介绍
上一次介绍了list队容器的迭代器模拟,这次模拟实现list的简单功能,尤其要注意构造函数、析构函数、以及赋值运算符重载的实现。
list容器需要接纳所有类型的数据,因此,结构设置与迭代器设置同理,需要引入结点,数据。
//结点结构
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode<T>* _next;
ListNode<T>* _last;
T _data;
ListNode(const T& x = T())
:_next(nullptr)
, _last(nullptr)
, _data(x)
{ }
};//list容器基本元素
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef _list_iterator<T> iterator;private:
Node* _node; //此结点为哨兵结点,前指头结点,后指尾结点,里面没有数据
};
一,构造函数
构造函数只需构造“ 哨兵结点 ”即可,因为这里使用链式结构存储,因此构造函数没有顺序结构那样的逻辑。代码如下:
list()
{
_node = new Node;
_node->_last = _node;
_node->_next = _node;
}
拷贝构造的实现可直接运用赋值运算符,这里要注意,由于这里的设计设计到动态空间的申请,所以实现时需进行深拷贝。
这里,我们先实现push_back尾插功能,代码如下:
//尾插功能
void push_back(const T& x = T())
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->_data = x;
node->_next = _node;
node->_last = _node->_last;
_node->_last->_next = node;
_node->_last = node;
}
下面是赋值运算符和拷贝构造的实现,唯一要注意的是在使用赋值运算符前,要先确定“ 哨兵结点 ”,即普通的构造函数。
//赋值运算符重载
list<T>& operator=(list<T>& L)
{
Node* node = (L._node)->_next;
while (node != L._node)
{
push_back(node->_data);
node = node->_next;
}
return *this;
}//拷贝构造函数
list(list<T>& L)
{//哨兵结点的构造
_node = new Node;
_node->_last = _node;
_node->_next = _node;//赋值运算符的使用
*this = L;
}
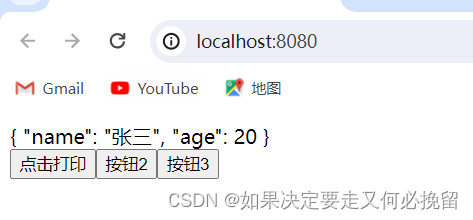
下面进行样例代码测试:
void test1()
{
list<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(4);
list<int> v2;
v2 = v1;
list<int> v3(v1);
std::cout << "List v2: ";
for (auto e : v2)
{
std::cout << e << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "List v3: ";
for (auto e : v3)
{
std::cout << e << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
测试数据结果:
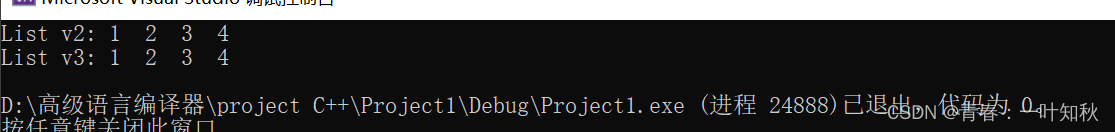
二,析构函数
析构函数的设计只需诼渐释放所有结点即可,包括“ 哨兵结点 ”。代码如下:
~list()
{
Node* t = _node->_next;
while (t != _node)
{
Node* next = t->_next;
delete t;
t = next;
}
delete t; //最后释放哨兵结点
t = nullptr;
}
三,list容器接口
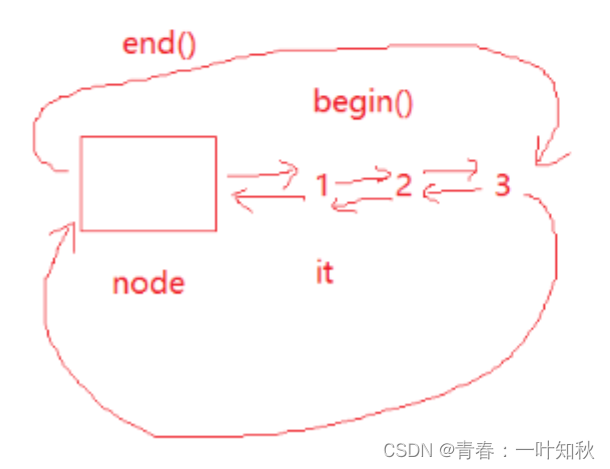
这里实现begin()、end()、push_back(这个接口上面已实现,这里不做演示)、pop_back、push_front、pop_front。代码如下:
iterator begin() //获取头结点
{
return _node->_next;
}
iterator end() //获取尾结点
{
return _node;
}
void pop_back() //尾删
{
assert(_node->_next != _node);
Node* node = _node->_last->_last;
delete _node->_last;
_node->_last = node;
node->_next = _node;
}
void push_front(const T& x = T()) //头插
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->_data = x;
node->_next = _node->_next;
node->_last = _node;
_node->_next->_last = node;
_node->_next = node;
}
void pop_front() //头删
{
assert(_node->_next != _node);
Node* node = _node->_next->_next;
delete _node->_next;
_node->_next = node;
node->_last = _node;
}
list容器常用功能有clear()、swap()、erase、insert。接口参数与实现如下:
void clear()
{
Node* t = _node->_next;
while (t != _node)
{
Node* next = t->_next;
delete t;
t = next;
}
t = nullptr;
}
void swap(list<T>& L)
{
std::swap(_node, L._node);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x = T())
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->_data = x;
node->_next = pos.node;
node->_last = (pos.node)->_last;
node->_next->_last = node;
node->_last->_next = node;
return node;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos.node != _node);
Node* next = (pos.node)->_next;
Node* last = (pos.node)->_last;
delete pos.node;
next->_last = last;
last->_next = next;
return next;
}
下面进行样例代码测试:
void test2()
{
list<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
list<int>::iterator it = ++v.begin();
v.insert(it, 9);
v.erase(v.begin());
for (auto e : v)
{
std::cout << e << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
测试数据结果如下:
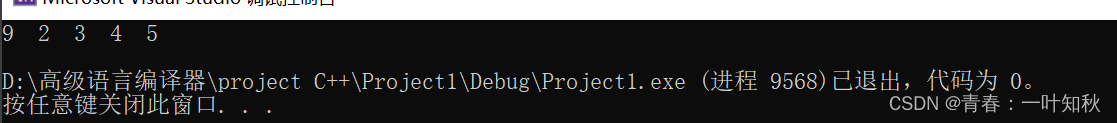
其它细节逻辑可自行测试,这里不再一一演示。
总:list容器的模拟实现跟部分容器可能有些难度,这里注重要注意类型使用和转换,迭代器的模拟以及构造赋值与析构。功能实现的逻辑基本与链式逻辑一样。





























![[pytorch入门] 5. DataLoader的使用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2b38dd340ae3411596d2b9d576ae56d5.png)