数据结构:队列

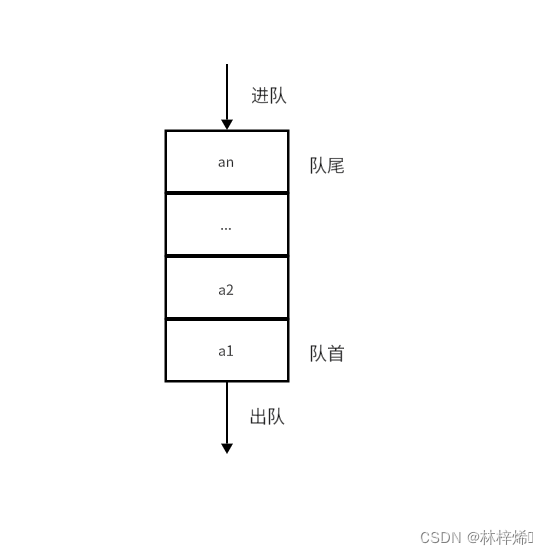
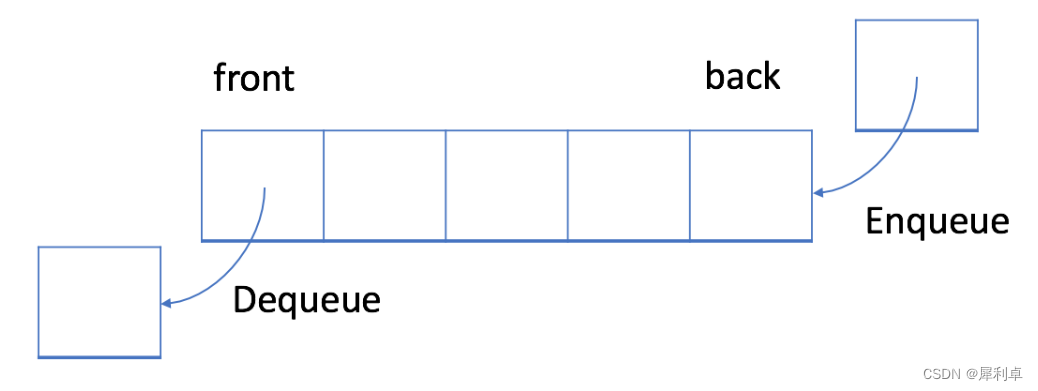
***「队列 queue」是一种遵循先入先出规则的线性数据结构。***队列模拟了排队现象,即新来的人不断加入队列尾部,而位于队列头部的人逐个离开。只有当队头的的人逐个离开后,队尾的人才能到队头。
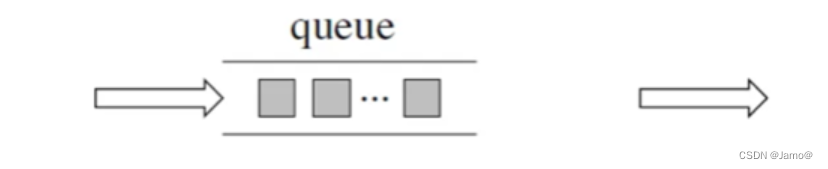
1.队列常用操作:
2.队列的实现
- 实现队列可以基于链表实现,也可以基于数组实现
优势在于链表来实现队列更加方便,因为链表更容易进行头删操作,效率更高,进行头删时链表时间复杂度为O(1)数组时间复杂度为O(N)
下面我将用链表(带头单向)实现队列:
Queue.h:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//基于 带头单向链表 实现队列
typedef int QueueDateType;
typedef struct MyQueueNode
{
QueueDateType val;
struct MyQueueNode* next;
}Queue;
// 初始化队列
Queue* Init();
//打印队列
void Print(Queue* head);
//创建节点
Queue* Createnewnode(QueueDateType data);
// 队尾入队列
void Push(Queue** head, QueueDateType data);
// 队头出队列
void Pop(Queue** head);
// 获取队列头部元素
QueueDateType Peek(Queue** head);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QueueDateType Back(Queue** head);
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int Size(Queue* head);
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
bool Empty(Queue* head);
// 销毁队列
void Destroy(Queue** head);
Queue.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
// 初始化队列
// 哨兵位初始化(创建链表的头结点)
Queue* Init()
{
Queue* head = Createnewnode(-1);
return head;
}
//打印队列
void Print(Queue* head)
{
assert(head);
Queue* tail = head->next;
if (tail == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空");
return;
}
while (tail)
{
printf("%d ", tail->val);
tail = tail->next;
}
}
//创建节点
Queue* Createnewnode(QueueDateType data)
{
Queue* newnode = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->val = data;
return newnode;
}
// 队尾入队列 (尾插)
void Push(Queue** head, QueueDateType data)
{
assert(head);
assert(*head);
// 创造一个新节点
Queue* newnode = Createnewnode(data);
//如果链表最初就为空(除去哨兵位)
if ((*head)->next == NULL)
{
(*head)->next = newnode;
}
//找尾
else
{
Queue* tail = (*head)->next;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
// 队头出队列 (头删)
void Pop(Queue** head)
{
assert(head);
assert((*head)->next != NULL);
Queue* first = (*head)->next;
(*head)->next = first->next;
free(first);
first = NULL;
}
// 获取队列头部元素
QueueDateType Peek(Queue** head)
{
assert(head);
assert((*head)->next != NULL);
return (*head)->next->val;
}
// 获取队列队尾元素
QueueDateType Back(Queue** head)
{
assert(head);
assert((*head)->next != NULL);
Queue* tail = (*head)->next;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
return tail->val;
}
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int Size(Queue* head)
{
assert(head);
int sum = 0;
while (head->next != NULL)
{
sum++;
head = head->next;
}
return sum;
}
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
bool Empty(Queue* head)
{
if (Size(head) == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// 销毁队列
void Destroy(Queue** head)
{
assert(head);
assert(*head);
Queue* cur = (*head)->next;
while (cur)
{
Queue* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(*head);
*head = NULL;
}
test.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
//入队列测试
void test1()
{
//初始化队列
Queue* head = Init();
Push(&head, 1);
Push(&head, 2);
Push(&head, 3);
Push(&head, 4);
Push(&head, 5);
Print(head);
Destroy(&head);
}
//队头出队列测试
void test2()
{
//初始化队列
Queue* head = Init();
Push(&head, 1);
Push(&head, 2);
Push(&head, 3);
Push(&head, 4);
Push(&head, 5);
Pop(&head);
Print(head);
Destroy(&head);
}
//获取头部元素测试
void test3()
{
//初始化队列
Queue* head = Init();
Push(&head, 1);
Push(&head, 2);
Push(&head, 3);
Push(&head, 4);
Push(&head, 5);
printf("%d\n", Peek(&head));
Destroy(&head);
}
// 获取队列队尾元素
void test4()
{
//初始化队列
Queue* head = Init();
Push(&head, 1);
Push(&head, 2);
Push(&head, 3);
Push(&head, 4);
Push(&head, 5);
QueueDateType ret = Back(&head);
printf("%d\n", ret);
Destroy(&head);
}
//获取元素个数测试
void test5()
{
Queue* head = Init();
Push(&head, 1);
Push(&head, 2);
Push(&head, 3);
Push(&head, 4);
Push(&head, 5);
printf("%d\n", Size(head));
Destroy(&head);
}
//检测链表是否为空
void test6()
{
Queue* head = Init();
Push(&head, 1);
Push(&head, 2);
Push(&head, 3);
Push(&head, 4);
Push(&head, 5);
if (Empty(head) == true)
{
printf("链表为空\n");
}
else
{
printf("链表不为空\n");
}
Destroy(&head);
}
int main()
{
//入队列测试
//test1();
//队头出队列测试
//test2();
//获取头部元素测试
//test3();
// 获取队列队尾元素
//test4();
//获取元素个数测试
//test5();
//检测链表是否为空
test6();
return 0;
}
3.队列典型应用
淘宝订单。购物者下单后,订单将加入队列中,系统随后会根据顺序处理队列中的订单。在双十一期间,短时间内会产生海量订单,高并发成为工程师们需要重点攻克的问题。
各类待办事项。任何需要实现“先来后到”功能的场景,例如打印机的任务队列、餐厅的出餐队列等,队列在这些场景中可以有效地维护处理顺序。






























![【移动通讯】【MIMO】[P1]【科普篇】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ceb2eaefb1da4f87b58e9ae3ab131f1a.png)