一、排序的概念
排序 ( s o r t ) (sort) (sort)
一串无序的数字,按照其中某些关键字的大小,递减或递增的序列。
二、桶排序
1. 概念
现在有一串编号: 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 1 1 1 3 3 3 4 4 4 3 3 3
| 出现次数 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下标 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
2. 易错点
数据提取
3 3 3 种型号手机共 1 e 5 1e5 1e5 部,分别为 1 1 1 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 . . . ... ...
因此,数组至少要开 4 4 4,因为有关的信息仅仅只是 3 3 3 种型号。
3. 例题
3.1 统计1~3出现的次数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, temp;
int cnt[5];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> temp; // 输入统计的内容
cnt[temp]++; // 套入桶
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) // 遍历cnt[]
{
cout << "数字" << i << "出现了" << cnt[i] << "次" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3.2 统计1~3出现的次数并按照升序输出
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, temp;
int cnt[5];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> temp; // 输入统计的内容
cnt[temp]++; // 套入桶
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) // 遍历输出数字
{
for (int j = 1; j <= cnt[i]; j++) // 输出次数
{
cout << i << " ";
}
}
return 0;
}
3.3 统计出现的种类
3.3.1 方法1:判断有没有数字
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, temp;
int cnt[5];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> temp; // 输入统计的内容
cnt[temp]++; // 套入桶
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) // 遍历输出数字
{
if (cnt[i] > 0) // 判断有没有这个数字
{
cout << i << " ";
}
}
return 0;
}
3.3.2:改bool类型数组
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, temp;
bool cnt[5];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> temp; // 输入统计的内容
cnt[temp]++; // 套入桶
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) // 遍历输出数字
{
if (cnt[i]) // 判断这个数字有没有出现过
{
cout << i << " ";
}
}
return 0;
}
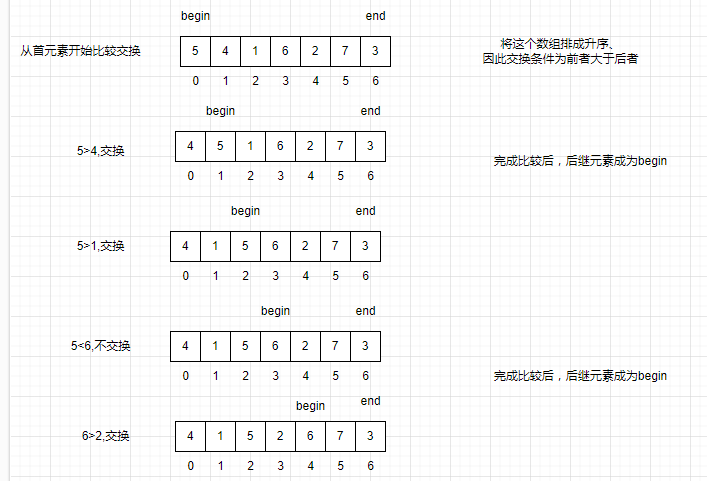
三、冒泡排序
1. 概念
| 数组 | 9 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一轮 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 3 | 2 |
| 5 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 2 | |
| 5 | 8 | 3 | 9 | 2 | |
| 5 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 9 | |
| 第二轮 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 9 |
| 5 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 9 | |
| 5 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 9 | |
| 第三轮 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 8 | 9 |
| 3 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 9 | |
| 第四轮 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 9 |
2. 伪代码
for (i = 1 ~ n-1) // 轮数
{
for (j = 1 ~ n-i) // 每轮次数
{
if (a[j] > a[j+1])
{
swap(a[j], a[j+1])
}
}
}
3. 代码示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void bubbleSort(int a[], int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n-1; i++) // 轮数
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n-i; j++) // 每轮次数
{
if (a[j] > a[j+1])
{
swap(a[j], a[j+1]) // 冒泡
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
bubbleSort(a, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}