本文记录了CV算法题的学习。
CV算法面试题学习
1 点在多边形内(point in polygon)
参考自文章1,其提供的代码没有考虑一些特殊情况,所以做了改进。
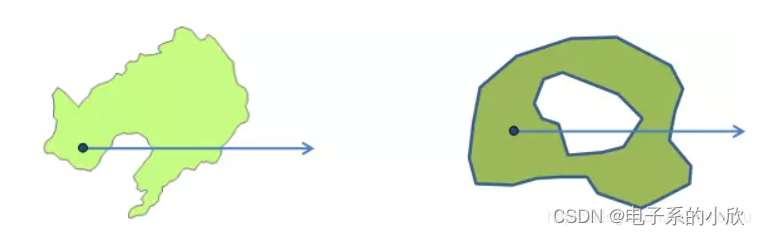
做法:射线法。以待判断点A为端点,画出方向水平朝右的射线,统计该射线与多边形B的交点个数。奇数:内,偶数:外。(需考虑点A是否在B的某个点或边上是否有平行的边。)
图片来自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ba03c600a557。
代码:
def is_in_poly(p, poly):
"""
:param p: [x, y]
:param poly: [[], [], [], [], ...]
:return:
"""
px, py = p
is_in = False
for i, corner in enumerate(poly):
next_i = i + 1 if i + 1 < len(poly) else 0
x1, y1 = corner
x2, y2 = poly[next_i]
if (x1 == px and y1 == py) or (x2 == px and y2 == py): # 点p是否在多边形的某个点上
is_in = True
break
if y1 == y2 : #边是水平的,如果点在边上则break,如果不在,则跳过这一轮判断
if min(x1, x2) < px < max(x1, x2)and y1==py:
is_in = True
break
elif min(y1, y2) <= py <= max(y1, y2): #边不是水平的
x = x1 + (py - y1) * (x2 - x1) / (y2 - y1)
if x == px: # 点是否在射线上
is_in = True
break
elif x > px: # 点是否在边左侧,即射线是否穿过边
is_in = not is_in
return is_in
if __name__ == '__main__':
#第一组,内
point = [3, 10/7]
poly = [[0, 0], [7, 3], [8, 8], [5, 5]]
print(is_in_poly(point, poly))
#第二组,外
point = [3, 8/7]
poly = [[0, 0], [7, 3], [8, 8], [5, 5]]
print(is_in_poly(point, poly))
#第三组,有平行边,射线与边重合,外
point = [-2, 0]
poly = [[0, 0], [7, 0], [7, 8], [5, 5]]
print(is_in_poly(point, poly))
#第四组,有平行边,射线与边重合,内
point = [2, 0]
poly = [[0, 0], [7, 0], [7, 8], [5, 5]]
print(is_in_poly(point, poly))
#第五组,在某点上
point = [7, 3]
poly = [[0, 0], [7, 3], [8, 8], [5, 5]]
print(is_in_poly(point, poly))
2 高斯滤波器
参考文章2
高斯滤波器为线性平滑滤波器,通常假定图像包含高斯白噪声,可以通过高斯滤波来抑制噪声。
二维高斯分布公式:
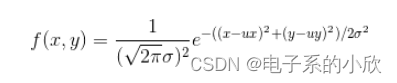
其中的ux和uy是中心点坐标。
3x3滤波核的生成:
- 先得到相对于中心点的坐标模板。
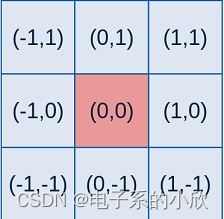
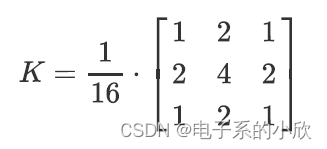
- 根据公式和坐标模板得到滤波核的每个位置的值。当标准差 σ \sigma σ为1.3时,得到的整数形式的滤波核为:
代码:
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Gaussian filter
def gaussian_filter(img, K_size=3, sigma=1.3):
if len(img.shape) == 3:
H, W, C = img.shape
else:
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=-1)
H, W, C = img.shape
## Zero padding
pad = K_size // 2
out = np.zeros((H + pad * 2, W + pad * 2, C), dtype=np.float)
out[pad: pad + H, pad: pad + W] = img.copy().astype(np.float)
## prepare Kernel
K = np.zeros((K_size, K_size), dtype=np.float)
for x in range(-pad, -pad + K_size):
for y in range(-pad, -pad + K_size):
K[y + pad, x + pad] = np.exp( -(x ** 2 + y ** 2) / (2 * (sigma ** 2)))
K /= (2 * np.pi * sigma * sigma)
K /= K.sum() #归一化
print(K)
K=K[:,:,np.newaxis].repeat(C,axis=2)# 扩展维度至(K_size,K_size,C)
print(K[:,:,0])
print(K[:,:,1])
tmp = out.copy()
# filtering
for y in range(H):
for x in range(W):
# for c in range(C):
out[pad + y, pad + x, :] = np.sum(np.sum(K * tmp[y: y + K_size, x: x + K_size, :],axis=0),axis=0)
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
out = out[pad: pad + H, pad: pad + W].astype(np.uint8)
return out
# Read image
img = cv2.imread("./lena.png")
# Gaussian Filter
out = gaussian_filter(img, K_size=3, sigma=1.3)
# Save result
cv2.imwrite("out.jpg", out)
cv2.imshow("result", out)
cv2.imshow("origin", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
结果:
3 ViT
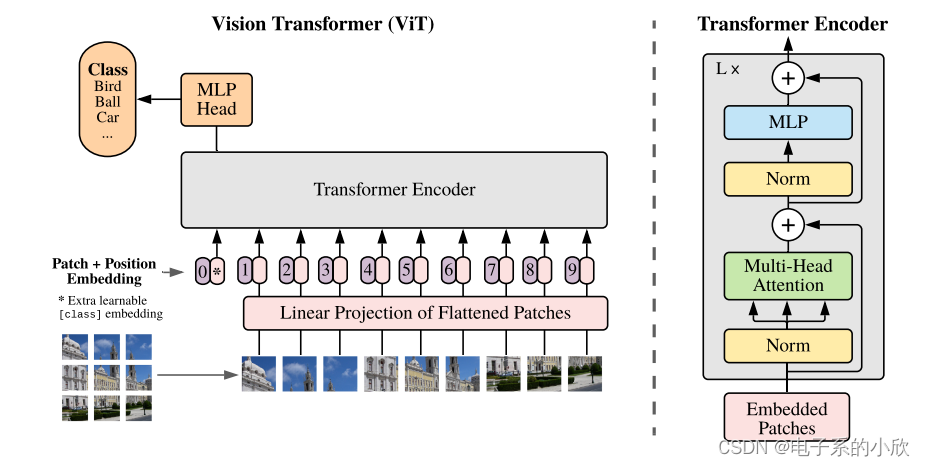
Patch Embedding
作用:将图像切块,得到用向量表示的图像局部信息。减少了计算和存储开销。
ViT中,利用卷积实现,卷积核kernel与步长stride取相同的值patchsize。
设原图像大小为224x224,patchsize为16,则经过patchembedding后,得到的patch数量为:
( 224 / 16 ) ∗ ( 224 / 16 ) = 196 (224/16)*(224/16)=196 (224/16)∗(224/16)=196
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import cv2
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
"""
2D Image to Patch Embedding
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=16, in_c=3, embed_dim=768, norm_layer=None):
super().__init__()
img_size = (img_size, img_size)
patch_size = (patch_size, patch_size)
self.img_size = img_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.grid_size = (img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1])
self.num_patches = self.grid_size[0] * self.grid_size[1] #patchembedding后,patch数量
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_c, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
assert H == self.img_size[0] and W == self.img_size[1], \
f"Input image size ({
H}*{
W}) doesn't match model ({
self.img_size[0]}*{
self.img_size[1]})."
# flatten: [B, C, H, W] -> [B, C, HW]
# transpose: [B, C, HW] -> [B, HW, C]
x = self.proj(x).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.norm(x)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = cv2.resize(cv2.imread("./lena.png"),(224,224))
trans = transforms.ToTensor()
imgtensor = trans(img).unsqueeze(0)
print(imgtensor.shape)
patch = PatchEmbed(img_size=imgtensor.shape[2])
print(patch.num_patches)
print(patch(imgtensor).shape)
结果:
Position Embedding
patch处理后,每个块之间是没有顺序信息的,所以需要添加位置信息。
在VisionTransformer中定义self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches + self.num_tokens, embed_dim))
其中的self.num_tokens是1或2,对应一个cls token和一个distilled token(后者没用,他是DeiT的结构)
Transformer Encoder
Transformer Encoder将序列[196+1,768]进行编码,其结果如ViT框架图的右侧。
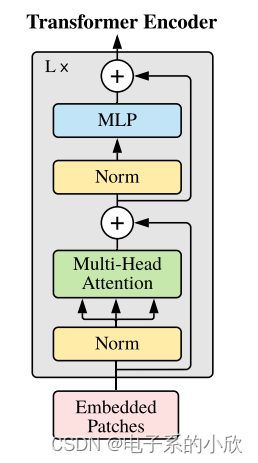
Multi-head Attention 代码:先通过linear映射得到q k v,然后进行矩阵乘法(除以scale避免值溢出)得到attention,然后矩阵乘法得到输出结果(concat所有head,然后再通过一个linear层)。
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dim, # 输入token的dim
num_heads=8,
qkv_bias=False,
qk_scale=None,
attn_drop_ratio=0.,
proj_drop_ratio=0.):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads #多头,计算每个头的dim
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5 # 这对应attention里的根号下dk,避免qk内积值过大导致溢出。
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop_ratio)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
# [batch_size, num_patches + 1, total_embed_dim]
B, N, C = x.shape
# qkv(): -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, 3 * total_embed_dim]
# reshape: -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, 3, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# permute: -> [3, batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
# [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
# transpose: -> [batch_size, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head, num_patches + 1]
# @: multiply -> [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, num_patches + 1]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale # 除以根号下dk等于乘以dk的负0.5次方
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
# @: multiply -> [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
# transpose: -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# reshape: -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, total_embed_dim]
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
MLP 代码:2层linear实现,都有drop防止过拟合,第一层还有激活函数。
class Mlp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer() #激活函数
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop) #2层linear共用,
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
Encoder Block 代码:通过上面的Attention和MLP实现block。输入x先通过norm1归一化,再attention,然后通过norm2和mlp。代码中有一个drop_path,它和droupout一样是用于防止过拟合的。后者是随机将batch中的某些值置0,前者是将batch中某个样本的所有值置0。
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dim,
num_heads,
mlp_ratio=4.,
qkv_bias=False,
qk_scale=None,
drop_ratio=0.,
attn_drop_ratio=0.,
drop_path_ratio=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super(Block, self).__init__()
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = Attention(dim, num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
attn_drop_ratio=attn_drop_ratio, proj_drop_ratio=drop_ratio)
# NOTE: drop path for stochastic depth, we shall see if this is better than dropout here
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path_ratio) if drop_path_ratio > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
完整的ViT模型
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=16, in_c=3, num_classes=1000,
embed_dim=768, depth=12, num_heads=12, mlp_ratio=4.0, qkv_bias=True,
qk_scale=None, representation_size=None, distilled=False, drop_ratio=0.,
attn_drop_ratio=0., drop_path_ratio=0., embed_layer=PatchEmbed, norm_layer=None,
act_layer=None):
super(VisionTransformer, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.num_features = self.embed_dim = embed_dim # num_features for consistency with other models
self.num_tokens = 2 if distilled else 1
norm_layer = norm_layer or partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6)
act_layer = act_layer or nn.GELU
self.patch_embed = embed_layer(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_c=in_c, embed_dim=embed_dim)
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
self.dist_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim)) if distilled else None
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches + self.num_tokens, embed_dim))
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_ratio)
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_ratio, depth)] # stochastic depth decay rule
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*[
Block(dim=embed_dim, num_heads=num_heads, mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop_ratio=drop_ratio, attn_drop_ratio=attn_drop_ratio, drop_path_ratio=dpr[i],
norm_layer=norm_layer, act_layer=act_layer)
for i in range(depth)
])
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
# Representation layer
if representation_size and not distilled:
self.has_logits = True
self.num_features = representation_size
self.pre_logits = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("fc", nn.Linear(embed_dim, representation_size)),
("act", nn.Tanh())
]))
else:
self.has_logits = False
self.pre_logits = nn.Identity()
# Classifier head(s)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.head_dist = None
if distilled:
self.head_dist = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
# Weight init
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=0.02)
if self.dist_token is not None:
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.dist_token, std=0.02)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=0.02)
self.apply(_init_vit_weights)
def forward_features(self, x):
# [B, C, H, W] -> [B, num_patches, embed_dim]
x = self.patch_embed(x) # [B, 196, 768]
# [1, 1, 768] -> [B, 1, 768]
cls_token = self.cls_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
if self.dist_token is None:
x = torch.cat((cls_token, x), dim=1) # [B, 197, 768]
else:
x = torch.cat((cls_token, self.dist_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1), x), dim=1)
x = self.pos_drop(x + self.pos_embed)
x = self.blocks(x)
x = self.norm(x)
if self.dist_token is None:
return self.pre_logits(x[:, 0])
else:
return x[:, 0], x[:, 1]
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x) #1 patch、2cat cls_token、3加位置编码并dropout、4通过depth个encoder block、5norm归一化、6将cls_token通过self.pre_logits(1层linear和1层tanh激活层)
if self.head_dist is not None: #不执行
x, x_dist = self.head(x[0]), self.head_dist(x[1])
if self.training and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
# during inference, return the average of both classifier predictions
return x, x_dist
else:
return (x + x_dist) / 2
else: #执行,通过分类头
x = self.head(x)
return x
4 SE模块
论文。
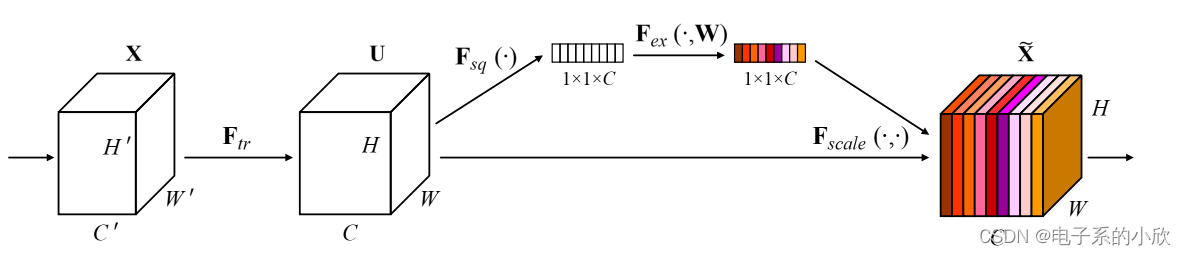
作用:自适应学习通道间的关系。
模块流程:输入X经过卷积卷积Fr(·)得到特征图U,U经过SE模块得到信息矫正后的特征图。
组成:
- Squeeze操作通过全局平均池化将特征图的空间维度压缩为1(称为通道描述符),获取全局信息。
- Excitation操作通过2层linear(有激活函数)对通道描述符进行加权,学习到更具价值的权重值。
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class SE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chnls, ratio):
super(SE, self).__init__()
self.squeeze = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.excitation =nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_chnls, in_chnls//ratio,bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(in_chnls//ratio, in_chnls,bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.squeeze(x)
out = out.squeeze()
out = self.excitation(out).unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
print("out_shape: ",out.shape)
return x+out.expand_as(x)
if __name__ == "__main__":
U = torch.randn((2,256,32,32))
print("U_shape: ",U.shape)
se = SE(256,4)
U_se = se(U)
5 Dense Block
论文,参考文章5_1和文章5_2。
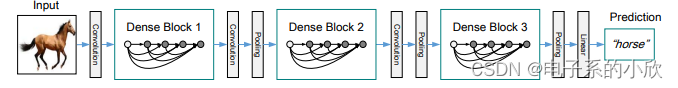
dense block:每一层的输出与之前的所有层的输出concat,作为下一层的输入。
优势:
- 实现了比resnet(与前一层进行像素级相加)更密集的连接方式。
- 每层都与最后的loss有更直接的连接,使得特征利用更充分,减少了冗余的参数量。
- 缓解梯度消失,加速收敛。
代码:
import torch
import torch.functional as F
from torch import nn
class BN_Conv2d(nn.Module):
"""
CONV_BN_RELU
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels: object, out_channels: object, kernel_size: object, stride: object, padding: object,
dilation=1, groups=1, bias=False) -> object:
super(BN_Conv2d, self).__init__()
self.seq = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=bias),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.seq(x)
class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channels, num_layers, growth_rate):
super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.k0 = input_channels #输入通道数
self.k = growth_rate #每一个layer的输出通道数
self.layers = self.__make_layers()
def __make_layers(self):
layer_list = []
for i in range(self.num_layers):
layer_list.append(nn.Sequential(
BN_Conv2d(self.k0+i*self.k, 4*self.k, 1, 1, 0),
BN_Conv2d(4 * self.k, self.k, 3, 1, 1)
))
return layer_list
def forward(self, x):
feature = self.layers[0](x) #B,self.k,H,W
out = torch.cat((x, feature), 1) #B,self.k0+self.k,H,W
for i in range(1, len(self.layers)):
feature = self.layers[i](out) #B,self.k,H,W
out = torch.cat((feature, out), 1) #B,self.k0+(i+1)*self.k,H,W
return out
if __name__ == "__main__":
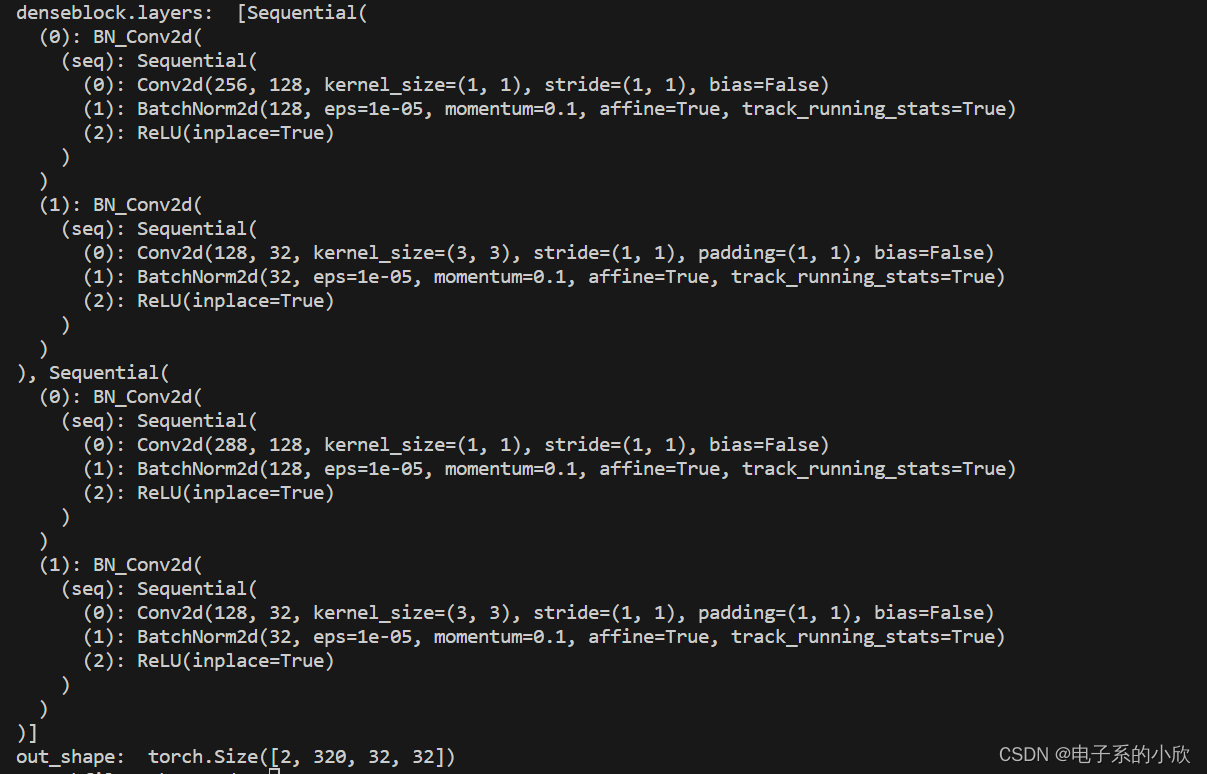
denseblock =DenseBlock(256,2,32)
print("denseblock.layers: "denseblock.layers)
x = torch.randn((2,256,32,32))
out = denseblock(x)
print("out_shape: ",out.shape)
结果: