目录
前言
本篇文章介绍库函数qsort()的使用以及利用冒泡排序的思想模拟对任何类型的数据进行排序。
一、qsort()的介绍及使用
1.1 qsort()的介绍
下面是cplusplus对qsort()的叙述,详情https://cplusplus.com/reference/cstdlib/qsort/


qsort()可以对任意类型的数据进行排序。
对qsort()参数进行介绍:
void* base:指向需要被排序数组的起始位置。
size_t num:待排序的元素个数
size_t size:待排序的元素的大小(单位:字节)
int (*compar)(const void*, const void*):函数指针,指向比较函数,可以实现自定义比较规则。
1.2 qsort()的使用
1.2.1 使用qsort|()对整型数组按照升序排序
//升序
int compare_asc(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
40, 10, 100, 90, 20, 25 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), compare_asc);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
1.2.2 使用qsort()对整型数组按照降序排序
//降序
int compare_dec(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*(int*)e2 - *(int*)e1);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
40, 10, 100, 90, 20, 25 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), compare_dec);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
1.2.3 使用qsort()对结构体数组数据进行排序
按照年龄升序排序:
//定义结构体
struct Stu {
char name[20];
int age;
float height;
};
//输出结构体数组数据
void print_stu(struct Stu* stu,int sz)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%s\t%-6d\t%.2f\n", (stu + i)->name, (stu + i)->age, (stu + i)->height);
}
}
//按照年龄升序进行排序
int compare_stuByAge_asc(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (((struct Stu*)e1)->age - ((struct Stu*)e2)->age);
}
int main()
{
struct Stu student[3] = {
{
"zhangsan", 18, 170.50f},
{
"lisi", 20, 185.25f},
{
"wangwu", 17, 165.55f} };
int sz = sizeof(student) / sizeof(student[0]);
printf("原顺序\n");
print_stu(student, sz);
//按照年龄升序排序
qsort(student, sz, sizeof(student[0]), compare_stuByAge_asc);
printf("按照年龄升序\n");
print_stu(student, sz);
return 0;
}
二、利用冒泡排序模拟实现对任何数据进行排序
2.1 冒泡排序
void bubble_sort(int arr[], int sz)
{
int i = 0;
int flag = 1;//假设数据有序
//排序趟数
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
//每趟要比较数据的个数
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
//按照升序排序
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
//交换
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = tmp;
flag = 0;
}
}
//当进行第一趟排序时,flag未改变,说明没有进行交换,数组有序
if (1 == flag)
{
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
40, 10, 100, 90, 20, 25 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubble_sort(arr, sz);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
对比qsort()发现,bubble_sort()只能对整型数组数据进行排序,为了增加bubble_sort()的通用性,可以模仿qsort()的写法实现bubble_sort()对任何数据类型的排序。
2.2 模仿qsort()实现bubble_sort()对任何数据类型的数据排序
2.2.1 代码实现
//每次交换一个字节的内容
//循环交换width个字节的内容
void Swap(char* e1, char* e2, int width)
{
char tmp = 0;
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
tmp = *e1;
*e1 = *e2;
*e2 = tmp;
e1++;
e2++;
}
}
void bubble_sort(void* base, int sz,int width, int(*compare)(const void* e1, const void* e2))
{
int i = 0;
int flag = 1;//假设数据有序
//排序趟数
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
//每趟要比较数据的个数
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
//利用compare()回调函数, >0进行交换
if (compare((char*)base+j*width, (char*)base+(j+1)*width) > 0)
{
//交换
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width,width);
flag = 0;
}
}
//当进行第一趟排序时,flag未改变,说明没有进行交换,数组有序
if (1 == flag)
{
break;
}
}
}
compare((char*)base+j*width, (char*)base+(j+1)*width) > 0;
返回值有三个
返回值为 =0,说明e1和e2指向的数据值相等
返回值为<0,有两种情况:
- e1指向的数据值小于e2指向的数据值
- e1指向的数据值大于e2指向的数据值
返回值为>0,有两种情况
- e1指向的数据值小于e2指向的数据值
- e1指向的数据值大于e2指向的数据值
为什么出现两种情况?
原因:因为compare()的返回值是两个值相减,但无法确定哪个是减数
升序和降序的控制
升序:当e1指向的数据值作为被减数时,即e1-e2
降序:当e2指向的数据值作为被减数时,即e2-e1。
注意:e1-e2只是作为说明,具体怎么比较,由自定义实现比较规则。(具体看例子)
为什么选择compare((char*)base+j*width, (char*)base+(j+1)width) > 0作为判断交换的条件?
因为默认把e1-e2作为升序,即从小到大排序。
如果把compare((char)base+j*width, (char*)base+(j+1)width) > 0
换成compare((char)base+j*width, (char*)base+(j+1)*width) < 0
那么默认e1-e2是降序,即从大到小排序。
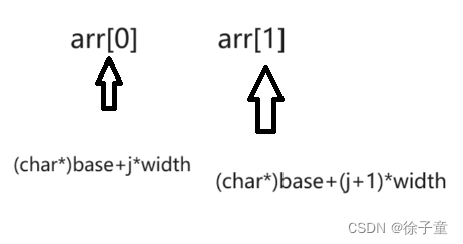
(char*)base + j * width //指向要比较的第一个元素
(char*)base + (j + 1) * width //指向要比较的第二个元素
//利用(char*)base强制类型转换,分别指向被比较元素的起始位置
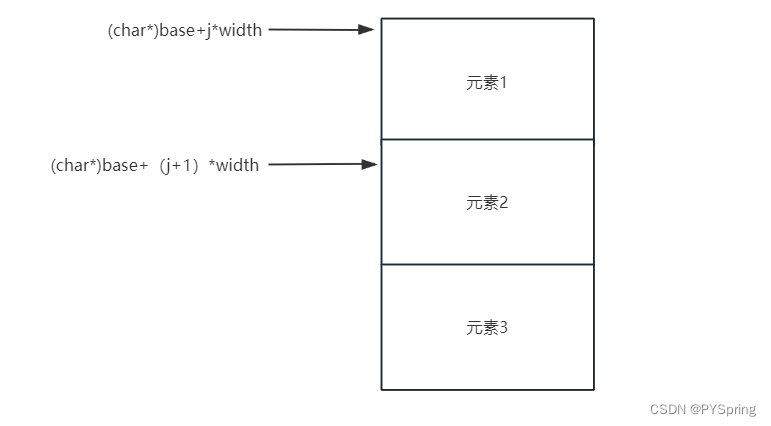
void Swap(char* e1, char* e2, int width);
实现的是交换每个字节的内容,width是每个元素的大小。由于是char*类型的指针,所以一次交换只能交换一个字节的内容,为了能够交换整个元素的内容,所以需要交换width次。
2.2.2 测试对整型数组排序
//对数组进行升序
int compare_int_asc(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2);
}
//降序
int compare_int_dec(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (*(int*)e2 - *(int*)e1);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
40, 10, 100, 90, 20, 25 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubble_sort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]),compare_int_dec);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
2.2.3 测试对结构体数组数据排序
//定义结构体
struct Stu {
char name[20];
int age;
float height;
};
//输出结构体数据
void print_stu(struct Stu* stu,int sz)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%s\t%-6d\t%.2f\n", (stu + i)->name, (stu + i)->age, (stu + i)->height);
}
}
//按照年龄升序进行排序
int compare_stuByAge_asc(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return (((struct Stu*)e1)->age - ((struct Stu*)e2)->age);
}
//按照名字的字母序排序
int compare_stuByName(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct Stu*)e1)->name, ((struct Stu*)e2)->name);
}
int main()
{
struct Stu student[3] = {
{
"zhangsan", 18, 170.50f},
{
"lisi", 20, 185.25f},
{
"wangwu", 17, 165.55f} };
int sz = sizeof(student) / sizeof(student[0]);
printf("原顺序\n");
print_stu(student, sz);
//按照年龄升序排序
//bubble_sort(student, sz, sizeof(student[0]), compare_stuByAge_asc);
//按照名字字母序
bubble_sort(student, sz, sizeof(student[0]), compare_stuByName);
//printf("按照年龄升序\n");
printf("按照名字字母序\n");
print_stu(student, sz);
return 0;
}
总结
本篇文章介绍了库函数qsort()的使用,以及模仿qsort(),利用冒泡排序模拟实现对任何数据类型的数据进行排序。






















![达梦数据库报错 执行失败(语句1) -2111: 第1 行附近出现错误: 无效的列名[system]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ac26cb0770b34e6980b8e6e131c202c1.png)










![Flask+Bootstrap4案例[有源码]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/4321a8938fe24f0cae90bb2a3c461614.png#pic_center)