1.避免同一个函数头文件被多次引用
在函数声明中,例:Add.h头文件
#ifndef _ADD_H_ //如果没有定义,再往下
#define _ADD_H_ //定义这个函数
//函数声明
int Add (int x, int y);
#endif
2.函数递归
把大事化小,与原问题相似的问题(函数自己调用自己)
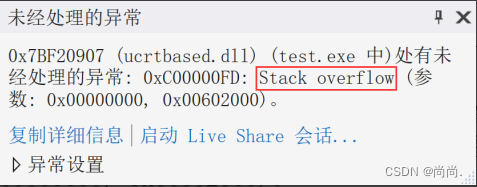
递归常见错误:stack overflow(栈溢出)
栈区:局部变量、函数形参
内存 堆区: 动态开辟的内存
静态区:全局变量、static修饰的变量
(1)最简单的递归-栈溢出
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
//最简单递归-栈溢出
int main()
{
printf("hehe\n");
main();
return 0;
}

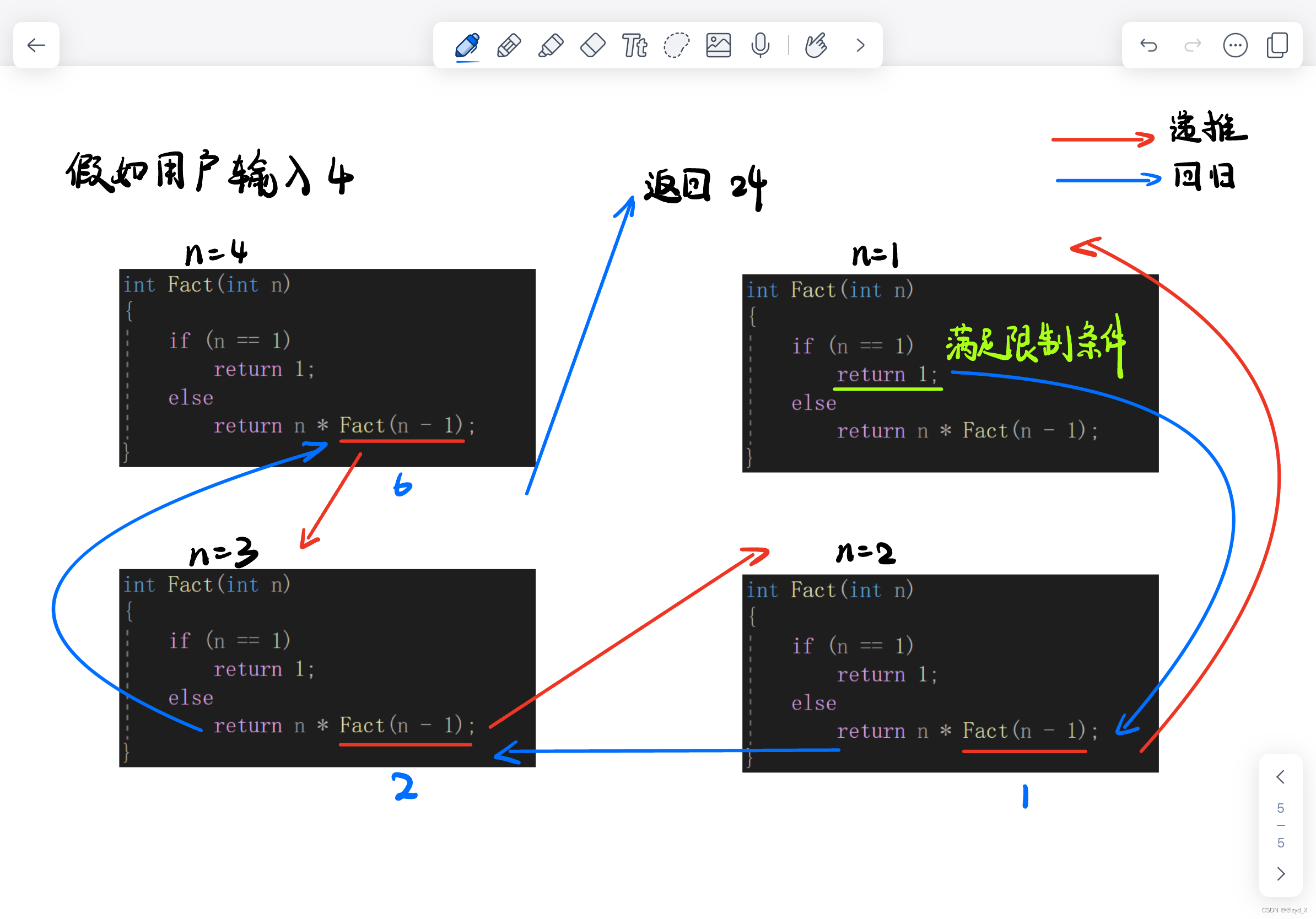
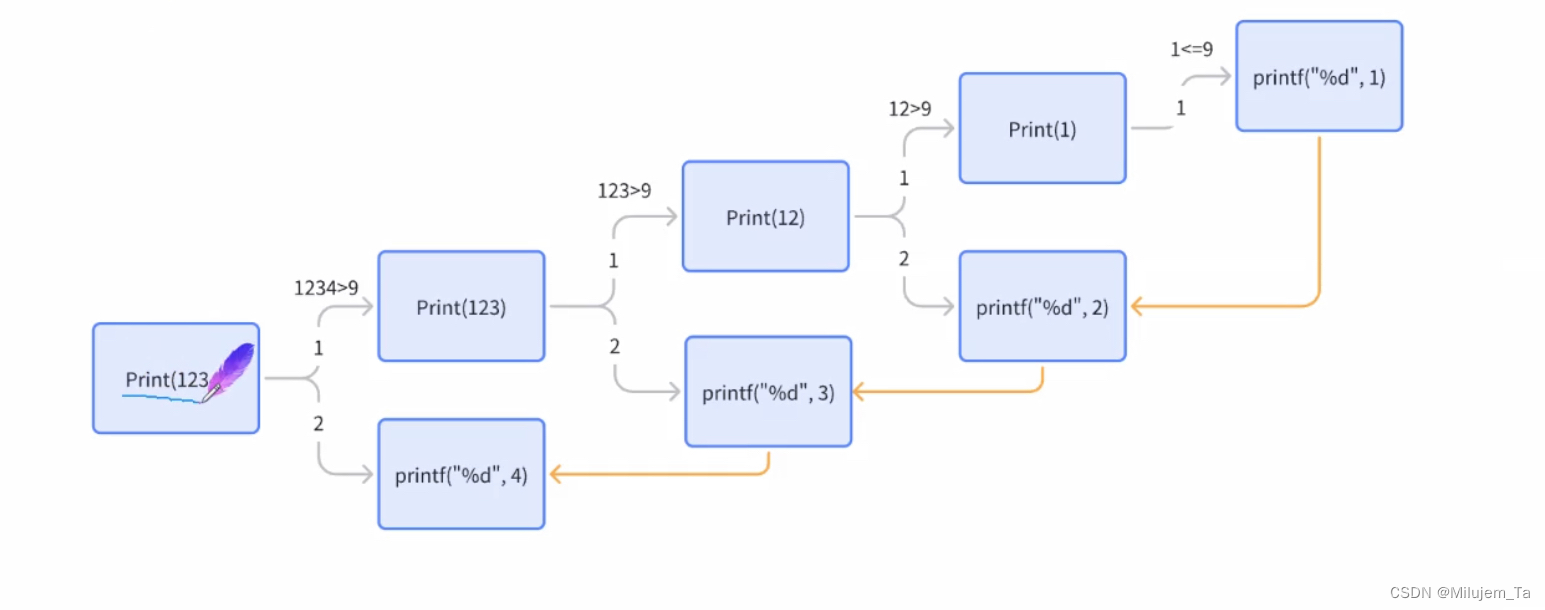
(2)接收一个无符号整型数,并按顺序打印它的每一位。
从后往前依次输出,因为后面的调用执行完,前面函数才能继续往下。
例:输入1234
逻辑抽象,逐次拆解:
print(1234)
print(123)4
print(12)34
print(1)234
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
//接收无符号数,按顺序打印每一位
void print (unsigned int n)
{
if(n>9)
{
print(n/10);
}
printf("%d ",n%10);
}
int main()
{
unsigned int num = 0;
printf("请输入:\n");
scanf("%d",&num);
print(num);
return 0;
}

(3)函数递归的两个必要条件
1.存在限制条件,当满足这个限制条件时,递归不再继续;
2.每次递归调用后越来越接近这个限制条件。
(4)循环:求字符串长度
数组名是数组首元素地址,数组元素地址连续,对数组名解引用就是数组元素内容,对数组名++,可访问数组各个元素地址,再解引用可访问数组各个元素。
对字符串数组来说,char占一个字节,所以arr++就可以访问字符数组各个元素,一个内存单元占一个字节。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
//循环:求字符串长度
int my_strlen (char* str)
{
int count = 0;
while(*str!='\0')
{
count++;
str++;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
char arr [20] = {0};
int len = 0;
printf("请输入字符串:\n");
scanf("%s",arr);
len = my_strlen(arr);
printf("字符串长度为%d\n",len);
return 0;
}
(5)递归:求字符串长度(不创建临时变量)
把大事化小(相似问题求解)
my_strlen("hello")
1+my_strlen("ello")
1+1+my_strlen("llo")
......
1+1+1+1+1+0//到 \0
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
//递归:求字符串长度(不创建临时变量)
int my_strlen (char*str)
{
if(*str!='\0')
{
return 1+my_strlen(str+1);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
int main()
{
char arr [20] = {0};
int len = 0;
printf("请输入字符串:\n");
scanf("%s",arr);
len = my_strlen(arr);
printf("字符串长度为:%d\n",len);
return 0;
}
3.思维导图



![第<span style='color:red;'>九</span>章[<span style='color:red;'>函数</span>]:9.3:<span style='color:red;'>递</span><span style='color:red;'>归</span><span style='color:red;'>函数</span>](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f100d6ef2d78a48590ba77fa5e9281a2.jpeg)