本章主要介绍playbook中的控制语句
- 使用when判断语句
- block-rescue判断
- 循环语句
一个play中可以包括多个task,如果不想所有的task全部执行,可以设置只有满足某个条件才执行这个task,不满足条件则不执行task。本章主要讲解when和block-rescue两种判断语句
1.1 判断语句when
when作为一个判断语句,出现在某个task下,格式如下
tasks:
- name: aa
模块1
when: 条件1
如果条件1成立,则执行模块1,否则不执行
注意:在when中引用变量是是不用加{ {}}的
本章实验都在dome3文件夹下操作,先把demo3目录创建出来并把ansible.cfg和hosts拷贝进去,命令如下
[jin@rhel801 ~]$ mkdir demo3
[jin@rhel801 ~]$ cd demo3/
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ls
ansible.cfg hosts
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$1.1.1 when判断中>、<、!=的使用
练习1:写一个playbook,判断某条件是否成立,成立了才执行task,否则不执行,命令 如下。
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: task1
debug: msg="111"
when: 1<2
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$这里有一个task,判断1<2是否成立,如果成立则执行task1,屏幕上会显示111;如果不成立则不执行taskl,屏幕上不会显示111。这里明显是成立的,所以会执行task1。运行结果如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task1] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "111"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ when后面可以有多个条件,用or或and作为连接符
如果用or作为连接符,只要有一个条件成立即可,只有所有的条件都不成立时,整体才不成立
练习2:修改when-1.yml的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: task1
debug: msg="111"
when: 1<2 or 2>3
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$此处用or作为连接符,只要有一个条件成立就会成立,2>3不成立,但是1<2成立,所以整体上就是成立的。运行结果如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task1] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "111"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$仍然会执行task1
练习3:修改when-1.yml的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: task1
debug: msg="111"
when: 1>2 or 2>3
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$此处用or作为连接符,1>2不成立且2>3也不成立,所以整体上就是不成立的,不会执行task1。运行结果如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task1] *******************************************************************
skipping: [rhel802]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$也可以用and作为连接符,如果用and作为连接符,需要所有条件全部成立,只要有一个条件不成立,整体上就是不成立的
练习4:修改when-1.yml的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: task1
debug: msg="111"
when: 1<2 and 2>3
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$这里虽然2>1是成立的,但是2>3不成立,所以整体上就是不成立的,因为用and作为连接符,需要所有的条件都成立才可以,所以不会执行task1。运行结果如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task1] *******************************************************************
skipping: [rhel802]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$在判断中,or 和 and是可以混用的,为了看得更清晰,可以使用小括号
练习5:修改 when-1.yml 的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: task1
debug: msg="111"
when: (1>2 or 2!=1) and 2>3
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$这里(1>2 or 2!=1)作为一个整体,1>2不成立,但是2!=1(=是不等于的意思)成立,所以此处( 1>2 or 2!=1)作为一个整体是成立的。and后面2>3不成立,所以整个when后面的判断是不成立的,不会执行此 task1。运行结果如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task1] *******************************************************************
skipping: [rhel802]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$常见的判断符包括以下6种
(1)==:等于
(2)!=:不等于
(3)>:大于
(4)>=:大于等于
(5)<:小于
(6)<=:小于等于
练习6:如果rhel802的系统主版本是7(RHEL/CentOS7),则打印111,否则不打印。 playbook的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-2.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: task2
debug: msg="111"
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$因为rhel802的系统是RHEL8,所以不会执行此task2,即不会显示111
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-2.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task2] *******************************************************************
skipping: [rhel802]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$注意:ansible_distribution major version的值是一个字符串,所以when判断中=后面的7是要加引号 的。
练习7:修改when-2.yml 的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-2.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: task2
debug: msg="111"
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "8"
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$再次运行此playbook,命令如下,会显示111
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-2.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task2] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "111"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$再次提醒:在when 中引用变量时是不用加{ {}}的
1.2 when判断中in的用法
在when语句中,除可以使用上面的大于、小于等判断方法外,还可以使用 in,用法如下
value in 列表如果此值在这个列表中,则判断成立,否则不成立
练习:判断某值是否在列表中,编写 when-3.yml,命令如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-3.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
list1: [1,2,3,4]
tasks:
- name: task3
debug: msg="333"
when: 2 in list1
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$此处定义了一个列表 list1,里面有4个值,分别为1、2、3、4;定义了一个task打印333, 会不会执行这个task,就要看when后面的判断是否成立。如果2在列表list1中,则执行;如果不在,则不执行,很明显2在列表list1中,所以会执行此task,即屏幕上会显示333。运行结果如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-3.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task3] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "333"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$因为2在列表list1中,when判断成立,可以正确执行task3,所以屏幕上会显示333。修改when-3.yml的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-3.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
list1: [1,2,3,4]
tasks:
- name: task3
debug: msg="333"
when: 2 not in list1
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$这里判断的是2不在列表list1中,但2是在列表list1中的,所以判断不成立。运行结果如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-3.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task3] *******************************************************************
skipping: [rhel802]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$因为when判断不成立,所以屏幕上不会显示333。回想前面的例子
1.3 when判断中is的用法
is可以用于判断变量是否被定义,常见的判断包括以下3种
(1)is defined:变量被定义
(2)is undefined:等同于is not defined,变量没有被定义
(3)is none:变量被定义了,但是值为空
看下面的例子
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-4.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
aa: 1
bb:
tasks:
- name: task1
debug: msg="111"
when: aa is undefined
- name: task2
debug: msg="222"
when: bb is undefined
- name: task3
debug: msg="333"
when: cc is not defined
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ 首先定义了两个变量:aa和 bb,其中bb的值为空,此处并没有定义cc。后面定义了以下 3个task
(1)如果aa被定义了,则显示111,这里aa被定义了,所以判断成立,会执行task1
(2)如果b没有被定义,则显示222,这里bb被定义了,所以判断不成立,不会执行 task2
(3)如果cc没有被定义,则显示333,这里cc没有被定义,所以判断成立,会执行 task3
这里is undefined 和is not defined是一个意思。 查看运行的结果,如下所示
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-4.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task1] *******************************************************************
skipping: [rhel802]
TASK [task2] *******************************************************************
skipping: [rhel802]
TASK [task3] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "333"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=2 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$练习:写一个playbook,内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat when-5.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: 执行一个系统命令
shell: "ls /aa.txt"
register: aa
ignore_errors: yes
- name: task2
fail: msg="命令执行错了001"
when: aa.rc != 0
- name: task3
debug: msg="OK123"
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$运行此playbook命令如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook when-5.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [执行一个系统命令] ****************************************************************
fatal: [rhel802]: FAILED! => {"changed": true, "cmd": "ls /aa.txt", "delta": "0:00:00.005440", "end": "2023-12-22 10:20:22.042127", "msg": "non-zero return code", "rc": 2, "start": "2023-12-22 10:20:22.036687", "stderr": "ls: 无法访问'/aa.txt': 没有那个文件或目录", "stderr_lines": ["ls: 无法访问'/aa.txt': 没有那个文件或目录"], "stdout": "", "stdout_lines": []}
...ignoring
TASK [task2] *******************************************************************
fatal: [rhel802]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "msg": "命令执行错了001"}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=1 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=1
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$1.2 判断语句block-resuce
对于when来说,只能做一个判断,成立就执行,不成立就不执行。block和rescue一般同用,类似于shell判断语句中的if-else,在block下面可以包含多个模块,来判断这多个模块是否执行成功了
block-rescue的用法如下
1 block:
2 ‐ 模块1
3 ‐ 模块2
4 ‐ 模块3
5 rescue:
6 ‐ 模块1
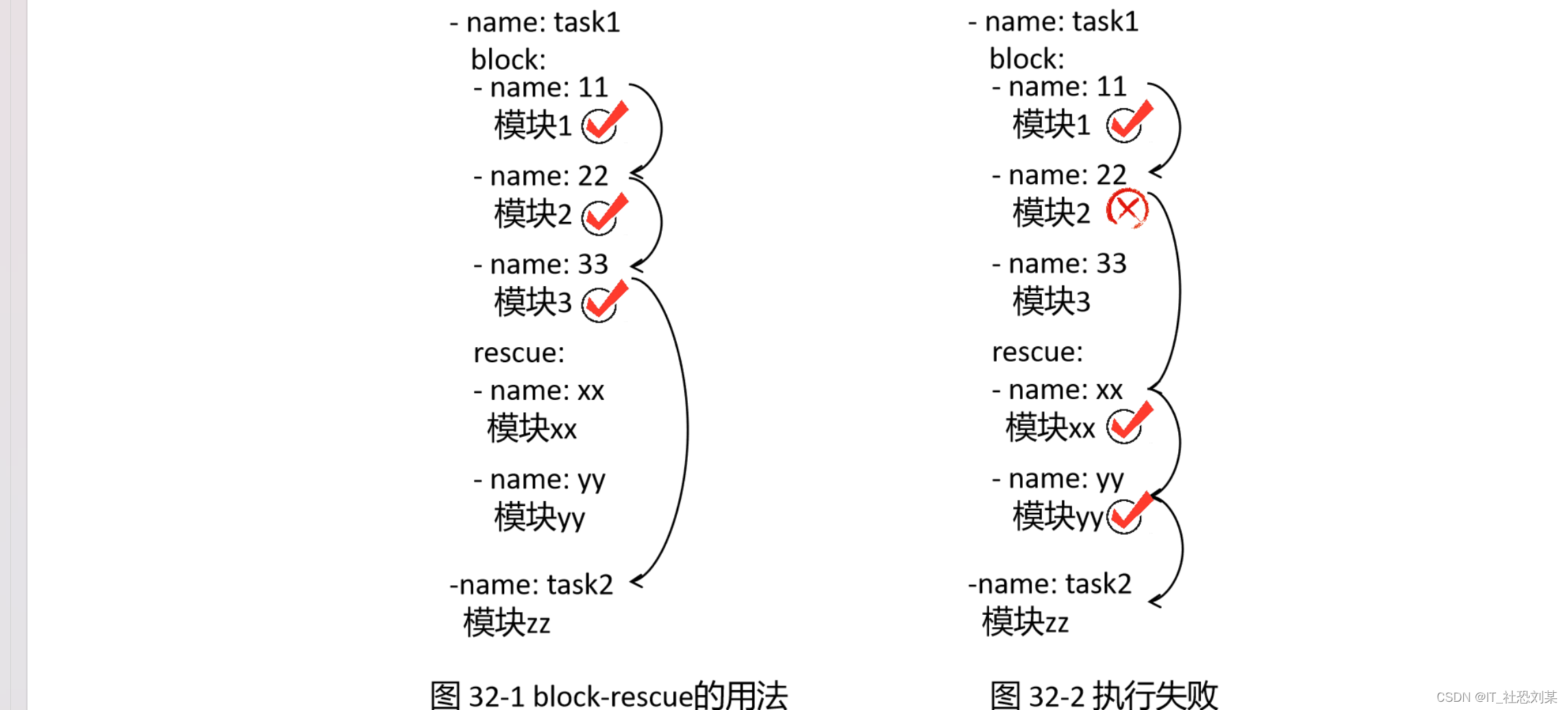
7 ‐ 模块2先执行 block中的模块1,如果没有报错,则继续执行模块2,如果block中的所有模块都 执行成功了,则跳过rescue 中的所有模块,直接执行下一个task中的模块,如图
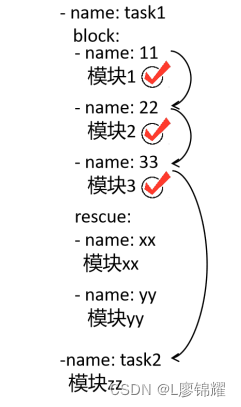
这里有2个task : task1和 task2,在 task1的block中有3个模块,rescue中有2个模块。 如果block1中的所有模块都正确执行了,则不执行rescue中的模块,直接执行task2
如果 block中的任一模块执行失败,block中其他后续的模块都不再执行,然后会跳转执行rescue 中的模块,如图

这里block1中的模块1执行完成之后会执行模块2,如果模块2报错,则不会执行模块3, 直接跳转到rescue中,执行模块x。rescue中的所有模块全部正确执行完成之后,则执 task2
如果rescue中的某个模块执行失败,则退出整个playbook,如图

这里 block中的模块2执行失败,则跳转到rescue中执行模块x,如果模块x执行失败,则退 出整个 playbook,即也不会执行task2了
如果某个报错模块有 ignore_errors: yes选项,则会忽略此模块的错误,继续执行下一个模块,如图

这里block中的模块2执行失败了,但是因为加了ignore_errors: yes选项,所以会忽略这个报错模块,继续执行模块3
练习1:按上面的描述写一个playbook
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat block-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: task1
block:
- name: 11
debug: msg="1111"
- name: 22
shell: "ls /aa.txt"
- name: 33
debug: msg="3333"
rescue:
- name: xx
debug: msg="xxxx"
- name: yy
debug: msg="yyyy"
- name: task2
debug: msg="zzzz"
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$这里在task1的block中运行了3个模块,第一个模块可以正确执行,第二个模块是执行一 个系统命令ls /aa.txt,但是在rhel802中是不存在/aa.txt这个文件的,所以这个模块会执行失败。block中的第三个模块不再执行,直接跳转到rescue中的模块。rescue中的2个模块均可正确执行,然后执行task2
所以,屏幕上会显示1111, xxxx, yyyy, zzzz。运行结果如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook block-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [debug] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "1111"
}
TASK [shell] *******************************************************************
fatal: [rhel802]: FAILED! => {"changed": true, "cmd": "ls /aa.txt", "delta": "0:00:00.007141", "end": "2023-12-22 10:50:17.481727", "msg": "non-zero return code", "rc": 2, "start": "2023-12-22 10:50:17.474586", "stderr": "ls: 无法访问'/aa.txt': 没有那个文件或目录", "stderr_lines": ["ls: 无法访问'/aa.txt': 没有那个文件或目录"], "stdout": "", "stdout_lines": []}
TASK [xx] **********************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "xxxx"
}
TASK [yy] **********************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "yyyy"
}
TASK [task2] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "zzzz"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=5 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=1 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$练习2: 修改block-1.yml的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat block-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
tasks:
- name: task1
block:
- name: 11
debug: msg="1111"
- name: 22
shell: "ls /aa.txt"
ignore_errors: yes
- name: 33
debug: msg="3333"
rescue:
- name: xx
debug: msg="xxxx"
- name: yy
debug: msg="yyyy"
- name: task2
debug: msg="zzzz"
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$与上面的例子相比,在 block的第二个模块中增加了一个 ignore_errors: yes选项,这样block中的第二个模块即使报错了,也会忽略这个报错继续执行第三个模块。然后执行task2, 所以屏幕上会显示1111,3333,zzzz。运行结果如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook block-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [debug] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "1111"
}
TASK [shell] *******************************************************************
fatal: [rhel802]: FAILED! => {"changed": true, "cmd": "ls /aa.txt", "delta": "0:00:00.006718", "end": "2023-12-22 10:54:12.209091", "msg": "non-zero return code", "rc": 2, "start": "2023-12-22 10:54:12.202373", "stderr": "ls: 无法访问'/aa.txt': 没有那个文件或目录", "stderr_lines": ["ls: 无法访问'/aa.txt': 没有那个文件或目录"], "stdout": "", "stdout_lines": []}
...ignoring
TASK [debug] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "3333"
}
TASK [task2] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => {
"msg": "zzzz"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=5 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=1
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$1.3 循环语句
在shell红for循环的用法如下
for i in A B C ... ; do
命令 $
done这里首先把A赋值给i,执行do和done之间的命令;然后把B赋值给i,执行do和 done之间的命令,以此类推,直到把in后面所有的值执行完毕。for后面的变量可以随便命名
再回顾一下前面介绍的列表
1 employee:
2 ‐ uname: lisi
3 age: 22
4 sex: man
5
6 ‐ uname: wangwu
7 age: 24
8 sex: man
9
10 ‐ uname: xiaohua
11 age: 24
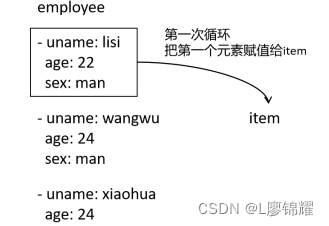
12 sex: woman这里列表employee中有3个元素,分别记录了lisi、wangwu、xiaohua的信息。我们把这3个元素当成刚讲的for循环中的A、B、C。先把第一个元素赋值给变量,执行某个操作, 完成之后再把第二个元素赋值给变量
用for循环A、B、C,在playbook中用loop来循环列表中的元素。在for循环中,指定一个变量如i,然后分别把A、B、C赋值给i
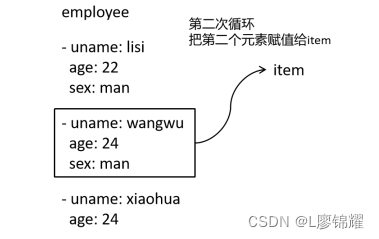
在loop中,使用一个固定的变量 item,然后把每个元素赋值给item,如图
第二次循环,如图
练习1:定义一个列表users,然后循环这个列表中的每个元素,命令如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat loop-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
users:
- uname: tom
age: 20
sex: man
- uname: bob
age: 22
sex: man
- uname: mary
age: 20
sex: woman
tasks:
- name: task1
debug: msg={
{ item }}
loop: "{
{ users }}"
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$这里定义了一个列表users,里面包含了3个用户的信息,在taskl中用loop开始循环这个列表。loop后面写列表名时,需要使用引号引起来,这里的关键字loop可以换成关键字 with_items
这里首先把users的第一个元素赋值给item,用debug 打印;然后把users的第二个元素赋值给item,用 debug打印,直到把所有的元素都赋值给 item
运行此 playbook
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook loop-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task1] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => (item={'uname': 'tom', 'age': 20, 'sex': 'man'}) => {
"msg": {
"age": 20,
"sex": "man",
"uname": "tom"
}
}
ok: [rhel802] => (item={'uname': 'bob', 'age': 22, 'sex': 'man'}) => {
"msg": {
"age": 22,
"sex": "man",
"uname": "bob"
}
}
ok: [rhel802] => (item={'uname': 'mary', 'age': 20, 'sex': 'woman'}) => {
"msg": {
"age": 20,
"sex": "woman",
"uname": "mary"
}
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$如果不想打印每个元素的所有条目,只想打印每个元素的uname呢?答案:可以通过练习2解决
练习2:修改loop-1.yml的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat loop-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
users:
- uname: tom
age: 20
sex: man
- uname: bob
age: 22
sex: man
- uname: mary
age: 20
sex: woman
tasks:
- name: task1
debug: msg={
{ item.uname }}
loop: "{
{ users }}"
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$列表的每个元素都是一个字典,所以 item就是字典,要获取这个字典中的uname变量,用 item.uname即可
运行此 playbook
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook loop-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task1] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => (item={'uname': 'tom', 'age': 20, 'sex': 'man'}) => {
"msg": "tom"
}
ok: [rhel802] => (item={'uname': 'bob', 'age': 22, 'sex': 'man'}) => {
"msg": "bob"
}
ok: [rhel802] => (item={'uname': 'mary', 'age': 20, 'sex': 'woman'}) => {
"msg": "mary"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$练习3:如果想打印所有性别为男的那些用户名,修改loop-1.yml 的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ cat loop-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
users:
- uname: tom
age: 20
sex: man
- uname: bob
age: 22
sex: man
- uname: mary
age: 20
sex: woman
tasks:
- name: task1
debug: msg={
{ item.uname }}
when: item.sex == "man"
loop: "{
{ users }}"
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$在此playbook中,我们用when加了一个判断。循环列表时,首先把第一个元素赋值给item,然后判断item.sex的值是否为man,如果是则判断成立,执行debug模块;如果不是则判断不成立,不执行debug模块
第一次循环结束之后,开始第二次循环,把第二个元素赋值给item之后,做相同的判断。运行此 playbook
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$ ansible-playbook loop-1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [task1] *******************************************************************
ok: [rhel802] => (item={'uname': 'tom', 'age': 20, 'sex': 'man'}) => {
"msg": "tom"
}
ok: [rhel802] => (item={'uname': 'bob', 'age': 22, 'sex': 'man'}) => {
"msg": "bob"
}
skipping: [rhel802] => (item={'uname': 'mary', 'age': 20, 'sex': 'woman'})
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo3]$这样就把所有性别为男的用户名打印出来了