47. Permutations II
Given a collection of numbers, nums, that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations in any order.
Example 1:
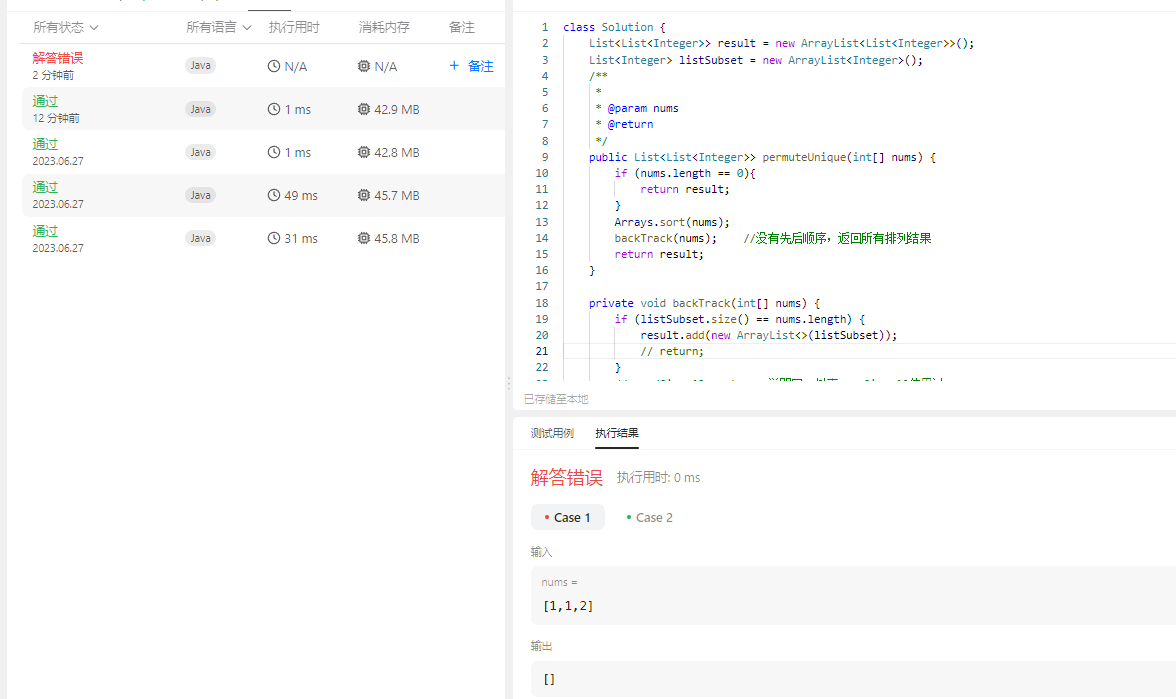
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output:
[[1,1,2],
[1,2,1],
[2,1,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 8
- -10 <= nums[i] <= 10
From: LeetCode
Link: 47. Permutations II
Solution:
Ideas:
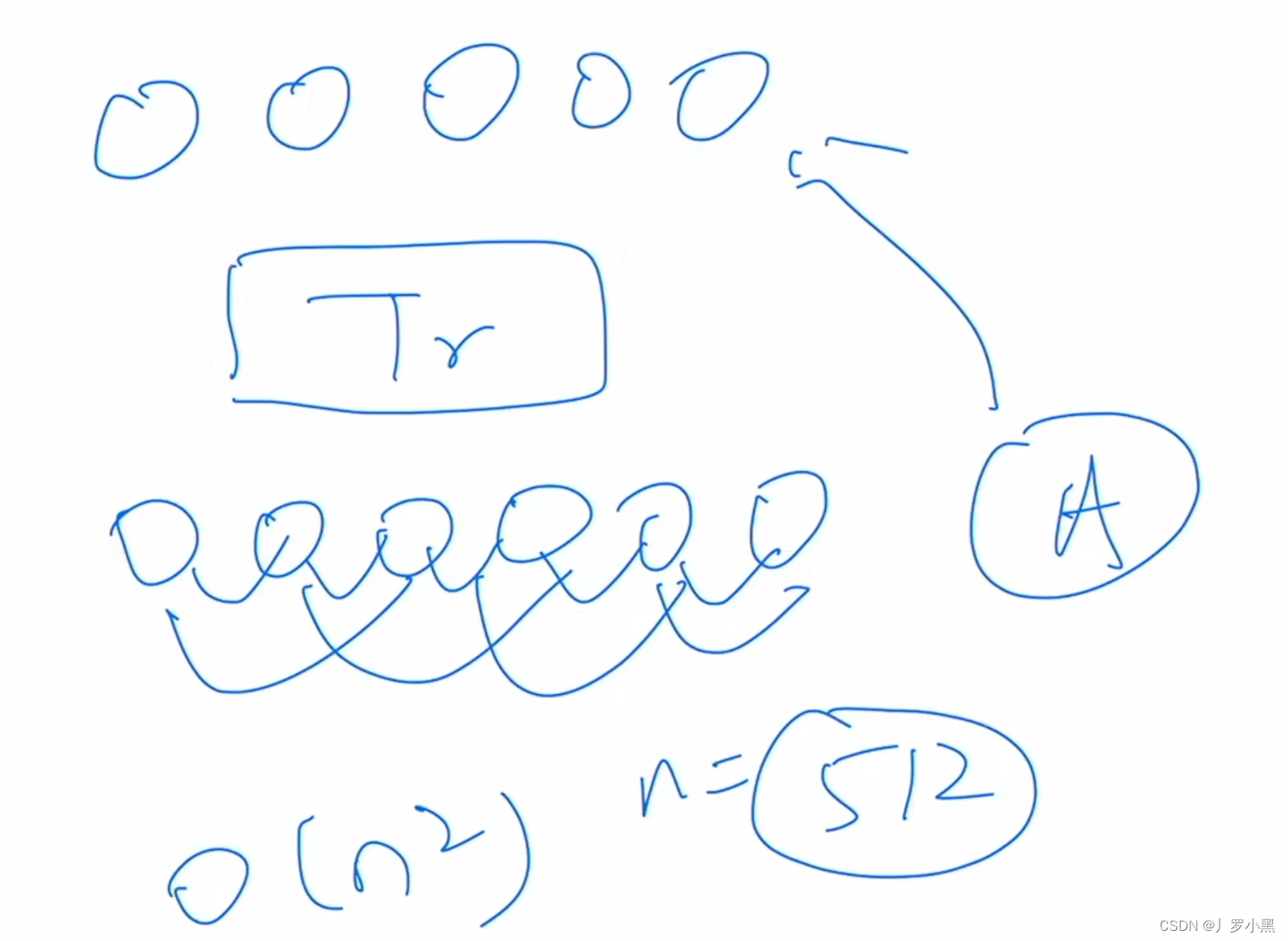
1. Sorting the Array: The function starts by sorting the array. This step is crucial because it brings duplicates together, which simplifies the process of skipping over duplicate numbers when generating permutations.
2. Backtracking Algorithm: The core of the function is a backtracking algorithm. Backtracking is a recursive technique for solving problems by trying to build a solution incrementally, one piece at a time, removing those solutions that fail to satisfy the constraints of the problem as the solution is developed.
3. Using a ‘Used’ Array: To manage and control which elements have already been included in the current permutation path, a boolean array named used is employed. This array tracks whether an element has been included in the current permutation. If an element is marked as used, it is skipped in the current recursive call.
4. Skipping Duplicates: To ensure that no duplicate permutations are generated, the function checks if the current element is the same as the one before it and whether the previous element has not been used in the current permutation path. If both conditions are true, the function skips the current element. This check is effective only because the array is sorted, ensuring that duplicates are adjacent.
5. Recursive Function Calls: The function recursively calls itself to explore all possible paths of permutations by swapping elements. After each recursive call, it backtracks by marking the current element as unused, allowing it to be included in other permutations.
6. Memory Management: Dynamic memory allocation is used to store the results. The function allocates memory for each permutation and a corresponding array that holds the size of each permutation. This memory management is crucial for returning the results to the caller, who is responsible for freeing the allocated memory.
7. Complexity Considerations: The function handles up to 8 elements, reflecting the constraint that permutations can grow factorially with the number of elements. Memory and processing needs are managed to handle this maximum efficiently.
Code:
void backtrack(int* nums, int numsSize, int level, int** results, int* resultSize, int* currentPermutation, bool* used, int** returnColumnSizes) {
if (level == numsSize) {
results[*resultSize] = (int*)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(int));
memcpy(results[*resultSize], currentPermutation, numsSize * sizeof(int));
(*returnColumnSizes)[*resultSize] = numsSize;
(*resultSize)++;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {
if (used[i]) continue;
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) continue;
used[i] = true;
currentPermutation[level] = nums[i];
backtrack(nums, numsSize, level + 1, results, resultSize, currentPermutation, used, returnColumnSizes);
used[i] = false;
}
}
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
return (*(int*)a - *(int*)b);
}
int** permuteUnique(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) {
qsort(nums, numsSize, sizeof(int), compare);
int** results = (int**)malloc(40320 * sizeof(int*)); // Max 8! permutations
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(40320 * sizeof(int));
*returnSize = 0;
int* currentPermutation = (int*)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(int));
bool* used = (bool*)calloc(numsSize, sizeof(bool));
backtrack(nums, numsSize, 0, results, returnSize, currentPermutation, used, returnColumnSizes);
free(currentPermutation);
free(used);
return results;
}























![[PTA] [C数据结构] 链表分段逆转 共享后缀的链表](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/fc466573d9fc43bf84bc7269c773204a.png)