一、call_once 单例模式 Singleton
大家可以先看这篇文章:https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/call_once
/*
std::call_once
void call_once( std::once_flag& flag, Callable&& f, Args&&... args );
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
std::once_flag flag1, flag2;
void simple_do_once() {
std::call_once(flag1, []() {
std::cout << "简单样例:调用一次\n";
});
}
void test1() {
std::thread st1(simple_do_once);
std::thread st2(simple_do_once);
std::thread st3(simple_do_once);
std::thread st4(simple_do_once);
st1.join();
st2.join();
st3.join();
st4.join();
}
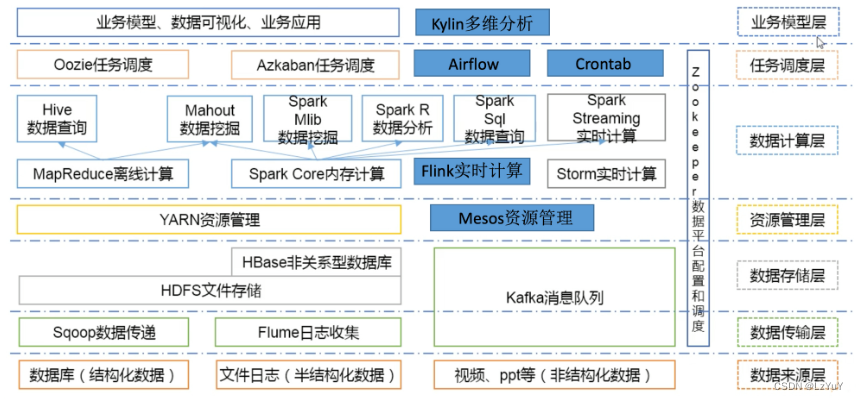
void may_throw_function(bool do_throw) {
if (do_throw) {
std::cout << "抛出:call_once 会重试\n"; // 这会出现不止一次
throw std::exception();
}
std::cout << "没有抛出,call_once 不会再重试\n"; // 保证一次
}
void do_once(bool do_throw) {
try {
std::call_once(flag2, may_throw_function, do_throw);
}
catch (...) {}
}
void test2() {
std::thread t1(do_once, true);
std::thread t2(do_once, true);
std::thread t3(do_once, false);
std::thread t4(do_once, true);
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
t4.join();
}
int main() {
test1();
test2();
return 0;
}
call_once 应用在单例模式,以及关于单例模式我的往期文章推荐:C++ 设计模式----“对象性能“模式_爱编程的大丙 设计模式-CSDN博客![]() https://heheda.blog.csdn.net/article/details/131466271
https://heheda.blog.csdn.net/article/details/131466271
懒汉是一开始不会实例化,什么时候用就什么时候new,才会实例化
饿汉在一开始类加载的时候就已经实例化,并且创建单例对象,以后只管用即可
--来自百度文库#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <string>
// 日志类:在整个项目中,有提示信息或者有报错信息,都通过这个类来打印
// 这些信息到日志文件,或者打印到屏幕上。显然,全局只需要一个日志类的
// 对象就可以完成所有的打印操作了。不需要第二个类来操作,这个时候就可以
// 使用单例模式来设计它
std::once_flag onceFlag;
class Log {
public:
Log(const Log& log) = delete;
Log& operator=(const Log& log) = delete;
// static Log& getInstance() {
// static Log log; // 饿汉模式
// return log;
// }
static Log& getInstance() { // 懒汉模式
std::call_once(onceFlag, []() {
std::cout << "简单样例:调用一次\n";
log = new Log;
});
return *log;
}
void PrintLog(std::string msg) {
std::cout << __TIME__ << msg << std::endl;
}
private:
Log() {};
static Log* log;
};
Log* Log::log = nullptr;
void func() {
Log::getInstance().PrintLog("这是一个提示");
}
void print_error() {
Log::getInstance().PrintLog("发现一个错误");
}
void test() {
std::thread t1(print_error);
std::thread t2(print_error);
std::thread t3(func);
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
二、condition_variable 与其使用场景
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
std::queue<int> queue;
std::condition_variable cond;
std::mutex mtx;
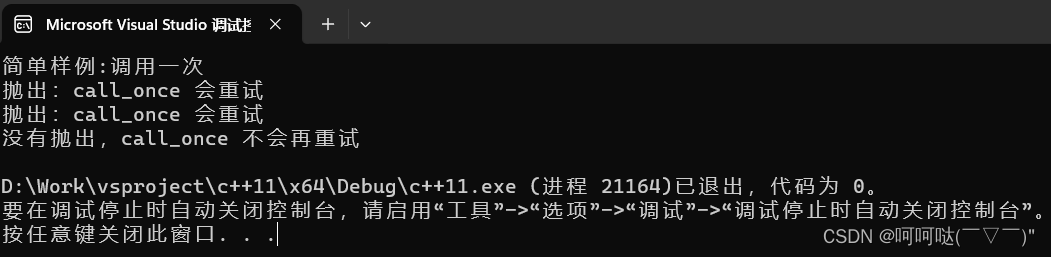
void Producer() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(mtx);
queue.push(i);
cond.notify_one();
std::cout << "Producer : " << i << std::endl;
}
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(100));
}
}
void Consumer() {
while (1) {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(mtx);
cond.wait(locker, []() {
return !queue.empty();
});
int value = queue.front();
queue.pop();
std::cout << "Consumer :" << value << std::endl;
}
}
int main() {
std::thread t1(Producer);
std::thread t2(Consumer);
t1.join();
t2.join();
return 0;
}
三、C++11 手撕线程池 + 单例模式(call_once)
- ThreadPool.h
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <string>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
std::once_flag onceFlag;
class ThreadPool {
private:
ThreadPool();
public:
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool& obj) = delete;
ThreadPool& operator=(const ThreadPool& obj) = delete;
static ThreadPool& getInstance();
~ThreadPool();
template<class F, class... Args>
void enqueue(F&& f, Args&&... args) {
std::function<void()> task =
std::bind(std::forward<F>(f), std::forward<Args>(args)...);
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(mtx);
tasks.emplace(std::move(task));
}
cond.notify_one();
}
inline void setNum(int num) {
threadNum = num;
}
inline void printNum() {
std::cout << "线程数量为:" << threadNum << std::endl;
}
private:
static ThreadPool* pool;
std::vector<std::thread> threads;// 线程数组
std::queue<std::function<void()>> tasks;//任务队列
std::mutex mtx;// 互斥锁
std::condition_variable cond;//条件变量
bool stop;
int threadNum;// 线程数量
};
- ThreadPool.cpp
#include "ThreadPool.h"
#include <iostream>
ThreadPool* ThreadPool::pool = nullptr;
ThreadPool::ThreadPool() {
stop = false;
threadNum = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; ++i) {
threads.emplace_back([this]() {
while (1) {
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(mtx);
cond.wait(locker, [this]() {
return !tasks.empty() || stop;
});
if (stop && tasks.empty()) {
return;
}
std::function<void()> task(std::move(tasks.front()));
tasks.pop();
task();// 执行这个任务
}
});
}
}
ThreadPool::~ThreadPool() {
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(mtx);
stop = true;
}
cond.notify_all();
for (auto& t : threads) {
t.join();
}
}
ThreadPool& ThreadPool::getInstance() { // 懒汉模式
std::call_once(onceFlag, []() {
std::cout << "懒汉模式:调用一次" << std::endl;
pool = new ThreadPool();
});
return *pool;
}- main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "ThreadPool.h"
#include <thread>
void addTask() {
ThreadPool& pool = ThreadPool::getInstance();
pool.setNum(8);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
pool.enqueue([i]() {
std::cout << "task : " << i << " is runing!" << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(10));
std::cout << "task : " << i << " is done!" << std::endl;
});
}
}
void test() {
std::thread t1(addTask);
std::thread t2(addTask);
std::thread t3(addTask);
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}运行结果:
懒汉模式:调用一次
task : 0 is runing!
task : 0 is done!
task : 0 is runing!
task : 0 is done!
task : 1 is runing!
task : 1 is done!
task : 0 is runing!
task : 0 is done!
task : 1 is runing!
task : 1 is done!
task : 1 is runing!
task : 1 is done!
task : 2 is runing!
task : 2 is done!
task : 3 is runing!
task : 3 is done!
task : 2 is runing!
task : 2 is done!
task : 4 is runing!
task : 4 is done!
task : 3 is runing!
task : 3 is done!
task : 2 is runing!
task : 2 is done!
task : 3 is runing!
task : 3 is done!
task : 4 is runing!
task : 4 is done!
task : 5 is runing!
task : 5 is done!
task : 4 is runing!
task : 4 is done!
task : 5 is runing!
task : 5 is done!
task : 6 is runing!
task : 6 is done!
task : 7 is runing!
task : 7 is done!
task : 8 is runing!
task : 8 is done!
task : 9 is runing!
task : 9 is done!
task : 6 is runing!
task : 6 is done!
task : 7 is runing!
task : 7 is done!
task : 5 is runing!
task : 5 is done!
task : 6 is runing!
task : 6 is done!
task : 8 is runing!
task : 8 is done!
task : 9 is runing!
task : 9 is done!
task : 7 is runing!
task : 7 is done!
task : 8 is runing!
task : 8 is done!
task : 9 is runing!
D:\Work\vsproject\c++11\x64\Debug\c++11.exe (进程 32636)已退出,代码为 0。
要在调试停止时自动关闭控制台,请启用“工具”->“选项”->“调试”->“调试停止时自动关闭控制台”。
按任意键关闭此窗口. . .未完待续~