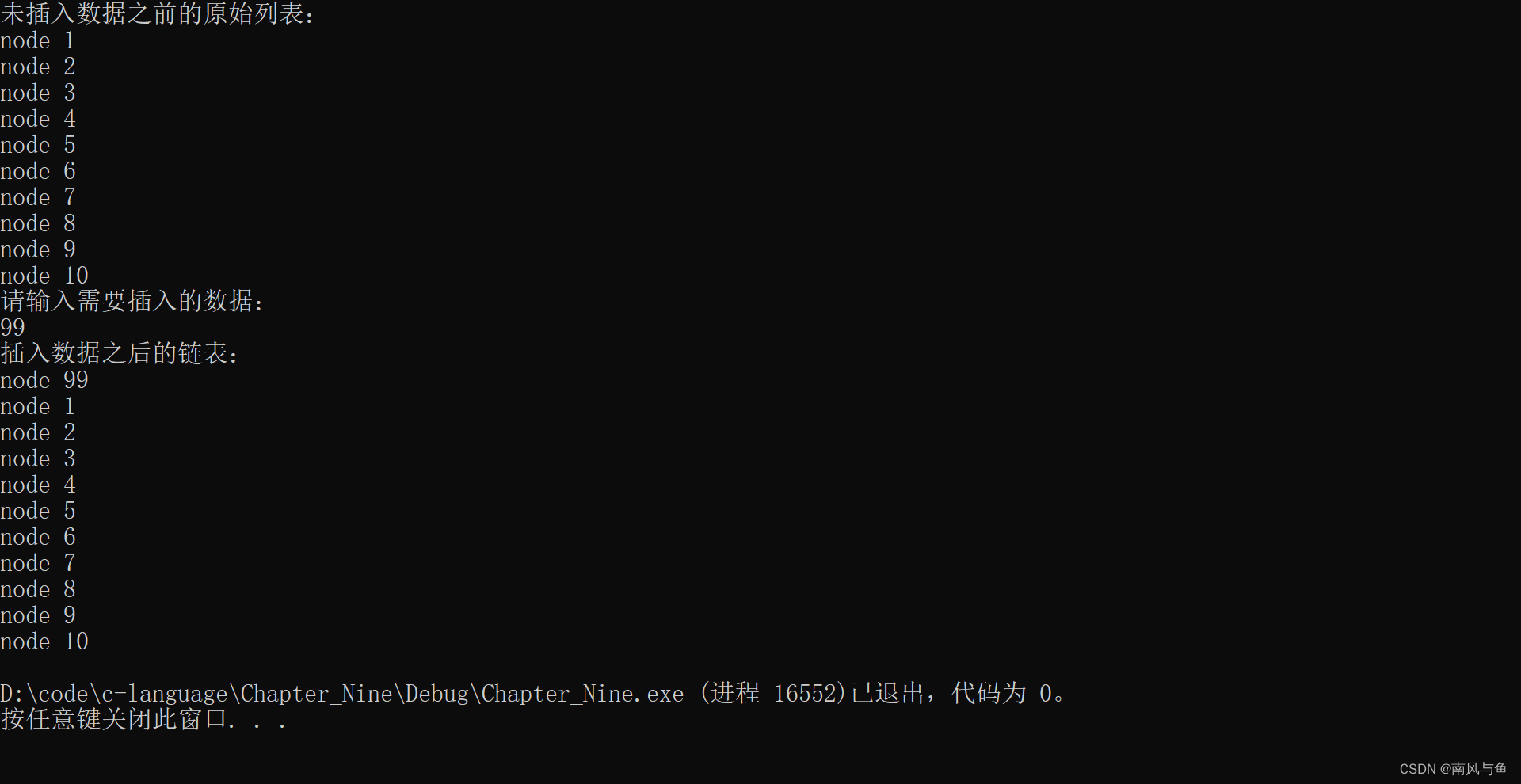
8. 写一个函数 insert,用来向一个动态链表插入结点。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef struct node { int num; struct node* next; }node; void insert(node* p, int n) { //创建节点 node* newNode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); newNode->num = n; //链接 newNode->next = p->next; p->next = newNode; } node* creat(int n) { //创建含有n个有效数据的节点 //创建一个带头的链表 node* head = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); head->num = 0; head->next = NULL; node* p = head; //创建有效数据的节点 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { node* newNode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); newNode->num = i; newNode->next = NULL; p->next = newNode; p = p->next; } return head; } void printNode(node* head) { //从第一个有效数据开始打印 node* p = head->next; while (p != NULL) { printf("node %d\n", p->num); p = p->next; } } int main() { int n; node* head = creat(10); printf("未插入数据之前的原始列表:\n"); printNode(head); printf("请输入需要插入的数据:\n"); scanf("%d", &n); insert(head, n); printf("插入数据之后的链表:\n"); printNode(head); return 0; }
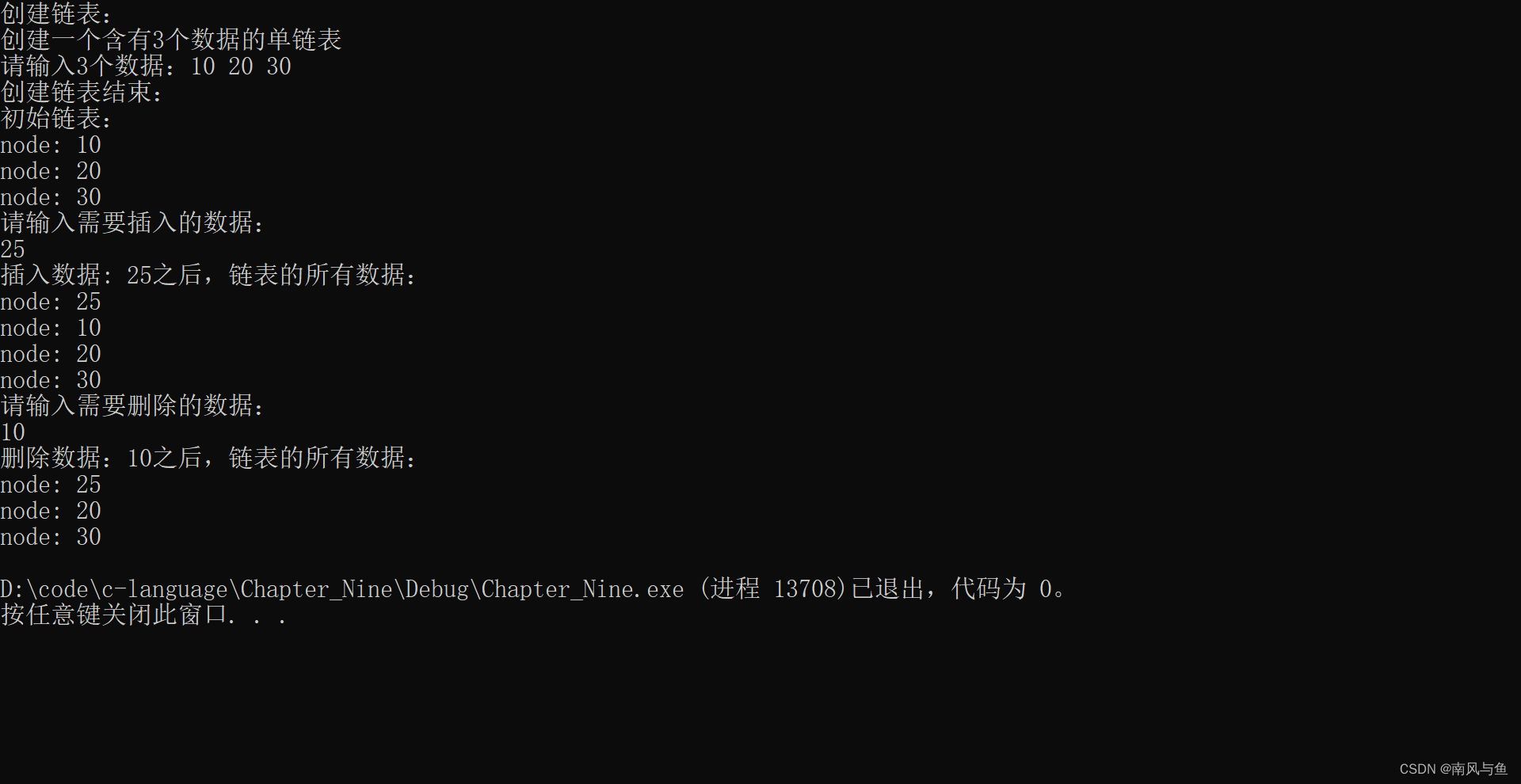
9.综合本章例9.9(建立链表的函数 creat)、例9.10(输出链表的函数 print)和本章习题第7题(删除链表中结点的函数dei)、第8题(插入结点的函数 insert),再编写一个主函数,先后调用这些函数。用以上5个函数组成一个程序,实现链表的建立、输出、删除和插入,在主函数中指定需要删除和插入的结点的数据。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define CNT 3 //定义节点 typedef struct node { int num; struct node* next; }node; //创建链表:从控制台输入数据 node* creat() { //首先创建一个头节点,不存放有效数据 node* head = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); head->next = NULL; head->num = 0; node* p = head; printf("创建一个含有%d个数据的单链表\n", CNT); printf("请输入%d个数据:", CNT); for (int i = 0; i < CNT; i++) { int n; scanf("%d", &n); node* newNode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); newNode->num = n; newNode->next = NULL; //链接 p->next = newNode; p = p->next; } return head; } //打印链表 void printNode(node* head) { node* p = head->next; while (p != NULL) { printf("node: %d\n", p->num); p = p->next; } } //删除节点 void del(node* head, int val) { //遍历链表,找到待删除的位置 node* p = head->next; node* prev = head; while (p != NULL) { if (p->num == val) { prev->next = p->next; free(p); break; } else { prev = p; p = p->next; } } } //插入节点 void insert(node* p, int val) { //给p节点的后面插入新的数据 node* newNode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); newNode->num = val; newNode->next = NULL; newNode->next = p->next; p->next = newNode; } int main() { printf("创建链表:\n"); node* head = creat(); printf("创建链表结束:\n"); printf("初始链表:\n"); printNode(head); printf("请输入需要插入的数据:\n"); int n; scanf("%d", &n); insert(head, n); printf("插入数据: %d之后,链表的所有数据:\n",n); printNode(head); printf("请输入需要删除的数据:\n"); scanf("%d", &n); del(head, n); printf("删除数据:%d之后,链表的所有数据:\n", n); printNode(head); return 0; }
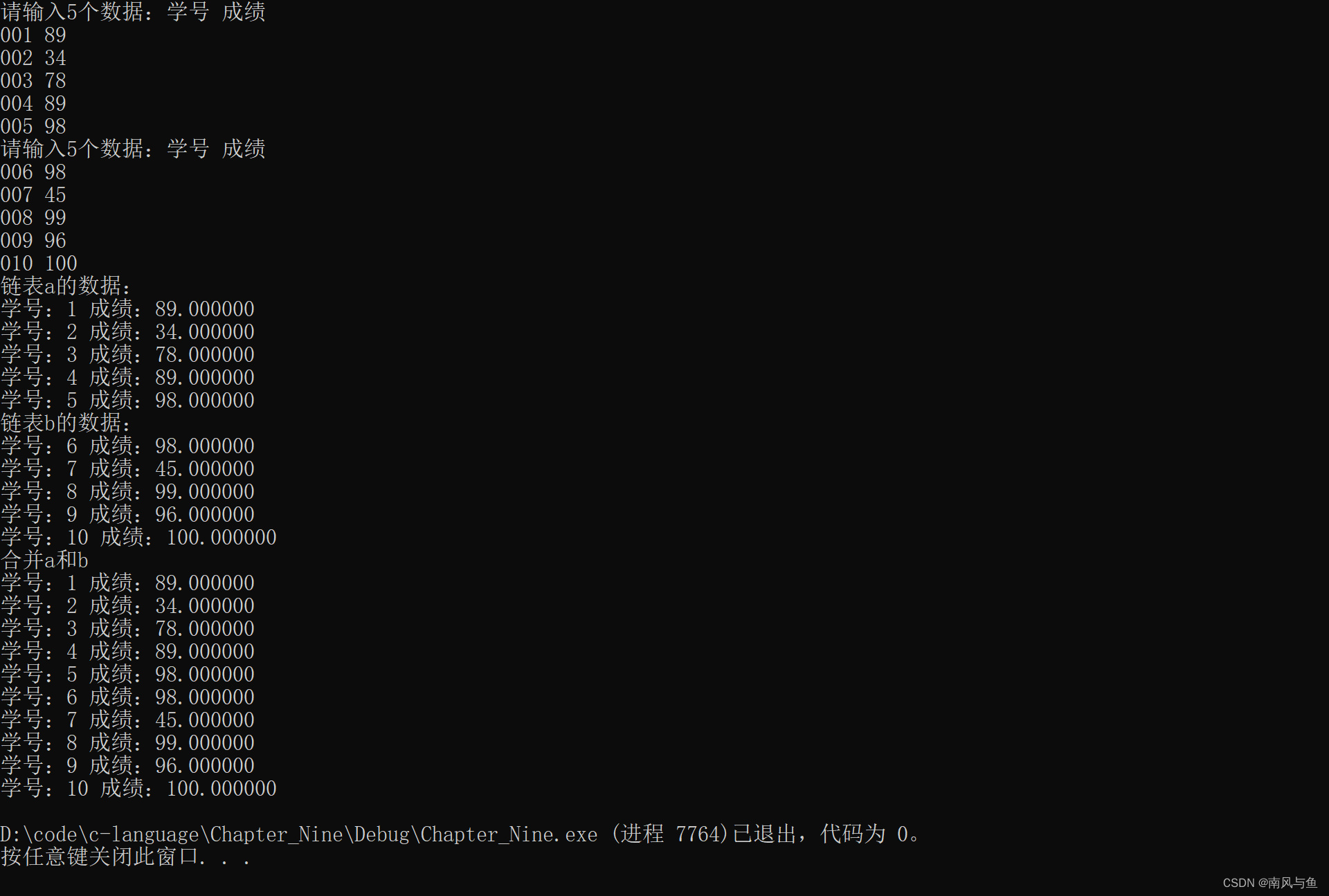
10.已有 a,b两个链表,每个链表中的结点包括学号、成绩。要求把两个链表合并,按学号升序排列。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define NUM 5 typedef struct node { int num; float score; struct node* next; }node; node* creat() { printf("请输入%d个数据:学号 成绩\n", NUM); node* head = NULL; //链表的表尾 node* tail = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++) { int num; float score; scanf("%d%f", &num, &score); //创建节点 node* newNode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); newNode->num = num; newNode->score = score; newNode->next = NULL; //插入到已有链表 //判断当前链表是否为空 if (head == NULL) { head = tail = newNode; } else { //把新的节点插入到尾节点后面 tail->next = newNode; tail = newNode; } } return head; } //合并,排序两个链表 node* mergeList(node* a, node* b) { //合并 node* head = a; while (head->next != NULL) { head = head->next; } head->next = b; head = a; //prev:未排序的第一个节点 node* prev = a; //排序,选择排序 while (prev->next != NULL) { //每次从未排序的节点中选择一个学号最小的 //放在第一个未排序节点的位置 node* cur = prev->next; while (cur) { if (prev->num > cur->num) { //把学号最小的数据往前移动 int num = prev->num; float score = prev->score; prev->num = cur->num; prev->score = cur->score; cur->num = num; cur->score = score; } cur = cur->next; } prev = prev->next; } return head; } void printNode(node* a) { while (a != NULL) { printf("学号:%d 成绩:%f\n", a->num, a->score); a = a->next; } } int main() { node* a = creat(); node* b = creat(); printf("链表a的数据:\n"); printNode(a); printf("链表b的数据:\n"); printNode(b); printf("合并a和b\n"); a = mergeList(a, b); printNode(a); return 0; }
11.有两个链表 a和b,设结点中包含学号、姓名。从a链表中删去与b链表中有相同学号的那些结点。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define LEN 20 typedef struct node { int num; char name[LEN]; struct node* next; }node; //返回新链表的表头 node* del(node* a, node* b) { node* head = a; //遍历b中的每一个节点 while (b) { //从a的表头开始遍历 node* prev = a; node* cur = prev->next; //用头节点和b当前指向的节点进行比较 if (prev->num == b->num) { prev->next = NULL; //更新表头 head = cur; } //用非头节点和b当前指向的节点进行比较 else { while (cur) { if (cur->num == b->num) { //删除当前节点 prev->next = cur->next; cur->next = NULL; break; } else { //继续向后遍历 prev = cur; cur = cur->next; } } } //处理b的下一个节点 b = b->next; } return head; } void printNode(node* head) { while (head) { printf("%d-->%s\n", head->num, head->name); head = head->next; } } int main() { //建立链表 node a[5] = { {3, "zhang"}, {1, "wang"},{15, "li"},{10, "zhou"},{8, "ren"} }; node b[3] = { {8, "ren"}, {3, "zhang"}, {10, "zhou"}}; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { a[i].next = &a[i + 1]; } a[4].next = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { b[i].next = &b[i + 1]; } b[2].next = NULL; printf("链表a:\n"); printNode(a); printf("链表b:\n"); printNode(b); node* head = del(a, b); printf("删除之后的链表:\n"); printNode(head); return 0; }
12.建立一个链表,每个结点包括:学号、姓名、性别、年龄。输入一个年龄,如果链表中的结点所包含的年龄等于此年龄,则将此结点删去。
#include <stdio.h> #define LEN 20 typedef struct node { int num; char name[LEN]; char gender[LEN]; int age; struct node* next; }node; node* del(node* a) { int age; printf("请输入需要删除的年龄:\n"); scanf("%d", &age); //遍历删除 node* prev = NULL; node* cur = a; node* head = a; while (cur) { if (cur->age == age) { //当前节点需要删除 //头节点 if (prev == NULL) { //更新头节点 head = cur->next; } //非头节点 else { prev->next = cur->next; } //查看下一个节点 cur = cur->next; } else { //当前节点不需要删除 prev = cur; cur = cur->next; } } return head; } void printNode(node* head) { while (head) { printf("%d %s %s %d\n", head->num, head->name, head->gender, head->age); head = head->next; } } int main() { node arr[] = { {1, "wang", "male", 20}, {2, "li", "female", 30}, {3, "zhang", "male", 20}, {4, "li", "female", 18}, {5, "cheng", "male", 20} }; //建立链表 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { arr[i].next = &arr[i + 1]; } arr[4].next = NULL; printf("链表的所有数据:\n"); printNode(arr); node* head = del(arr); printf("删除之后链表的剩余数据:\n"); printNode(head); return 0; }






























![[Flink01] 了解Flink](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/2986668a27ab8b3560e8d3595371f3a9.png)