Python 的 unittest 框架是用于编写和运行可重复的测试的一个强大工具。它允许你定义测试用例、测试套件、测试运行器和测试固件(fixtures),从而系统化地测试你的代码。以下是如何使用 unittest 框架来编写和运行单元测试的基本步骤:
1. 导入 unittest 模块
首先,你需要在你的测试脚本中导入 unittest 模块。
python复制代码
import unittest |
2. 编写测试用例
然后,你需要创建一个继承自 unittest.TestCase 的类,并在其中编写你的测试方法。测试方法必须以 test 开头,这样 unittest 框架才能识别并运行它们。
python复制代码
class TestStringMethods(unittest.TestCase): |
|
def test_upper(self): |
|
self.assertEqual('foo'.upper(), 'FOO') |
|
def test_isupper(self): |
|
self.assertTrue('FOO'.isupper()) |
|
self.assertFalse('Foo'.isupper()) |
|
def test_split(self): |
|
s = 'hello world' |
|
self.assertEqual(s.split(), ['hello', 'world']) |
|
# 检查带有分隔符的分割 |
|
with self.assertRaises(TypeError): |
|
s.split(2) |
3. 编写测试套件(可选)
如果你需要组织多个测试用例,可以将它们添加到测试套件中。这通常在你有很多测试用例分布在不同的测试类中时很有用。
python复制代码
# 假设你有另一个测试类 TestAnotherModule |
|
from another_module_tests import TestAnotherModule |
|
def suite(): |
|
suite = unittest.TestSuite() |
|
suite.addTest(unittest.makeSuite(TestStringMethods)) |
|
suite.addTest(unittest.makeSuite(TestAnotherModule)) |
|
return suite |
注意:从 Python 3.4 开始,你可以使用 unittest.TestLoader 来更简单地加载测试。
4. 运行测试
有几种方法可以运行你的测试:
使用命令行
你可以使用 Python 自带的 -m unittest 选项来运行你的测试。只需在命令行中指定包含测试用例的模块或文件即可。
bash复制代码
python -m unittest test_module.py |
或者,如果你已经定义了一个测试套件,可以在模块中这样运行它:
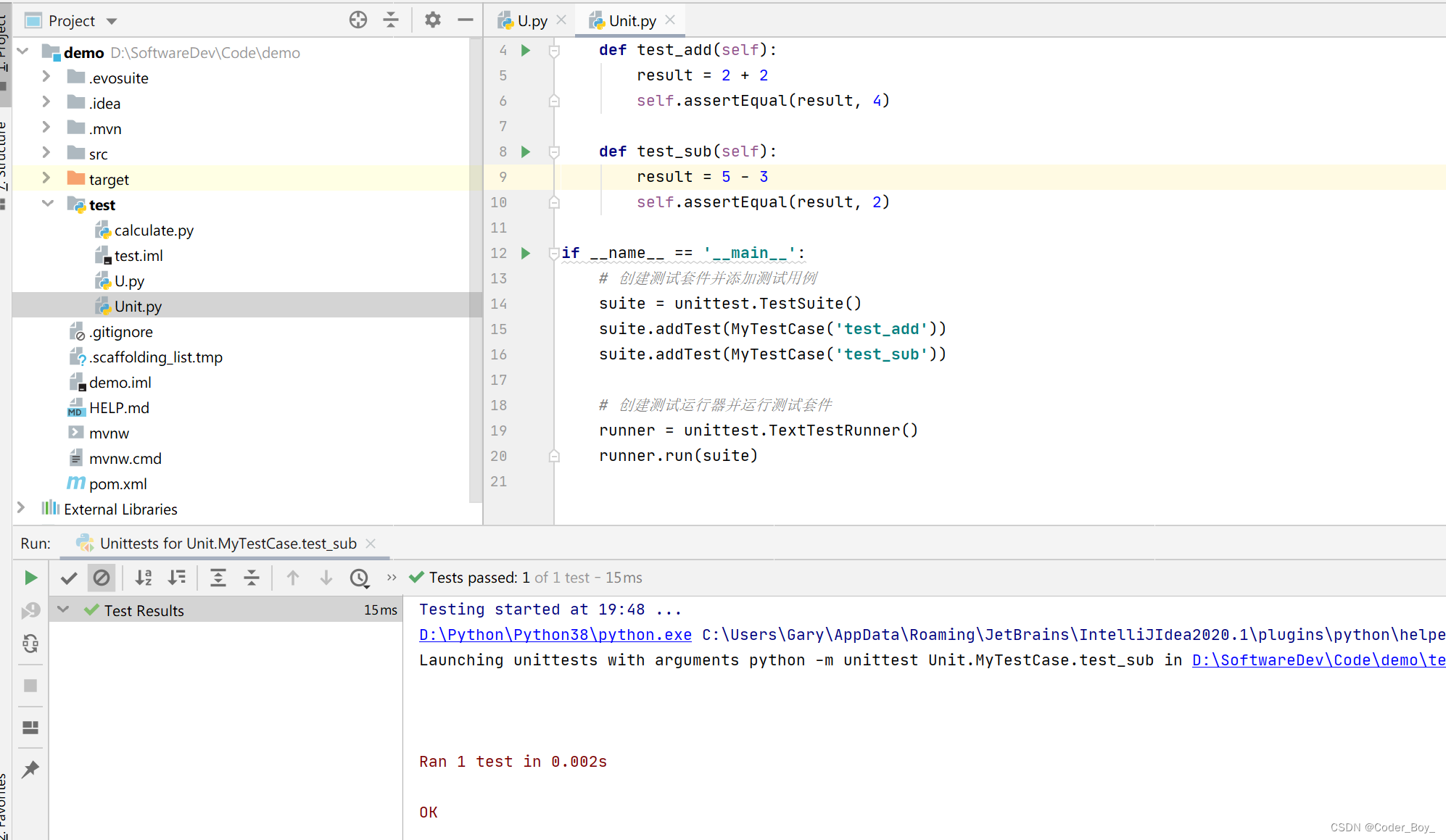
python复制代码
if __name__ == '__main__': |
|
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner() |
|
runner.run(suite()) |
使用 IDE
大多数现代的 Python IDE(如 PyCharm、VS Code 等)都内置了对 unittest 的支持,允许你直接在 IDE 中运行和调试测试。
5. 测试固件
测试固件(fixtures)是测试运行之前和之后运行的代码,用于设置和清理测试环境。unittest 提供了几种设置和清理测试环境的方法,包括 setUp(), tearDown(), setUpClass(), 和 tearDownClass()。
python复制代码
class TestStringMethods(unittest.TestCase): |
|
@classmethod |
|
def setUpClass(cls): |
|
print("Setup class once") |
|
def setUp(self): |
|
print("Setup before each test") |
|
def test_upper(self): |
|
self.assertEqual('foo'.upper(), 'FOO') |
|
def tearDown(self): |
|
print("Teardown after each test") |
|
@classmethod |
|
def tearDownClass(cls): |
|
print("Teardown class once") |
通过以上步骤,你可以有效地使用 unittest 框架来编写和运行你的单元测试,从而确保你的代码质量。