1 不使用MVC架构模式完成银行账户转账
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<base href="${pageContext.request.scheme}://${pageContext.request.serverName}:${pageContext.request.serverPort}${pageContext.request.contextPath}/">
<title>银行账户转账</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="transfer" method="post">
转出账户:<input type="text" name="fromActno"><br>
转入账户:<input type="text" name="toActno"><br>
转账金额:<input type="text" name="money"><br>
<input type="submit" value="转账">
</form>
</body>
</html>
异常类:
package com.powernode.bank.exceptions;
/**
* App异常
* @author 老杜
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
public class AppException extends Exception{
public AppException(){}
public AppException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}package com.powernode.bank.exceptions;
/**
* 余额不足异常
* @author 老杜
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
public class MoneyNotEnoughException extends Exception{
public MoneyNotEnoughException(){}
public MoneyNotEnoughException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
servlet:
package com.powernode.bank.web.servlet;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.AppException;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 在不使用MVC架构模式的前提下,完成银行账户转账。
* 分析这个程序存在哪些问题?
* 缺点1> 代码的复用性太差。(代码的重用性太差)
* 导致缺点1的原因?
* 因为没有进行“职能分工”,没有独立组件的概念,所以没有办法进行代码复用。代码和代码之间的耦合度太高,扩展力太差。
* 缺点2> 耦合度高,导致了代码很难扩展。
* 缺点3> 操作数据库的代码和业务逻辑混杂在一起,很容易出错。编写代码的时候很容易出错,无法专注业务逻辑的编写。
*
* 分析以下AccountTransferServlet他都负责了什么?
* 1> 负责了数据接收
* 2> 负责了核心的业务处理
* 3> 负责了数据库表中数据的CRUD操作(Create【增】 Retrieve【查】 Update【改】 Delete【删】)
* 4> 负责了页面的数据展示
* ....
*
* @author 老杜
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
@WebServlet("/transfer")
public class AccountTransferServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取响应流对象
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
// 获取转账相关的信息
String fromActno = request.getParameter("fromActno");
String toActno = request.getParameter("toActno");
double money = Double.parseDouble(request.getParameter("money"));
// 编写转账的业务逻辑代码,连接数据库,进行转账操作
// 1. 转账之前要判断转出账户的余额是否充足
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
PreparedStatement ps2 = null;
PreparedStatement ps3 = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mvc";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// 开启事务(不再自动提交了,改为手动提交,业务完成之后再提交。)
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// 获取预编译的数据库操作对象
String sql1 = "select balance from t_act where actno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
ps.setString(1, fromActno);
// 执行SQL语句,返回结果集
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 处理结果集
if (rs.next()) {
double balance = rs.getDouble("balance");
if(balance < money) {
// 余额不足(使用异常处理机制。)
throw new MoneyNotEnoughException("对不起,余额不足");
}
// 程序能够执行到这里,说明余额一定是充足的
// 开始转账
// act001账户减去10000
// act002账户加上10000
String sql2 = "update t_act set balance = balance - ? where actno = ?";
ps2 = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
ps2.setDouble(1, money);
ps2.setString(2, fromActno);
int count = ps2.executeUpdate();
// 模拟异常
/*String s = null;
s.toString();*/
String sql3 = "update t_act set balance = balance + ? where actno = ?";
ps3 = conn.prepareStatement(sql3);
ps3.setDouble(1, money);
ps3.setString(2, toActno);
// 累计
count += ps3.executeUpdate();
if (count != 2) {
throw new AppException("App异常,请联系管理员");
}
// 手动提交事务
conn.commit();
// 转账成功
out.print("转账成功!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 保险起见:回滚事务。
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.rollback();
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
// 异常处理,发生异常之后,你准备怎么做
//e.printStackTrace();
out.print(e.getMessage());
} finally {
// 释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (ps2 != null) {
try {
ps2.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (ps3 != null) {
try {
ps3.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}2 MVC架构模式
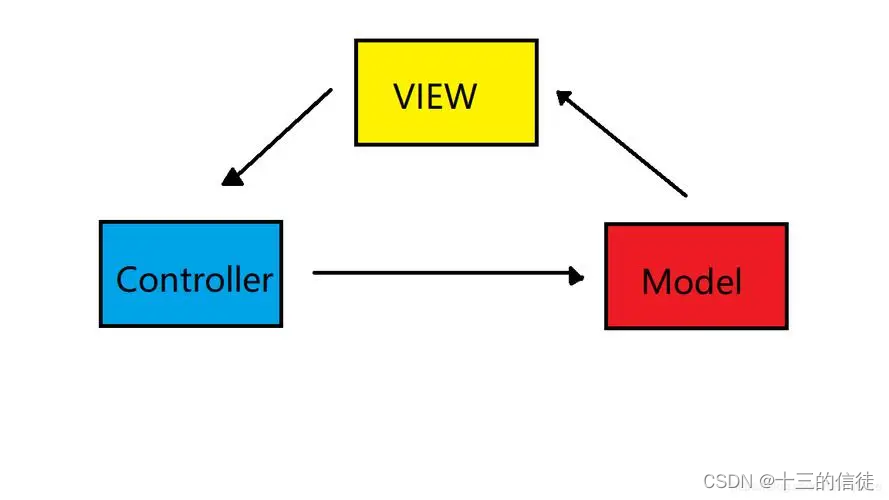
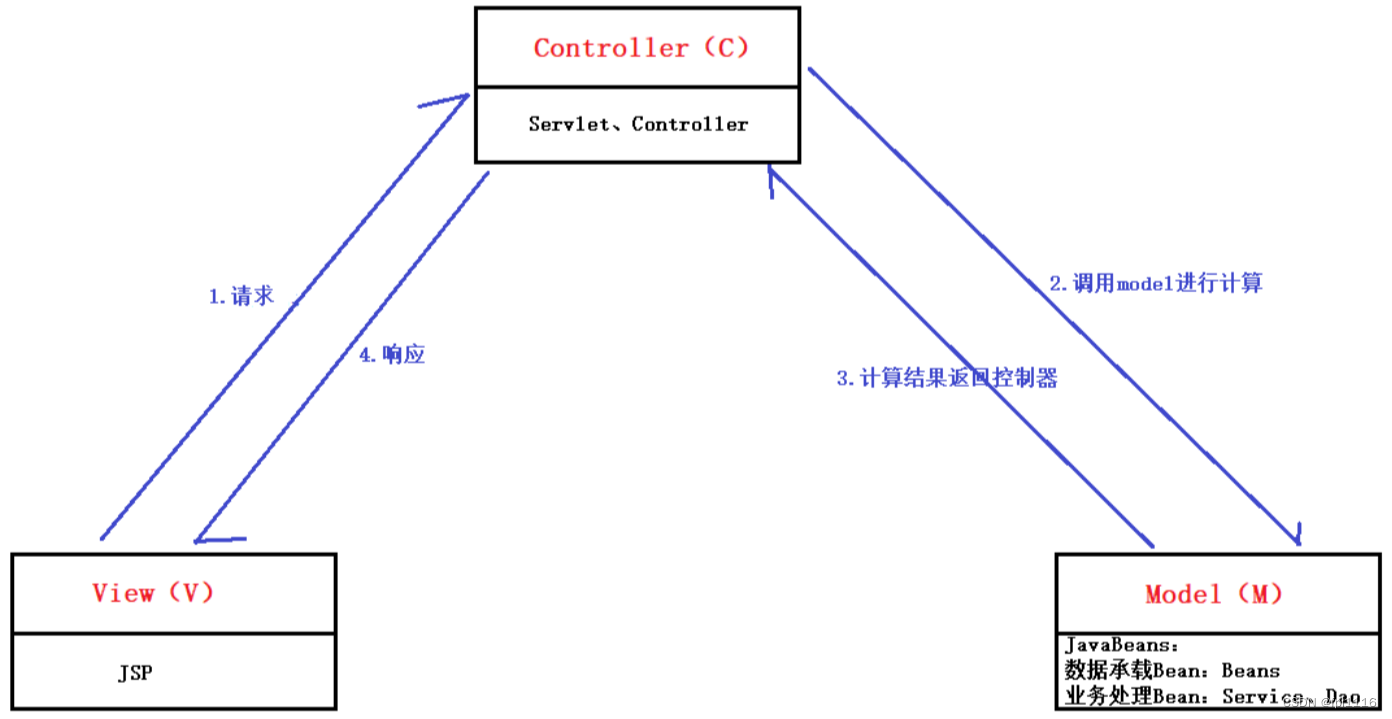
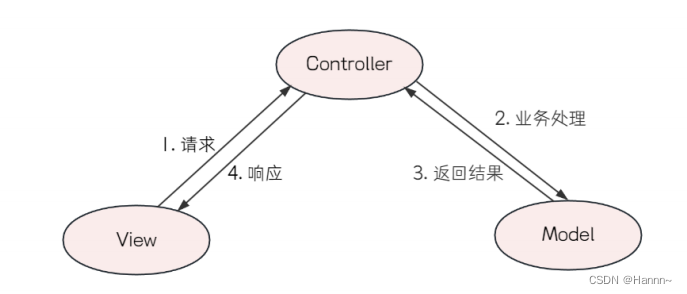
2.1 MVC架构模式的理论基础
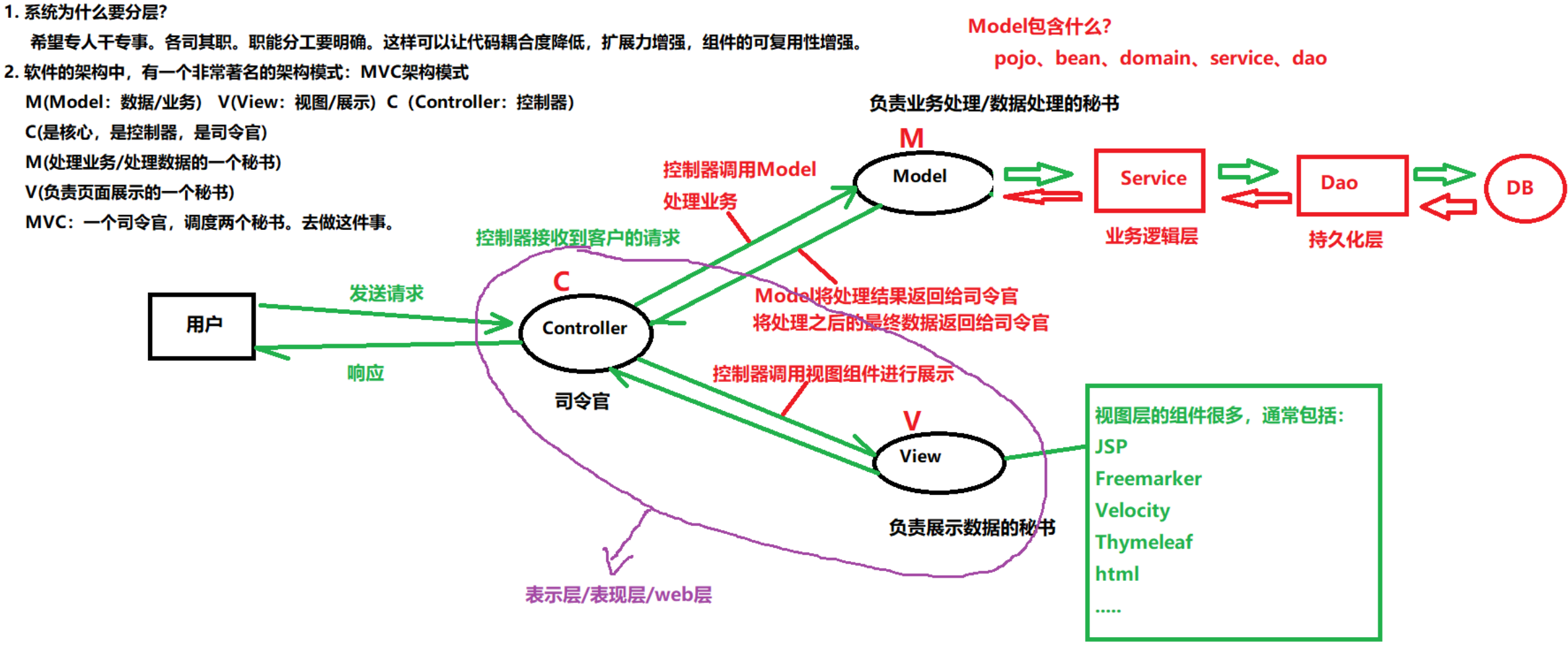
MVC架构模式的理解
2.2 JDBC工具类的封装
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mvc
user=root
password=rootpackage com.powernode.bank.utils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* JDBC工具类
* @author 老杜
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
public class DBUtil {
private static ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources/jdbc");
private static String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
private static String url = bundle.getString("url");
private static String user = bundle.getString("user");
private static String password = bundle.getString("password");
// 不让创建对象,因为工具类中的方法都是静态的。不需要创建对象。
// 为了防止创建对象,故将构造方法私有化。
private DBUtil(){}
// DBUtil类加载时注册驱动
static {
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 这里没有使用数据库连接池,直接创建连接对象。
* @return 连接对象
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return connection;
}
/**
* 关闭资源
* @param conn 连接对象
* @param stmt 数据库操作对象
* @param rs 结果集对象
*/
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs){
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}2.3 JavaEE设计模式之DAO模式以及DAO的编写
DAO:Data Access Object(数据访问对象)
package com.powernode.bank.mvc;
/**
* 账户实体类:封装账户信息的。
* 一般是一张表一个。
* pojo对象。Plain Ordinary Java Object,简单普通的Java对象
* 有的人也会把这种专门封装数据的对象,称为bean对象。(javabean:咖啡豆)
* 有的人也会把这种专门封装数据的对象,称为领域模型对象。domain对象。
* 不同的程序员有不同的习惯。
*
* pojo、bean、domain.....
*
* @author 老杜
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
public class Account { // 这种普通简单的对象被成为pojo对象。
/**
* 主键
*/
// 一般这种属性不建议设计为基本数据类型,建议使用包装类。防止null带来的问题。
//private long id;
private Long id;
/**
* 账号
*/
private String actno;
/**
* 余额
*/
//private double balance;
private Double balance;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", actno='" + actno + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getActno() {
return actno;
}
public void setActno(String actno) {
this.actno = actno;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public Account(Long id, String actno, Double balance) {
this.id = id;
this.actno = actno;
this.balance = balance;
}
public Account() {
}
}package com.powernode.bank.mvc;
import com.powernode.bank.utils.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* AccountDao是负责Account数据的增删改查的。
* 1. 什么是DAO?
* Data Access Object(数据访问对象)
* 2. DAO实际上是一种设计模式,属于JavaEE的设计模式之一。(不是23种设计模式。)
* 3. DAO只负责数据库表的CRUD,没有任何业务逻辑在里面。
* 4. 没有任何业务逻辑,只负责表中数据增删改查的对象,有一个特殊的称谓:DAO对象。
* 5. 为什么叫做AccountDao呢?
* 这是因为这个DAO是专门处理t_act这张表的。
* 如果处理t_user表的话,可以叫做:UserDao
* 如果处理t_student表的话,可以叫做:StudentDao
* 6. 一般情况下:一张表会对应一个DAO对象。
* 7. DAO中的方法名很固定了,一般都是:
* insert
* deleteByXxx
* update
* selectByXxx
* selectAll
*
*
* @author 老杜
* @since 1.0
* @version 1.0
*/
public class AccountDao {
/**
* 插入账户信息
* @param act 账户信息
* @return 1表示插入成功
*/
public int insert(Account act) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into t_act(actno, balance) values(?,?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, act.getActno());
ps.setDouble(2, act.getBalance());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 根据主键删除账户
* @param id 主键
* @return
*/
public int deleteById(Long id){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from t_act where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setLong(1, id);
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 更新账户
* @param act
* @return
*/
public int update(Account act) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "update t_act set balance = ? , actno = ? where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setDouble(1, act.getBalance());
ps.setString(2, act.getActno());
ps.setLong(3, act.getId());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 根据账号查询账户
* @param actno
* @return
*/
public Account selectByActno(String actno){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Account act = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,balance from t_act where actno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, actno);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
Long id = rs.getLong("id");
Double balance = rs.getDouble("balance");
// 将结果集封装成java对象
act = new Account();
act.setId(id);
act.setActno(actno);
act.setBalance(balance);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
return act;
}
/**
* 获取所有的账户
* @return
*/
public List<Account> selectAll() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<Account> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,actno,balance from t_act";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
// 取出数据
Long id = rs.getLong("id");
String actno = rs.getString("actno");
Double balance = rs.getDouble("balance");
// 封装对象
/*Account account = new Account();
account.setId(id);
account.setActno(actno);
account.setBalance(balance);*/
Account account = new Account(id, actno, balance);
// 加到List集合
list.add(account);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
return list;
}
}2.4 pojo bean domain的概念
POJO:Plain Ordinary Java Object(简单普通的Java对象)
有的人也会把这种专门封装数据的对象,称为bean对象。(javabean:咖啡豆)
有的人也会把这种专门封装数据的对象,称为领域模型对象。domain对象。
不同的程序员有不同的习惯。
DAO:Data Access Object(数据访问对象)
2.5 业务层抽取以及业务方法的实现
异常类:
package com.powernode.bank.exceptions;
/**
* 余额不足异常
* @author 老杜
* @version 2.0
* @since 2.0
*/
public class MoneyNotEnoughException extends Exception{
public MoneyNotEnoughException(){
}
public MoneyNotEnoughException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}package com.powernode.bank.exceptions;
/**
* App异常
* @author 老杜
* @version 2.0
* @since 2.0
*/
public class AppException extends Exception{
public AppException(){
}
public AppException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}service类:
package com.powernode.bank.mvc;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.AppException;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException;
/**
* service翻译为:业务。
* AccountService:专门处理Account业务的一个类。
* 在该类中应该编写纯业务代码。(只专注业务。不写别的。不和其他代码混合在一块。)
* 只希望专注业务,能够将业务完美实现,少量bug。
*
* 业务类一般起名:XxxService、XxxBiz.....
*
* @author 老杜
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
public class AccountService {
// 为什么定义到这里?因为在每一个业务方法中都可以需要连接数据库。
private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDao();
// 这里的方法起名,一定要体现出,你要处理的是什么业务。
// 我们要提供一个能够实现转账的业务方法(一个业务对应一个方法。)
/**
* 完成转账的业务逻辑
* @param fromActno 转出账号
* @param toActno 转入账号
* @param money 转账金额
*/
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, AppException {
// 查询余额是否充足
Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno);
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
throw new MoneyNotEnoughException("对不起,余额不足");
}
// 程序到这里说明余额充足
Account toAct = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno);
// 修改余额(只是修改了内存中java对象的余额)
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money);
// 更新数据库中的余额
int count = accountDao.update(fromAct);
// 模拟异常
String s = null;
s.toString();
count += accountDao.update(toAct);
if (count != 2) {
throw new AppException("账户转账异常!!!");
}
}
}2.6 Controller调度其他组件完成任务
package com.powernode.bank.mvc;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.AppException;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 账户小程序
* AccountServlet是一个司令官。他负责调度其他组件来完成任务。
* @author 老杜
* @version 2.0
* @since 2.0
*/
@WebServlet("/transfer")
public class AccountServlet extends HttpServlet { // AccountServlet作为Controller
private AccountService accountService = new AccountService();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 接收数据
String fromActno = request.getParameter("fromActno");
String toActno = request.getParameter("toActno");
double money = Double.parseDouble(request.getParameter("money"));
try {
// 调用业务方法处理业务(调度Model处理业务)
accountService.transfer(fromActno, toActno, money);
// 执行到这里了,说明成功了。
// 展示处理结果(调度View做页面展示)
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/success.jsp");
} catch(MoneyNotEnoughException e) {
// 执行到这里了,说明失败了。(余额不足)
// 展示处理结果(调度View做页面展示)
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/moneynotenough.jsp");
} catch(Exception e){
// 执行到这里了,说明失败了。
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/error.jsp");
}
}
}success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>转账成功</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>转账成功</h1>
</body>
</html>moneynotenough.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>转账失败</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>余额不足</h1>
</body>
</html>error.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>转账失败</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>转账失败</h1>
</body>
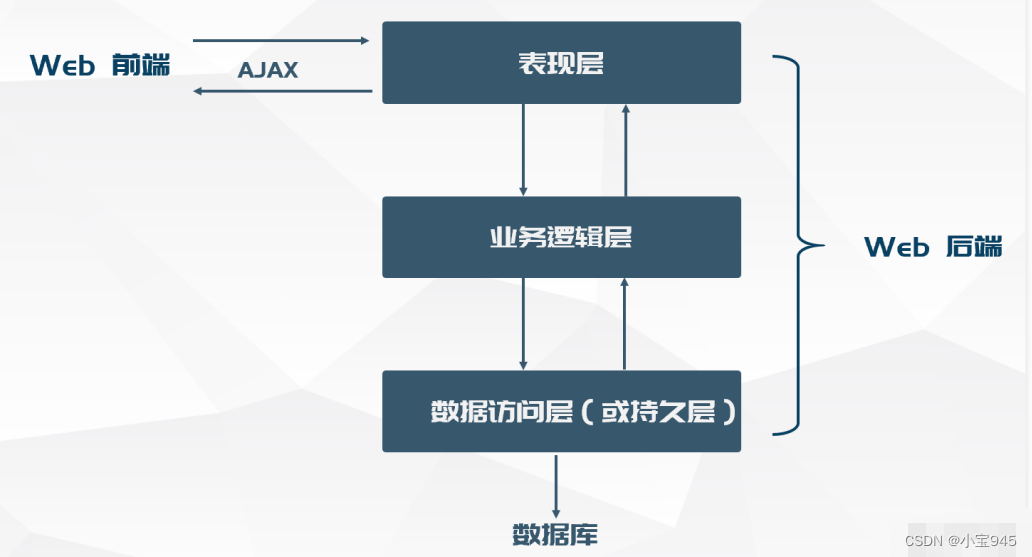
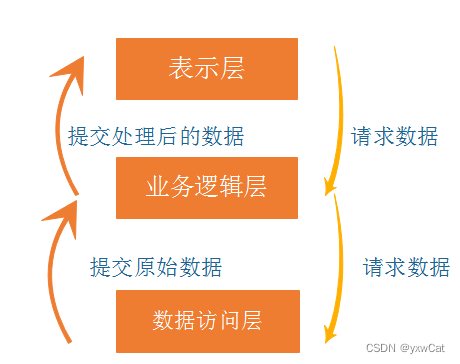
</html>2.7 MVC架构模式与三层架构的关系
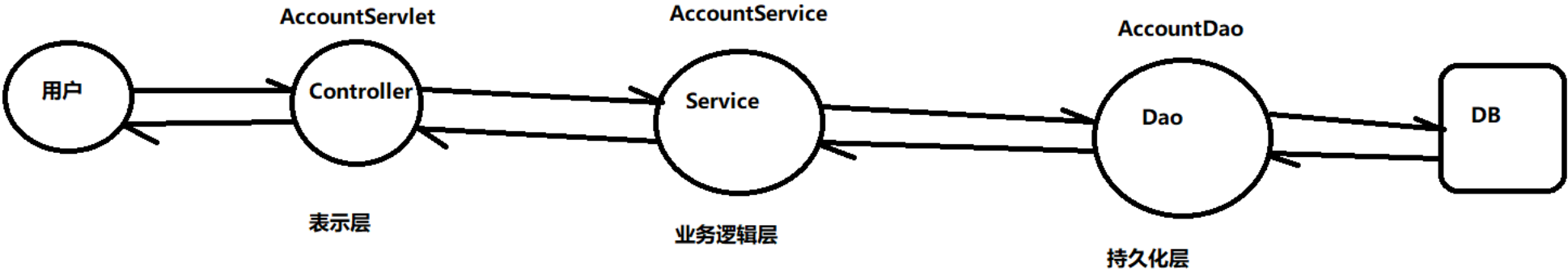
三层架构
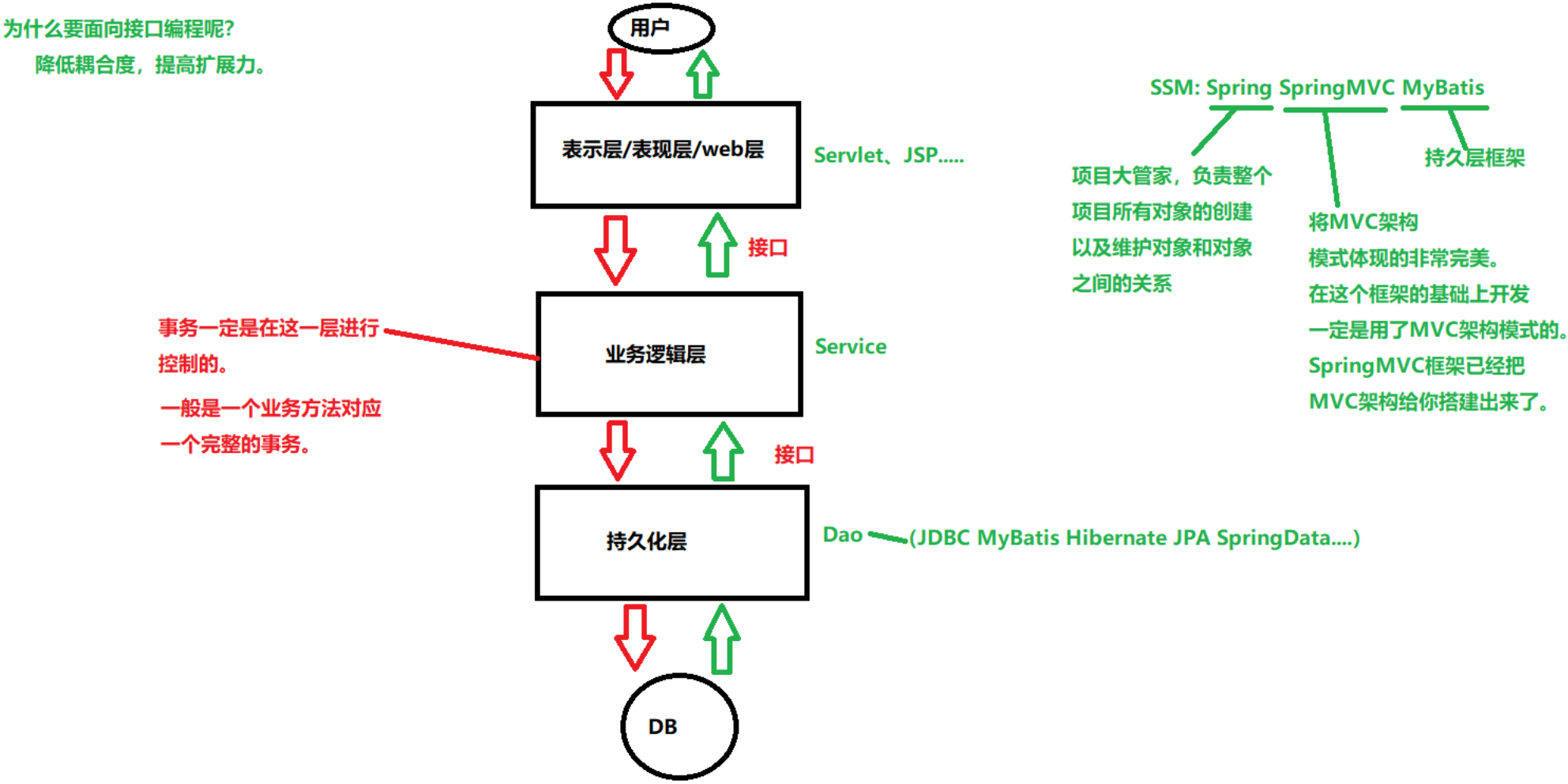
三层架构2
Spring:
项目大管家,负责整个项目所有对象的创建以及维护对象和对象之间的关系
SpringMVC:
将MVC架构模式体现的非常完美。在这个框架的基础上开发,一定是用了MVC架构模式的。SpringMVC框架已经把MVC架构给你搭建出来了。
MyBatis:
持久层框架
2.8 解决事务问题
package com.powernode.bank.mvc;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.AppException;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException;
import com.powernode.bank.utils.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* service翻译为:业务。
* AccountService:专门处理Account业务的一个类。
* 在该类中应该编写纯业务代码。(只专注业务。不写别的。不和其他代码混合在一块。)
* 只希望专注业务,能够将业务完美实现,少量bug。
*
* 业务类一般起名:XxxService、XxxBiz.....
*
* @author 老杜
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
public class AccountService {
// 为什么定义到这里?因为在每一个业务方法中都可以需要连接数据库。
private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDao();
// 这里的方法起名,一定要体现出,你要处理的是什么业务。
// 我们要提供一个能够实现转账的业务方法(一个业务对应一个方法。)
/**
* 完成转账的业务逻辑
* @param fromActno 转出账号
* @param toActno 转入账号
* @param money 转账金额
*/
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, AppException {
// service层控制事务
try (Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection()){
System.out.println(connection);
// 开启事务(需要使用Connection对象)
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
// 查询余额是否充足
Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno, connection);
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
throw new MoneyNotEnoughException("对不起,余额不足");
}
// 程序到这里说明余额充足
Account toAct = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno,connection);
// 修改余额(只是修改了内存中java对象的余额)
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money);
// 更新数据库中的余额
int count = accountDao.update(fromAct,connection);
// 模拟异常
/*String s = null;
s.toString();*/
count += accountDao.update(toAct,connection);
if (count != 2) {
throw new AppException("账户转账异常!!!");
}
// 提交事务
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new AppException("账户转账异常!!!");
}
}
}package com.powernode.bank.mvc;
import com.powernode.bank.utils.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* AccountDao是负责Account数据的增删改查的。
* 1. 什么是DAO?
* Data Access Object(数据访问对象)
* 2. DAO实际上是一种设计模式,属于JavaEE的设计模式之一。(不是23种设计模式。)
* 3. DAO只负责数据库表的CRUD,没有任何业务逻辑在里面。
* 4. 没有任何业务逻辑,只负责表中数据增删改查的对象,有一个特殊的称谓:DAO对象。
* 5. 为什么叫做AccountDao呢?
* 这是因为这个DAO是专门处理t_act这张表的。
* 如果处理t_user表的话,可以叫做:UserDao
* 如果处理t_student表的话,可以叫做:StudentDao
* 6. 一般情况下:一张表会对应一个DAO对象。
* 7. DAO中的方法名很固定了,一般都是:
* insert
* deleteByXxx
* update
* selectByXxx
* selectAll
*
*
* @author 老杜
* @since 1.0
* @version 1.0
*/
public class AccountDao {
/**
* 插入账户信息
* @param act 账户信息
* @return 1表示插入成功
*/
public int insert(Account act, Connection conn) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
String sql = "insert into t_act(actno, balance) values(?,?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, act.getActno());
ps.setDouble(2, act.getBalance());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 根据主键删除账户
* @param id 主键
* @return
*/
public int deleteById(Long id, Connection conn){
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
String sql = "delete from t_act where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setLong(1, id);
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 更新账户
* @param act
* @return
*/
public int update(Account act, Connection conn) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
System.out.println(conn);
String sql = "update t_act set balance = ? , actno = ? where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setDouble(1, act.getBalance());
ps.setString(2, act.getActno());
ps.setLong(3, act.getId());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 根据账号查询账户
* @param actno
* @return
*/
public Account selectByActno(String actno, Connection conn){
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Account act = null;
try {
System.out.println(conn);
String sql = "select id,balance from t_act where actno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, actno);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
Long id = rs.getLong("id");
Double balance = rs.getDouble("balance");
// 将结果集封装成java对象
act = new Account();
act.setId(id);
act.setActno(actno);
act.setBalance(balance);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, rs);
}
return act;
}
/**
* 获取所有的账户
* @return
*/
public List<Account> selectAll(Connection conn) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<Account> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
String sql = "select id,actno,balance from t_act";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
// 取出数据
Long id = rs.getLong("id");
String actno = rs.getString("actno");
Double balance = rs.getDouble("balance");
// 封装对象
/*Account account = new Account();
account.setId(id);
account.setActno(actno);
account.setBalance(balance);*/
Account account = new Account(id, actno, balance);
// 加到List集合
list.add(account);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, rs);
}
return list;
}
}3 ThreadLocal
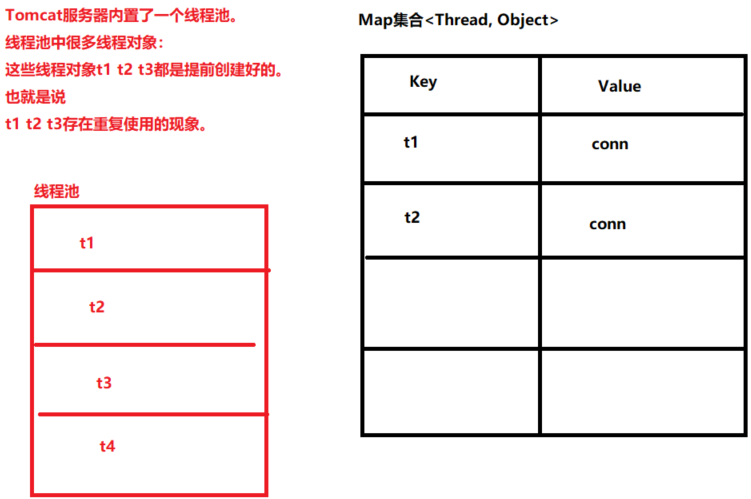
ThreadLocal
3.1 手撕ThreadLocal源码
package com.powernode.threadlocal;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 自定义一个ThreadLocal类
*/
public class MyThreadLocal<T> {
/**
* 所有需要和当前线程绑定的数据要放到这个容器当中
*/
private Map<Thread, T> map = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 向ThreadLocal中绑定数据
*/
public void set(T obj){
map.put(Thread.currentThread(), obj);
}
/**
* 从ThreadLocal中获取数据
* @return
*/
public T get(){
return map.get(Thread.currentThread());
}
/**
* 移除ThreadLocal当中的数据
*/
public void remove(){
map.remove(Thread.currentThread());
}
}package com.powernode.threadlocal;
public class Connection {
}package com.powernode.threadlocal;
public class DBUtil {
// 静态变量特点:类加载时执行,并且只执行一次。
// 全局的大Map集合
private static MyThreadLocal<Connection> local = new MyThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 每一次都调用这个方法来获取Connection对象
* @return
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection = local.get();
if (connection == null) {
// 第一次调用:getConnection()方法的时候,connection一定是空的。
// 空的就new一次。
connection = new Connection();
// 将new的Connection对象绑定到大Map集合中。
local.set(connection);
}
return connection;
}
}业务调用
package com.powernode.threadlocal;
// 张三发送请求,对应一个线程t1
// 李四发送请求,对应一个线程t2
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread);
// 调用service
UserService userService = new UserService();
userService.save();
}
}package com.powernode.threadlocal;
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
public void save(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread);
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
userDao.insert();
}
}package com.powernode.threadlocal;
public class UserDao {
public void insert(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread);
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
System.out.println("User DAO insert");
}
}3.2 项目中引入ThreadLocal
package com.powernode.bank.utils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* JDBC工具类
* @author 老杜
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
public class DBUtil {
private static ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources/jdbc");
private static String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
private static String url = bundle.getString("url");
private static String user = bundle.getString("user");
private static String password = bundle.getString("password");
// 不让创建对象,因为工具类中的方法都是静态的。不需要创建对象。
// 为了防止创建对象,故将构造方法私有化。
private DBUtil(){}
// DBUtil类加载时注册驱动
static {
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 这个对象实际上在服务器中只有一个。
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> local = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 这里没有使用数据库连接池,直接创建连接对象。
* @return 连接对象
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = local.get();
if (conn == null) {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
local.set(conn);
}
return conn;
}
/**
* 关闭资源
* @param conn 连接对象
* @param stmt 数据库操作对象
* @param rs 结果集对象
*/
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs){
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
// 思考一下:为什么conn关闭之后,这里要从大Map中移除呢?
// 根本原因是:Tomcat服务器是支持线程池的。也就是说一个人用过了t1线程,t1线程还有可能被其他用户使用。
local.remove();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}package com.powernode.bank.mvc;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.AppException;
import com.powernode.bank.exceptions.MoneyNotEnoughException;
import com.powernode.bank.utils.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* service翻译为:业务。
* AccountService:专门处理Account业务的一个类。
* 在该类中应该编写纯业务代码。(只专注业务。不写别的。不和其他代码混合在一块。)
* 只希望专注业务,能够将业务完美实现,少量bug。
*
* 业务类一般起名:XxxService、XxxBiz.....
*
* @author 老杜
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
public class AccountService {
// 为什么定义到这里?因为在每一个业务方法中都可以需要连接数据库。
private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDao();
// 这里的方法起名,一定要体现出,你要处理的是什么业务。
// 我们要提供一个能够实现转账的业务方法(一个业务对应一个方法。)
/**
* 完成转账的业务逻辑
* @param fromActno 转出账号
* @param toActno 转入账号
* @param money 转账金额
*/
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, AppException {
// service层控制事务
try (Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection()){
System.out.println(connection);
// 开启事务(需要使用Connection对象)
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
// 查询余额是否充足
Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno);
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
throw new MoneyNotEnoughException("对不起,余额不足");
}
// 程序到这里说明余额充足
Account toAct = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno);
// 修改余额(只是修改了内存中java对象的余额)
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money);
// 更新数据库中的余额
int count = accountDao.update(fromAct);
// 模拟异常
String s = null;
s.toString();
count += accountDao.update(toAct);
if (count != 2) {
throw new AppException("账户转账异常!!!");
}
// 提交事务
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new AppException("账户转账异常!!!");
}
}
}package com.powernode.bank.mvc;
import com.powernode.bank.utils.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* AccountDao是负责Account数据的增删改查的。
* 1. 什么是DAO?
* Data Access Object(数据访问对象)
* 2. DAO实际上是一种设计模式,属于JavaEE的设计模式之一。(不是23种设计模式。)
* 3. DAO只负责数据库表的CRUD,没有任何业务逻辑在里面。
* 4. 没有任何业务逻辑,只负责表中数据增删改查的对象,有一个特殊的称谓:DAO对象。
* 5. 为什么叫做AccountDao呢?
* 这是因为这个DAO是专门处理t_act这张表的。
* 如果处理t_user表的话,可以叫做:UserDao
* 如果处理t_student表的话,可以叫做:StudentDao
* 6. 一般情况下:一张表会对应一个DAO对象。
* 7. DAO中的方法名很固定了,一般都是:
* insert
* deleteByXxx
* update
* selectByXxx
* selectAll
*
*
* @author 老杜
* @since 1.0
* @version 1.0
*/
public class AccountDao {
/**
* 插入账户信息
* @param act 账户信息
* @return 1表示插入成功
*/
public int insert(Account act) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into t_act(actno, balance) values(?,?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, act.getActno());
ps.setDouble(2, act.getBalance());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 根据主键删除账户
* @param id 主键
* @return
*/
public int deleteById(Long id){
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from t_act where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setLong(1, id);
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 更新账户
* @param act
* @return
*/
public int update(Account act) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
String sql = "update t_act set balance = ? , actno = ? where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setDouble(1, act.getBalance());
ps.setString(2, act.getActno());
ps.setLong(3, act.getId());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 根据账号查询账户
* @param actno
* @return
*/
public Account selectByActno(String actno){
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Account act = null;
try {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
String sql = "select id,balance from t_act where actno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, actno);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
Long id = rs.getLong("id");
Double balance = rs.getDouble("balance");
// 将结果集封装成java对象
act = new Account();
act.setId(id);
act.setActno(actno);
act.setBalance(balance);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, rs);
}
return act;
}
/**
* 获取所有的账户
* @return
*/
public List<Account> selectAll() {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<Account> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,actno,balance from t_act";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
// 取出数据
Long id = rs.getLong("id");
String actno = rs.getString("actno");
Double balance = rs.getDouble("balance");
// 封装对象
/*Account account = new Account();
account.setId(id);
account.setActno(actno);
account.setBalance(balance);*/
Account account = new Account(id, actno, balance);
// 加到List集合
list.add(account);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null, ps, rs);
}
return list;
}
}4 项目分层
4.1 不同功能的类放在不同的包下
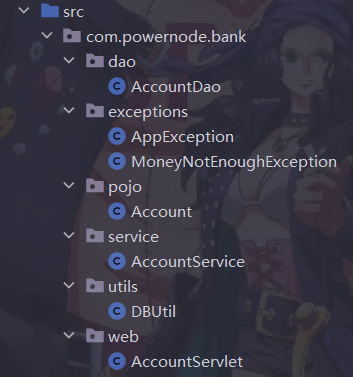
4.2 层与层之间应该使用接口进行衔接
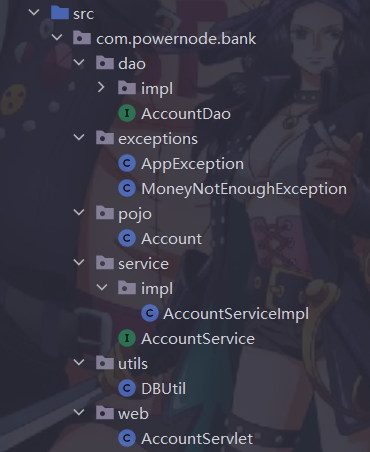
目前项目仍然存在缺陷:
1> 在service层控制了事务,service方法中的事务控制代码看着有点别扭,以后能不能不写????
可以使用动态代理机制解决这个问题。
2> 目前虽然面向接口编程了,但是并没有完全解决对象和对象之间的依赖关系。怎么办?可以使用spring的IoC容器来解决这个问题。
对象的创建我不用管了,对象和对象之间关系的管理我也不想管了,都交给spring容器来负责这件事。