P3371 【模板】单源最短路径(弱化版)
注意的点:
- 边有重复,选择最小边!
- 对于SPFA算法容易出现重大BUG,没有负权值的边时不要使用!!!
70分代码 朴素板dijsktra
- 爆空间
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int n, m, s, u, v, w;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m >> s;
vector<vector<int>>grid(n + 9, vector<int>(n + 9, INT_MAX));
vector<int>dist(n + 9, INT_MAX);
vector<bool>visited(n + 9, false);
while (m--) {
cin >> u >> v >> w;
grid[u][v] = min(grid[u][v], w);
}
dist[s] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int cur = 1;
int minDist = INT_MAX;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!visited[j] && dist[j] < minDist) {
minDist = dist[j];
cur = j;
}
}
visited[cur] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!visited[j] && grid[cur][j] != INT_MAX && dist[cur] + grid[cur][j] < dist[j]) {
dist[j] = dist[cur] + grid[cur][j];
}
}
/*cout << "select " << cur << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;*/
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0); std::cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
32分代码 SPFA
- 因为有重复指向的边,所有理论上边数可以无穷大,O(KM)的时间复杂度不确定性极大!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int n, m, s, u, v, w;
struct Edge {
int v, w;
Edge(int a, int b) :v(a), w(b) {}
};
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m >> s;
vector<list<Edge>>grid(n + 9, list<Edge>());
vector<int>dist(n + 9, INT_MAX); dist[s] = 0;
queue<Edge>q;
while (m--) {
cin >> u >> v >> w;
grid[u].push_back(Edge(v, w));
}
q.push({ s,0 });
while (!q.empty()) {
Edge cur = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto item : grid[cur.v]) {
if (item.w + dist[cur.v] < dist[item.v]) {
dist[item.v] = dist[cur.v] + item.w;
q.push(item);
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0); std::cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
AC代码 堆优化dijsktra
- 重复的边不影响
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int n, m, s, u, v, w;
struct Edge {
int v, w;
Edge(int a, int b) :v(a), w(b) {}
};
class cmp {
public:
bool operator()(const Edge& a, const Edge& b) {
return a.w > b.w;//从小排序
}
};
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m >> s;
vector<list<Edge>>grid(n + 9, list<Edge>());
vector<int>dist(n + 9, INT_MAX); dist[s] = 0;
vector<bool>visited(n + 9, false);
priority_queue<Edge, vector<Edge>, cmp>q;
while (m--) {
cin >> u >> v >> w;
grid[u].push_back(Edge(v, w));
}
q.push({ s,0 });
while (!q.empty()) {
Edge cur = q.top();
q.pop();
if (visited[cur.v]) {
continue;
}
visited[cur.v] = true;
for (auto item : grid[cur.v]) {
if (!visited[item.v]&&item.w + dist[cur.v] < dist[item.v]) {
dist[item.v] = item.w + dist[cur.v];
q.push({ item.v,dist[item.v] });
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0); std::cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
最短路计数
题目描述
给出一个 N N N 个顶点 M M M 条边的无向无权图,顶点编号为 1 ∼ N 1\sim N 1∼N。问从顶点 1 1 1 开始,到其他每个点的最短路有几条。
输入格式
第一行包含 2 2 2 个正整数 N , M N,M N,M,为图的顶点数与边数。
接下来 M M M 行,每行 2 2 2 个正整数 x , y x,y x,y,表示有一条连接顶点 x x x 和顶点 y y y 的边,请注意可能有自环与重边。
输出格式
共 N N N 行,每行一个非负整数,第 i i i 行输出从顶点 1 1 1 到顶点 i i i 有多少条不同的最短路,由于答案有可能会很大,你只需要输出 $ ans \bmod 100003$ 后的结果即可。如果无法到达顶点 i i i 则输出 0 0 0。
对于 100 % 100\% 100% 的数据, 1 ≤ N ≤ 1 0 6 1\le N\le10^6 1≤N≤106, 1 ≤ M ≤ 2 × 1 0 6 1\le M\le 2\times 10^6 1≤M≤2×106。
AC题解 堆优化dijsktra
- 多一段条件判断,不加入堆但是也起到了统计作用
else if (dist[cur.v] + item.w == dist[item.v]) {
ct[item.v] += ct[cur.v];
ct[item.v] %= 100003;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int n, m, x, y;
struct Edge {
int v, w;
Edge(int a, int b) :v(a), w(b) {};
};
class cmp {
public:
bool operator()(const Edge& a, const Edge& b) {
return a.w > b.w;
}
};
priority_queue<Edge,vector<Edge>,cmp>q;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
vector<list<Edge>>grid(n+ 9, list<Edge>());
vector<bool>visited(n+ 9, false);
vector<int>dist(n+9, INT_MAX);
vector<int>ct(n+9, 0);
while (m--) {
cin >> x >> y;
grid[x].push_back(Edge(y, 1));
grid[y].push_back(Edge(x, 1));
}
dist[1] = 0; ct[1] = 1;
q.push({ 1,0 });
while (!q.empty()) {
Edge cur=q.top();
q.pop();
if (visited[cur.v]) {
continue;
}
visited[cur.v] = true;
for (auto item : grid[cur.v]) {
if (dist[cur.v] + item.w < dist[item.v]) {
dist[item.v] = dist[cur.v] + item.w;
ct[item.v] = ct[cur.v];
q.push({ item.v,dist[item.v] });
}
else if (dist[cur.v] + item.w == dist[item.v]) {
ct[item.v] += ct[cur.v];
ct[item.v] %= 100003;
}
}
}
//for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// cout << dist[i] << " ";
//}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << ct[i] << endl;
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0); std::cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
【模板】全源最短路(Johnson)
题目描述
给定一个包含 n n n 个结点和 m m m 条带权边的有向图,求所有点对间的最短路径长度,一条路径的长度定义为这条路径上所有边的权值和。
注意:
边权可能为负,且图中可能存在重边和自环;
部分数据卡 n n n 轮 SPFA 算法。
输入格式
第 1 1 1 行: 2 2 2 个整数 n , m n,m n,m,表示给定有向图的结点数量和有向边数量。
接下来 m m m 行:每行 3 3 3 个整数 u , v , w u,v,w u,v,w,表示有一条权值为 w w w 的有向边从编号为 u u u 的结点连向编号为 v v v 的结点。
输出格式
若图中存在负环,输出仅一行 − 1 -1 −1。
若图中不存在负环:
输出 n n n 行:令 d i s i , j dis_{i,j} disi,j 为从 i i i 到 j j j 的最短路,在第 i i i 行输出 ∑ j = 1 n j × d i s i , j \sum\limits_{j=1}^n j\times dis_{i,j} j=1∑nj×disi,j,注意这个结果可能超过 int 存储范围。
如果不存在从 i i i 到 j j j 的路径,则 d i s i , j = 1 0 9 dis_{i,j}=10^9 disi,j=109;如果 i = j i=j i=j,则 d i s i , j = 0 dis_{i,j}=0 disi,j=0。
右图为样例 2 2 2 给出的有向图,红色标注的边构成了负环,注意给出的图不一定连通。
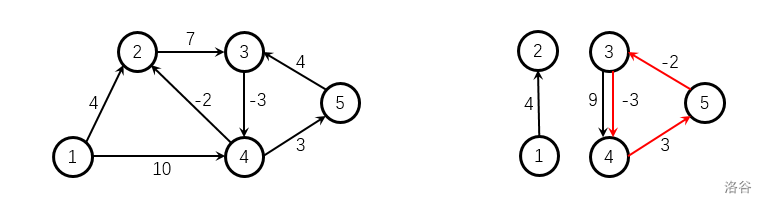
Johnson算法
- 数据溢出longlong的转换
h[item.v] = h[cur.v] + item.w;这段代码是Johnson算法的精髓,势能函数dist[j] + h[j] - h[st]由于路径上每一个边<i,j>都加入了h[i]-h[j],所以最短距离应该要 + 末位 - 首位,才是最终距离!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int n, m;
ll u,v,w;
void dijsktra(int st,vector<ll>dist);
struct Edge {
ll v, w;
Edge(ll a, ll b) :v(a), w(b) {};
};
class cmp {
public:
bool operator()(const Edge& a, const Edge& b) {
return a.w > b.w;
}
};
ll inf = ll(1e9);
queue<Edge>q;
vector<int>ct(3009, 0);
vector<list<Edge>>edges(3009, list<Edge>());
vector<ll>h(3009, inf);
vector<ll>dist(3009, inf);
priority_queue<Edge, vector<Edge>, cmp>s;
bool visited[3009];
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
while(m--) {
cin >> u >> v >> w;
edges[u].push_back({ v,w });
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
edges[0].push_back({ i,0 });
}
h[0] = 0;
q.push({ 0,0 }); ct[0] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
Edge cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if (ct[cur.v] >= n) {
cout << -1;
return;
}
for (auto item : edges[cur.v]) {
if (h[cur.v] + item.w < h[item.v]) {
h[item.v] = h[cur.v] + item.w;
ct[item.v] ++;
q.push(item);
}
}
}
/* cout << "h" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
cout << h[i]<<" ";
}
cout << endl;*/
/*重组edges数组*/
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (auto& item : edges[i]) {
item.w = item.w+h[i] - h[item.v];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dijsktra(i,dist);
}
}
void dijsktra(int st,vector<ll>dist) {
memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
dist[st] = 0; s.push({ st,0 });
while (!s.empty()) {
Edge cur = s.top();
s.pop();
if (visited[cur.v]) {
continue;
}
visited[cur.v] = true;
for (auto item : edges[cur.v]) {
if (!visited[item.v]&&dist[cur.v] + item.w < dist[item.v]) {
dist[item.v] = item.w+ dist[cur.v];
s.push({ item.v,dist[item.v] });
}
}
}
/*for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;*/
ll ans = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (dist[j] == inf) {
ans += ll(j) * dist[j];
}
else {
ans += ll(j) * (dist[j] + h[j] - h[st]);
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0); std::cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
今日总结
- dijsktra不能用于负权值
- Bellman可以用于检测负权回路
- SFPA算法不要轻易用!容易爆死!
- Floyd 算法时间复杂度O(n3),dijsktra O(mlogm),Johnson算法时间复杂度接近 O(nmlogn),相当于用SFPA扫除了dijsktra不能求负权值边的障碍,最终还是要归结于dijsktra算法堆优化版来!说人话就是Bellman和SFPA太慢,dijsktra用不了,所以采用Johnson算法!