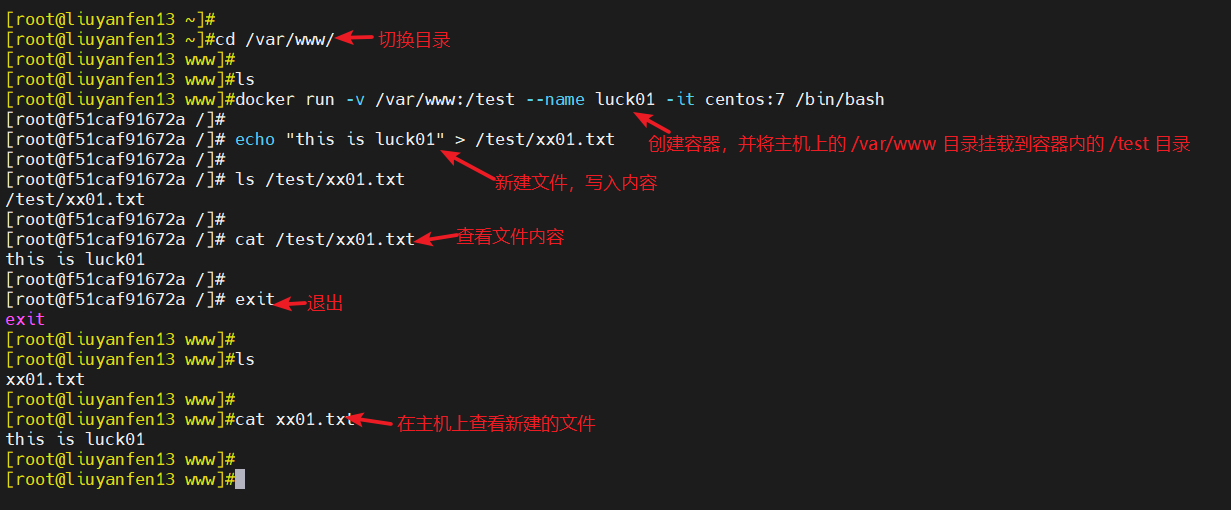
1. 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有结点
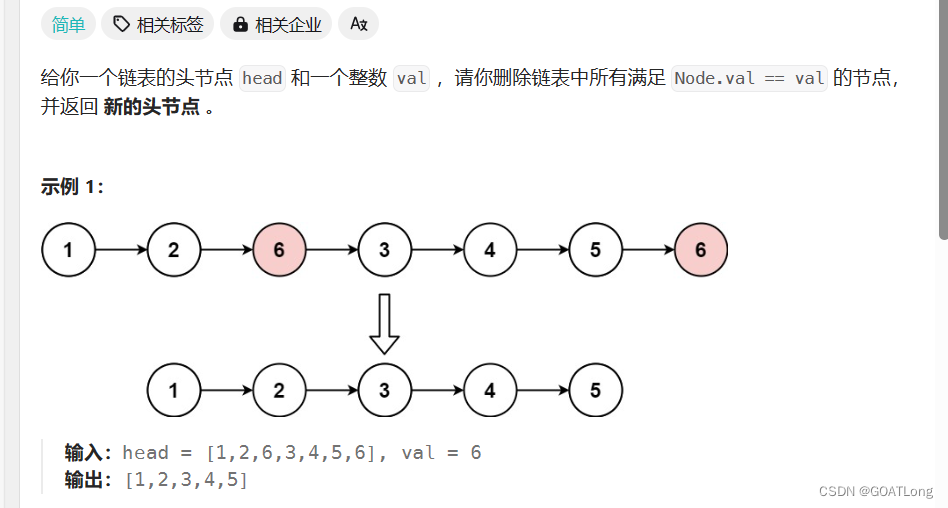
这里我们的思路就是先创建一个新链表,接着便利原链表把不是的值尾差到我们的新链表中就可以了代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode * pcur = head;
ListNode * newhead = NULL;
ListNode * newtail = NULL;
while(pcur)
{
if(pcur->val != val)
{
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = pcur;
}
else
{
newtail->next = pcur;
newtail = pcur;
}
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
if(newtail)
newtail->next = NULL;
return newhead;
}2. 反转一个单链表

这里我们需要在原链表中进行操作
我们定义三个指针如下图所示:

接下来就是改变l2指针的next指向l1之后l1指针走到l2,l2走到l3,l3走到l2的next,不断循环一直到l2为空指针这里有一个小细节如下图

当我们把最后一个节点next指针重置后此时要进行下一步时l1走到l2,l2走到l3,可当l3要移动到l2的下一个位置l2已经为空了,我们不能对空指针解引用因此我们每次在l3移动时应该加判断条件l2不能为空下面是代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode Listnode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
Listnode *l1 = NULL;
Listnode *l2 = head;
Listnode *l3 = head->next;
while(l2)
{
l2->next = l1;
l1 = l2;
l2 = l3;
if(l2!=NULL)
l3 =l2->next;
}
return l1;
}3.给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点

这里我们用了快慢指针让快指针每次走两步慢指针每次走一步也就是快指针走的路程是慢指针的两倍这样当快指针遍历完链表时直接返回慢指针此时指向的val值就可以了
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
ListNode * qfast = head;
ListNode * qslow = head;
while(qfast && qfast->next)
{
qfast = qfast->next->next;
qslow = qslow->next;
}
return qslow;
}4.输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点

思路同样是快慢指针让快指针想走k步接着两个指针同时走这样当快指针走到空指针时在返回慢指针的val就可以了
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
int kthToLast(struct ListNode* head, int k){
ListNode *fast = head,*slow = head;
while(k--)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow->val;
}5. 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有结点组成的

这里我们的思路就是先创建一个带头的新链表定义两个指针分别便利原链表然后进行比较把val值小的尾插到新链表中如果两个原链表都是空链表直接返回空如果其中一个为空则直接返回另一个链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
ListNode * newhead ,* newtail;
newhead = newtail = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
ListNode * l1 = list1;
ListNode * l2 = list2;
if(l1==NULL)
return l2;
if(l2==NULL)
return l1;
if(l1==NULL&&l2==NULL)
return NULL;
while(l1 && l2)
{
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
newtail->next = l1;
newtail = newtail->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
newtail->next = l2;
newtail = newtail->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if(l1)
newtail->next = l1;
if(l2)
newtail->next = l2;
ListNode * ret = newhead->next;
free(newhead);
newhead = NULL;
return ret;
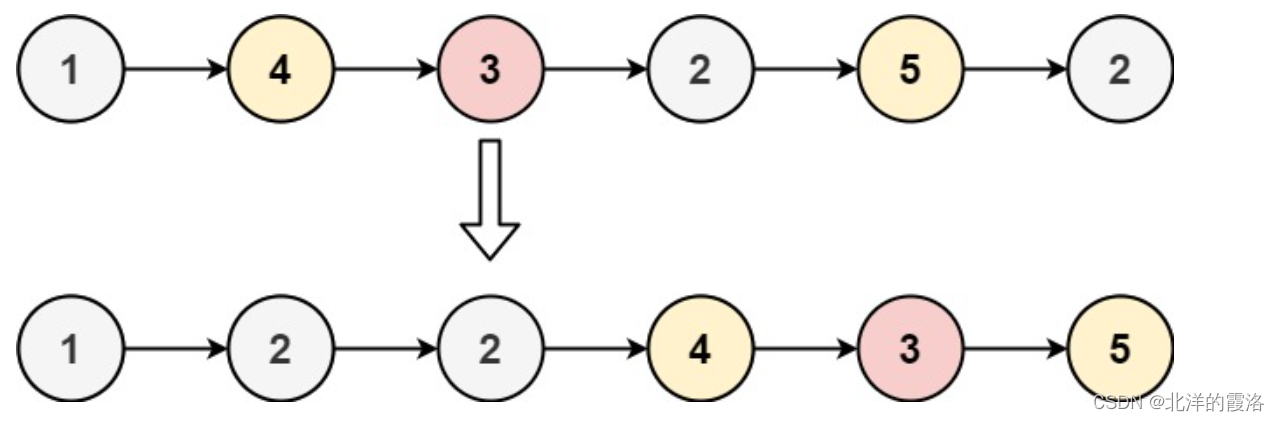
}6. 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前 。

这里我们创建两个新链表然后便利原链表把小的放在一个链表中,大的放在一个链表中最后将两个链表相连返回新链表就行。
如下图
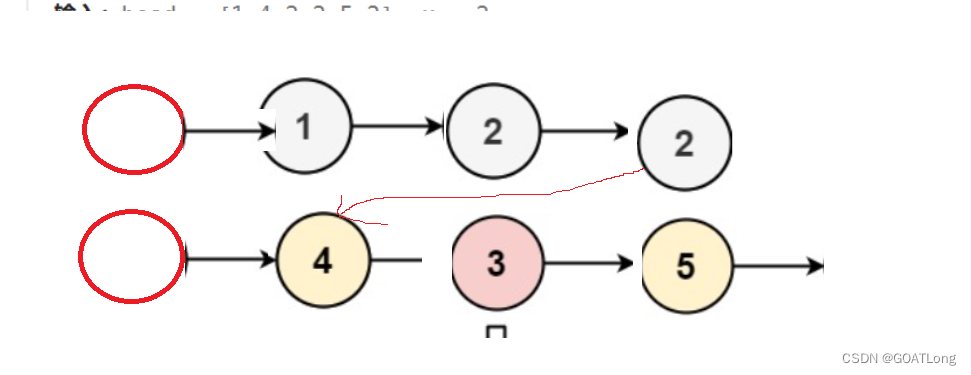
记得把存放大值的链表的尾指针的next置为空指针最后返回存放小值链表的头的next指针就可以了
最好再返回之前把哨兵位释放哈~
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x){
ListNode * newhead1 = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
ListNode * newhead2 = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newhead1->next = NULL;
newhead2->next = NULL;
ListNode * newtial1 = newhead1;
ListNode * newtial2 = newhead2;
ListNode * pcur =head;
while(pcur)
{
if(pcur->val < x)
{
newtial1->next = pcur;
newtial1 = pcur;
}else
{
newtial2->next = pcur;
newtial2 = pcur;
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
newtial1->next = newhead2->next;
newtial2->next = NULL;
ListNode * ret = newhead1->next;
free(newhead1);
free(newhead2);
newhead1 = NULL;
newhead2 = NULL;
return ret;
}7. 链表的回文结构

如下图我们先进行分析

这是偶数的分析下面是奇数

可以看到两者一致所以代码如下:
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
#include <cstddef>
class PalindromeList {
public:
//找到中间节点
ListNode * findmid(ListNode * head)
{
ListNode * pslow ,*pfast;
pslow = pfast = head;
while(pfast && pfast->next)
{
pfast = pfast->next->next;
pslow = pslow->next;
}
return pslow;
}
//逆置链表并返回新链表
ListNode * reserve(ListNode * head)
{
ListNode * l1 = NULL;
ListNode *l2 = head;
ListNode * l3 = head->next;
while(l2)
{
l2->next = l1;
l1 = l2;
l2 = l3;
if(l3!=NULL)
{
l3 = l3->next;
}
}
return l1;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
// write code here
ListNode * mid = findmid(A);
ListNode * rmid = reserve(mid);
while(A&&rmid)
{
if(A->val!=rmid->val)
{
return false;
}
A=A->next;
rmid = rmid ->next;
}
return true;
}
};8. 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点

判断链表是否相交我们直接看最后一个节点是否相等就行了
找相交链表我们就可以定义两个指针让他们从离交点相同的位置开始走一直到走到交点停止
如何找到刚开始指针出发的位置呢?
如下所示

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
//先找到尾部节点
ListNode *pcura = headA;
ListNode *pcurb = headB;
int lena =1;
int lenb =1;
while(pcura->next)
{
pcura = pcura->next;
lena++;
}
while(pcurb->next)
{
pcurb = pcurb->next;
lenb++;
}
if(pcura!=pcurb)
{
return NULL;
}
else
{
int ret = abs(lena-lenb);
ListNode *longlist = headA,*shortlist = headB;
if(lena<lenb)
{
longlist = headB;
shortlist = headA;
}
while(ret--)
{
longlist = longlist->next;
}
while(longlist != shortlist)
{
longlist = longlist->next;
shortlist = shortlist->next;
}
return longlist;
}
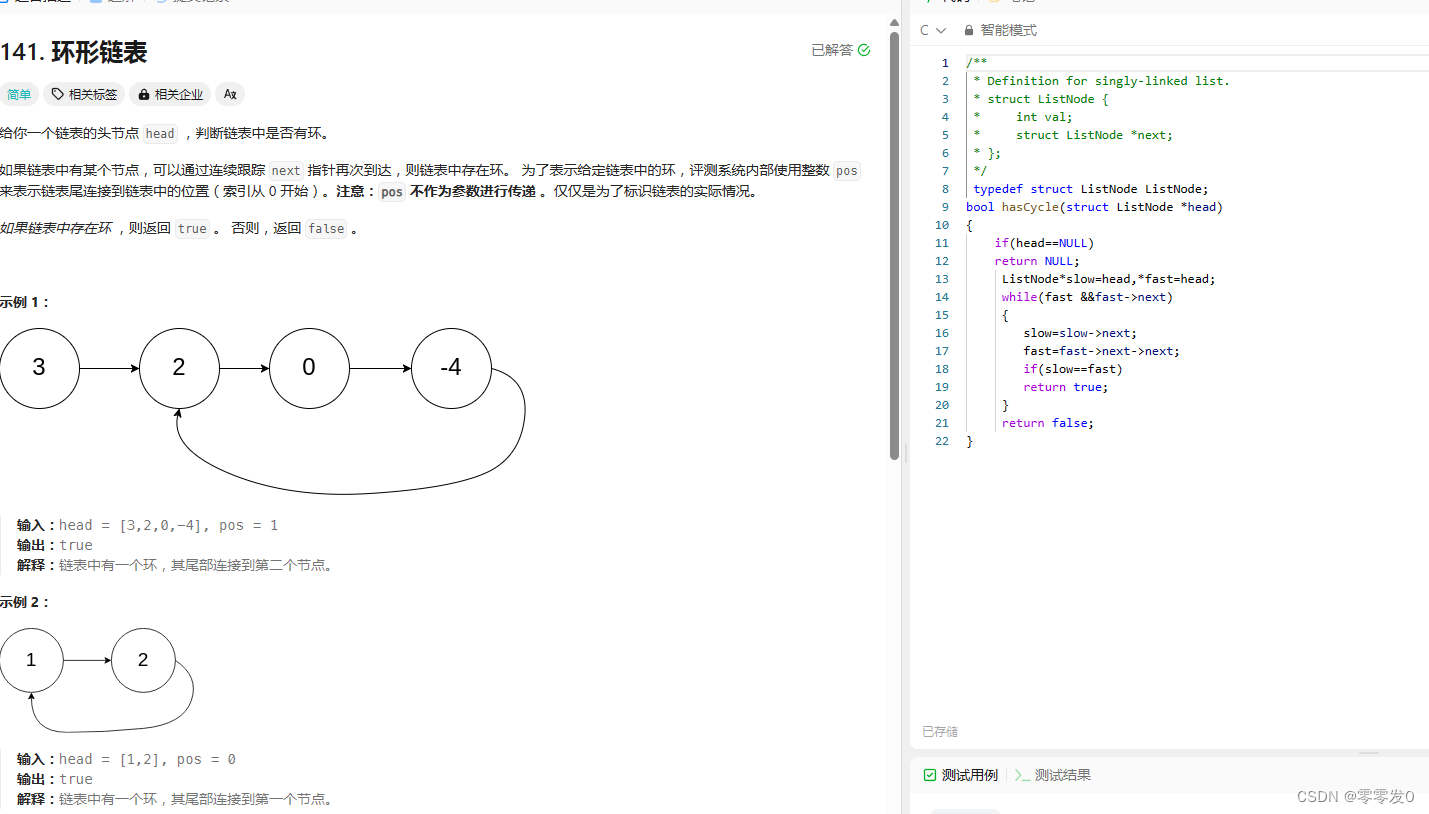
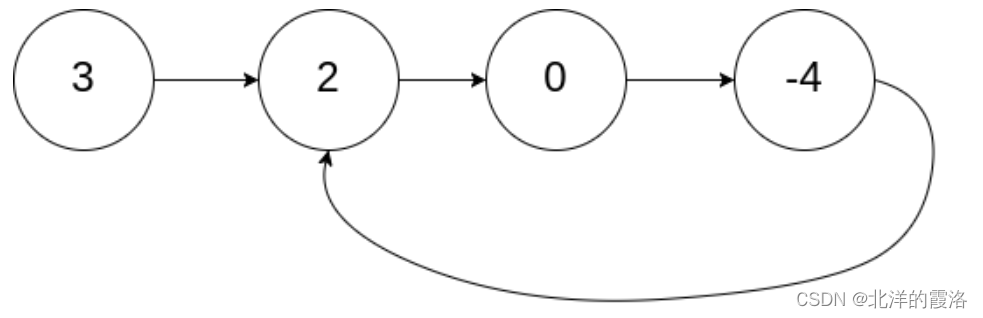
}9. 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环

下面是思路分析

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
ListNode * pslow = head,* pfast = head;
while(pfast && pfast->next)
{
pslow = pslow ->next;
pfast = pfast->next->next;
if(pfast == pslow)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}9.1 环形链表2

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
ListNode * pfast = head,*pslow = head;
while(pfast && pfast->next)
{
pfast = pfast->next->next;
pslow = pslow->next;
if(pfast==pslow)
{
ListNode * meet = pfast;
while(head != meet)
{
head = head->next;
meet = meet->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;
}9.2链表的扩展
【扩展问题】
为什么快指针每次走两步,慢指针走一步可以?
假设链表带环,两个指针最后都会进入环,快指针先进环,慢指针后进环。当慢指针刚进环时,可
能就和快指针相遇了,最差情况下两个指针之间的距离刚好就是环的长度。此时,两个指针每移动
一次,之间的距离就缩小一步,不会出现每次刚好是套圈的情况,因此:在满指针走到一圈之前,
快指针肯定是可以追上慢指针的,即相遇。
快指针一次走 3 步,走 4 步, ...n 步行吗?

11. 给定一个链表,每个结点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何结点或空结点。 要求返回这个链表的深度拷贝

/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
typedef struct Node Node;
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
Node * pcur = head;
while(pcur)
{
Node * copy = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
copy->val = pcur->val;
copy->next = pcur->next;
pcur ->next = copy;
pcur = copy->next;
}
//处理random指针
pcur = head;
while(pcur)
{
Node * copy = pcur->next;
if(pcur->random==NULL)
{
copy->random = NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random = pcur->random->next;
}
pcur = copy->next;
}
Node * newhead = NULL,*newtail = NULL;
pcur = head;
while(pcur)
{
Node * copy = pcur->next;
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = copy;
}
else
{
newtail ->next = copy;
newtail = copy;
}
pcur->next = copy->next;
pcur = copy->next;
}
return newhead;
}关于链表的知识我们就分享到这里
































![[随记]Mac安装Docker及运行开源Penpot](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/bb487d2e7fab40a480bb0f311d8c76e0.png)