目录
2.2.8 Insertfront()在指定位置之前插入元素
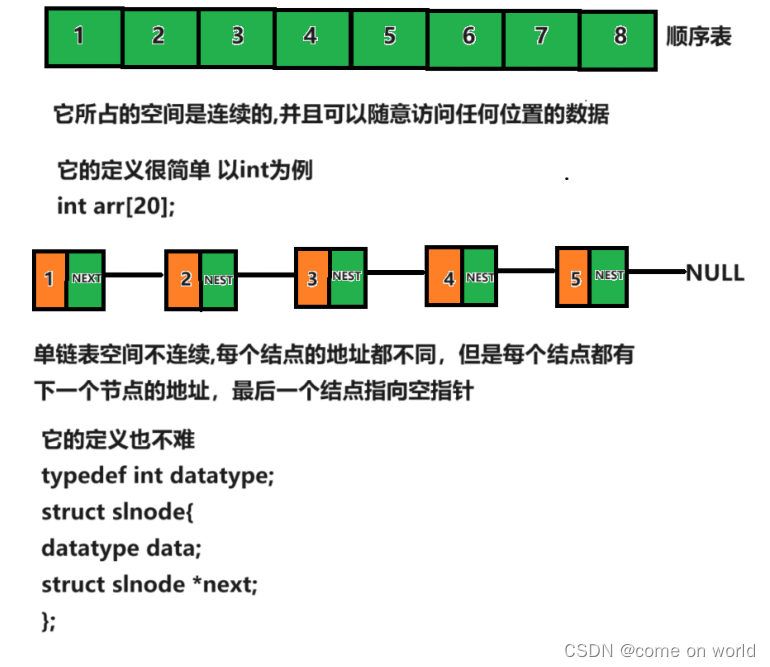
1.单链表的概念及结构
1.1 概念
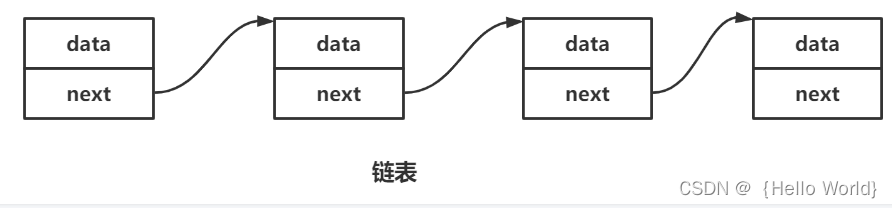
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续,非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的(指针就相当于链条,把每一个数据串了起来)。
与顺序表不同的是,链表里的每个节点都是独立申请来的空间,一般称为结点,结点的组成有两部分,当前结点要保存的数据和下一结点的地址。
data就是数据域
next就是指针域
2.单链表的实现
采用头文件与执行文件分离的方法:
2.1 List.h
源码:
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int Datatype;
struct List
{
Datatype data;
struct List* next;
};
typedef struct List List;
void init(List** ls);
List* Newnode(Datatype x);//生成节点
void print(List* ls);//打印
void Pushfront(List** sl, Datatype x);
void Pushback(List** sl, Datatype x);
void Popfront(List** sl);
void Popback(List** sl);
List* Find(List* sl, Datatype x);
void Insertfront(List** sl, List* pos, Datatype x);//指定位置之前
void Insertback(List** sl, List* pos, Datatype x);//指定位置之后
void Erasepos(List** sl, List* pos);//删除指定位置
void Eraseposback(List** sl, List* pos);//删除pos之后的
void Destory(List** sl);
void menu();
(1).在自定义头文件中存放单链表所需的头文件,定义结构体,以及函数的声明。
(2).在结构体中,Datatype data 为数据域, struct List* next 为指针域
2.2 List.cpp
源码
#include"List.h"
void init(List** sl)
{
(*sl)->next = NULL;
(*sl)->data = 0;
}
void menu()
{
printf("********************************\n");
printf("***1.Pushfront 2.Pushback***\n");
printf("***3.Popfront 4.Popback***\n");
printf("***5.Insertfront 6.Insertback***\n");
printf("***7.Erasepos 8.Eraseposback***\n");
printf("***9.Destory 10.print***\n");
printf("*********** 0.exit *************\n");
printf("********************************\n");
}
List* Newnode(Datatype x)//生成节点
{
List* node = (List*)malloc(sizeof(List));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc is failed\n");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
void print(List* ls)//打印
{
if (ls == NULL)
{
printf("ls is NULL\n");
return;
}
List* cur = ls;
while (cur)
{
cout << cur->data << ' ';
cur = cur->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
void Pushfront(List** sl, Datatype x)
{
if (sl == NULL)
{
printf("sl is NULL\n");
return;
}
List* node = Newnode(x);
node->next = (*sl);
(*sl) = node;
}
void Pushback(List** sl, Datatype x)
{
List* node = Newnode(x);
if (sl == NULL)
{
printf("sl is NULL\n");
return;
}
if ((*sl) == NULL)
{
(*sl) = node;
return;
}
List* cur = (*sl);
while (cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = node;
}
void Popfront(List** sl)
{
if (sl == NULL || (*sl) == NULL)
{
printf("ls is empty!\n");
return;
}
List* cur = (*sl)->next;
//free(*sl);
(*sl) = cur;
}
void Popback(List** sl)
{
if (sl == NULL || (*sl) == NULL)
{
printf("ls is empty!\n");
return;
}
List* pre = NULL; List* cur = (*sl);
if ((*sl)->next == NULL)
{
free(*sl);
*sl = NULL;
}
else
{
while (cur->next)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
pre->next = NULL;
}
}
List* Find(List* sl, Datatype x)
{
List* cur = sl;
while (cur && cur->data != x)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur == NULL)
{
printf("not have x\n");
return NULL;
}
return cur;
}
void Insertfront(List** sl, List* pos, Datatype x)//指定位置之前
{
if (sl == NULL)
{
printf("sl is NULL\n");
return;
}
List* node = Newnode(x);
List* pre = NULL;
List* cur = (*sl);
if (pos == *sl)
{
Pushfront(sl, x);
}
else
{
while (cur != pos)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
pre->next = node;
node->next = pos;
}
}
void Insertback(List** sl, List* pos, Datatype x)//指定位置之后
{
if (sl == NULL)
{
printf("sl is NULL\n");
return;
}
List* node = Newnode(x);
List* cur = (*sl);
while (cur != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
node->next = pos->next;
pos->next = node;
}
void Erasepos(List** sl, List* pos)//删除指定位置
{
if (sl == NULL)
{
printf("sl is NULL\n");
return;
}
if ((*sl) == NULL)
{
printf("sl is empty\n");
return;
}
List* cur = (*sl);
if (pos == *sl)
{
Popfront(sl);
}
else
{
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
}
void Eraseposback(List** sl, List* pos)//删除pos之后的
{
if (sl == NULL)
{
printf("sl is NULL\n");
return;
}
if ((*sl) == NULL)
{
printf("sl is empty\n");
return;
}
if (pos->next)
{
List* pre = pos->next;
pos->next = pos->next->next;
free(pre);
pre = NULL;
}
}
void Destory(List** sl)
{
if (sl == NULL)
{
printf("sl is destory\n");
return;
}
List* cur = *sl;
List* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
cur = NULL;
next = NULL;
*sl = NULL;
}
2.2.1 init()初始化函数
void init(List** sl)
{
(*sl)->next = NULL;
(*sl)->data = 0;
}(1).将最初的头结点初始化,把最初的头结点中next指针置为NULL,并把值赋值为0。
2.2.2 Newnode()创建新结点
List* Newnode(Datatype x)//生成节点
{
List* node = (List*)malloc(sizeof(List));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc is failed\n");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}(1).由于要创建新结点,所以要返回创建的新结点,函数返回值为List* 。
(2).函数只需要传递结点中要存放的值即可。
(3).使用malloc()函数来申请空间,申请完成后要判断是否申请成功。
(4).将新结点的数据域赋值为x,指针域赋为NULL。
(5).最后返回新结点。
2.2.3 Pushfront()头插函数
void Pushfront(List** head, Datatype x)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("head is NULL\n");
return;
}
List* newnode= Newnode(x);
newnode->next = (*head);
(*head) = newnode;
}
(1).首先判断头节点是否为空指针。
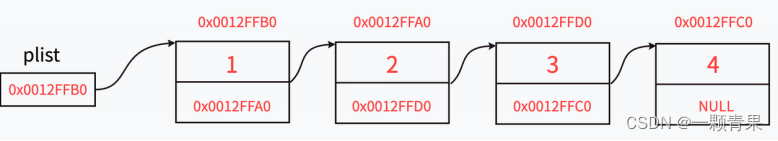
(2).头插,就是要创建一个新结点,然后拼接到链表前方,所以,定义一个结构体指针变量,用来存储创建的新结点,然后先把新结点的下一指针指向头节点,再让头节点指向新结点,这样就使得头节点再次成为最前面的结点了。
(3).图文解释:
newnode->next = (*head);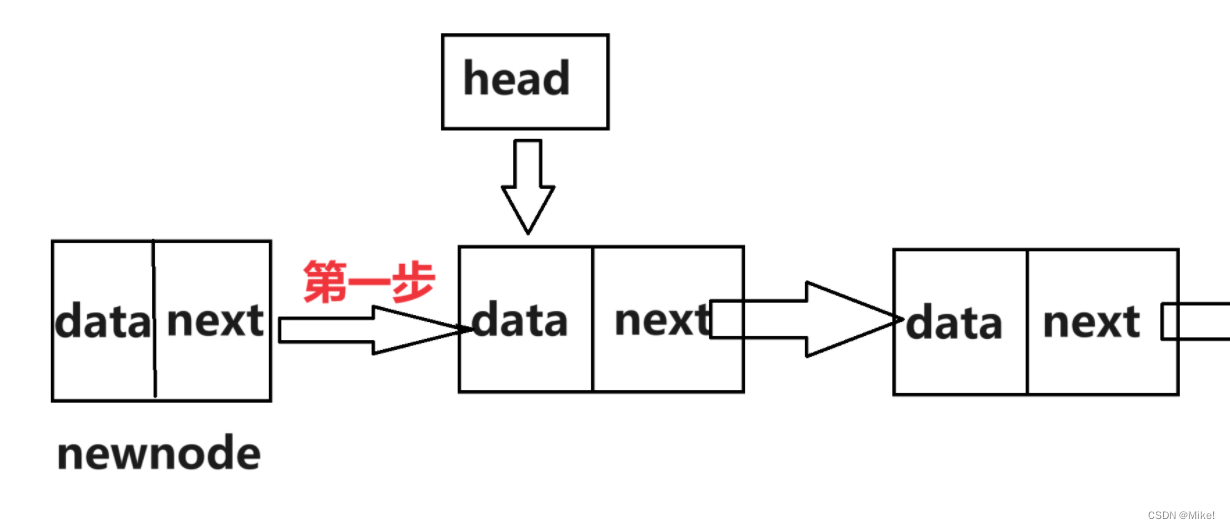
(*head) = newnode;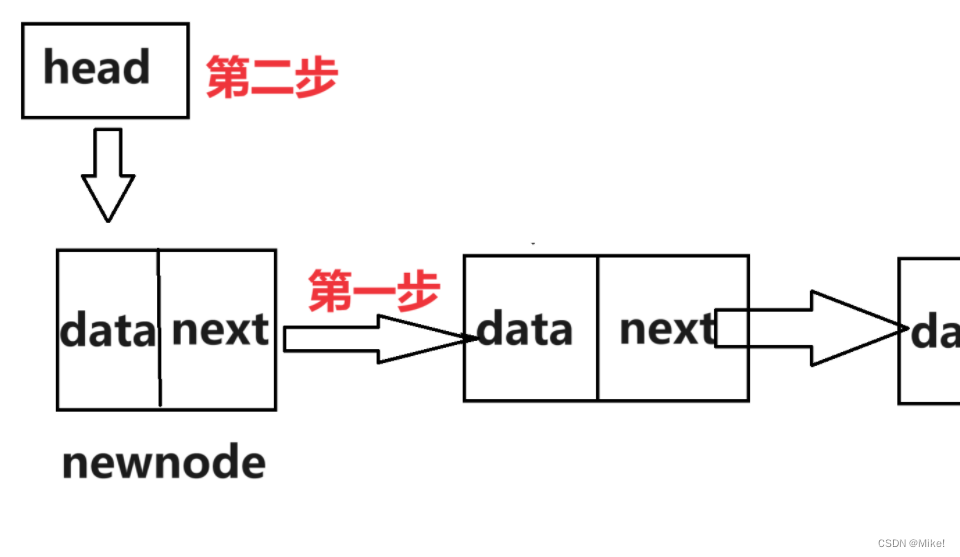
2.2.4 Pushback()尾插函数
void Pushback(List** head, Datatype x)
{
List* newnode= Newnode(x);
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("head is NULL\n");
return;
}
if ((*head) == NULL)
{
(*head) = newnode;
return;
}
List* cur = (*head);
while (cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newnode;
}
(1).首先判断头节点是否为空指针。
(2).在判断链表是否为空,若边表为空,则直接将头指针赋值为新结点。
(3).若链表不为空,则新定义一个结构体指针cur,使cur指向头节点,从链表初始位置遍历到链表最后一个位置,即cur->next==NULL时。cur到达最后一个结点后,使最后一个结点的next指向新创建的结点。
当链表尾空时,只有一个头指针。

(*head) = newnode;
while (cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newnode;

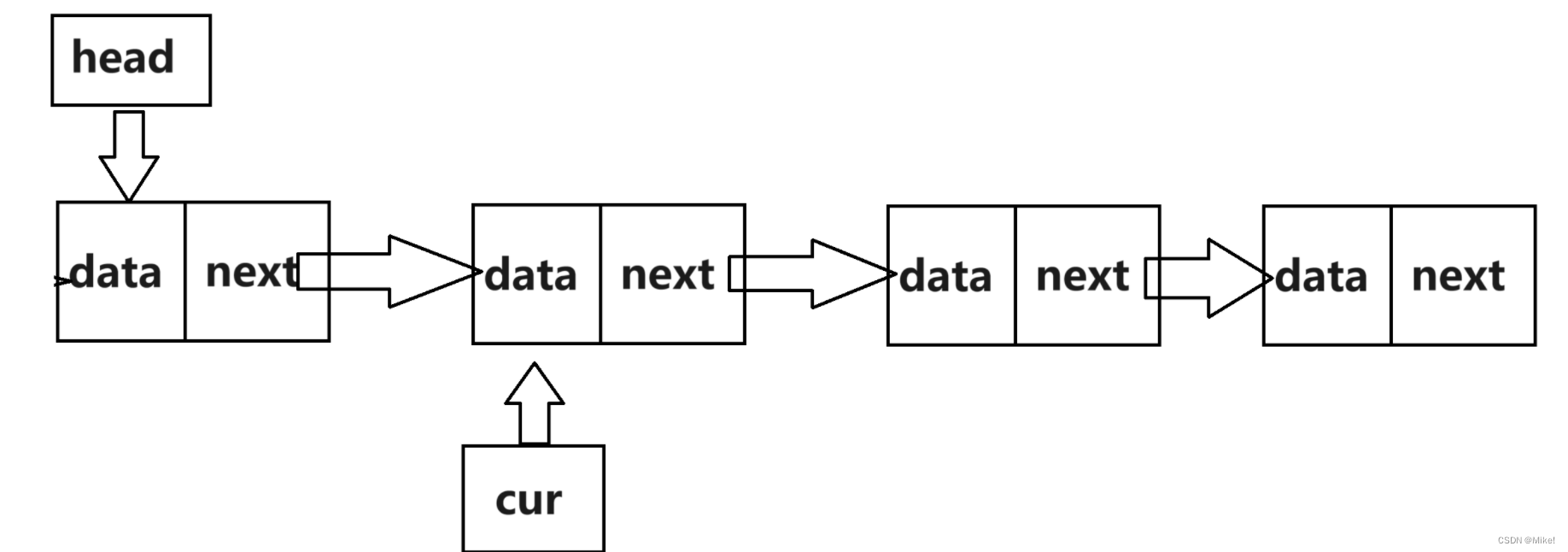

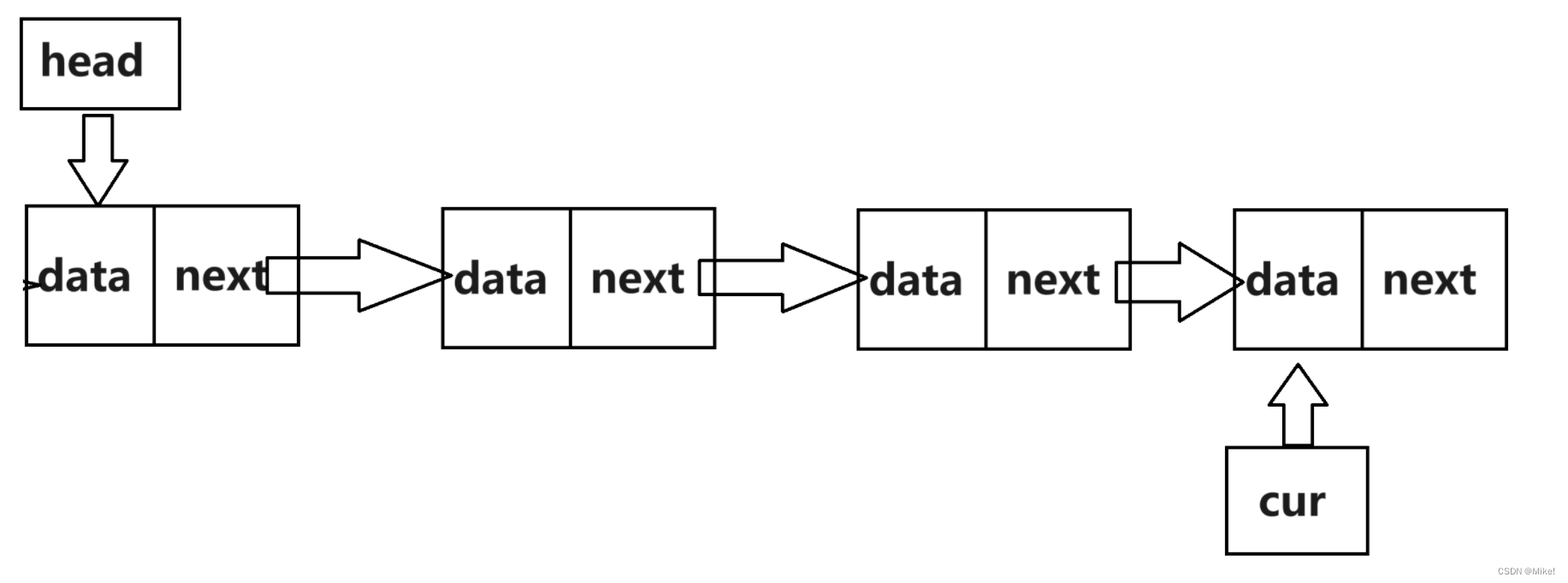 此时,cur->next==NULL成立,退出循环。
此时,cur->next==NULL成立,退出循环。
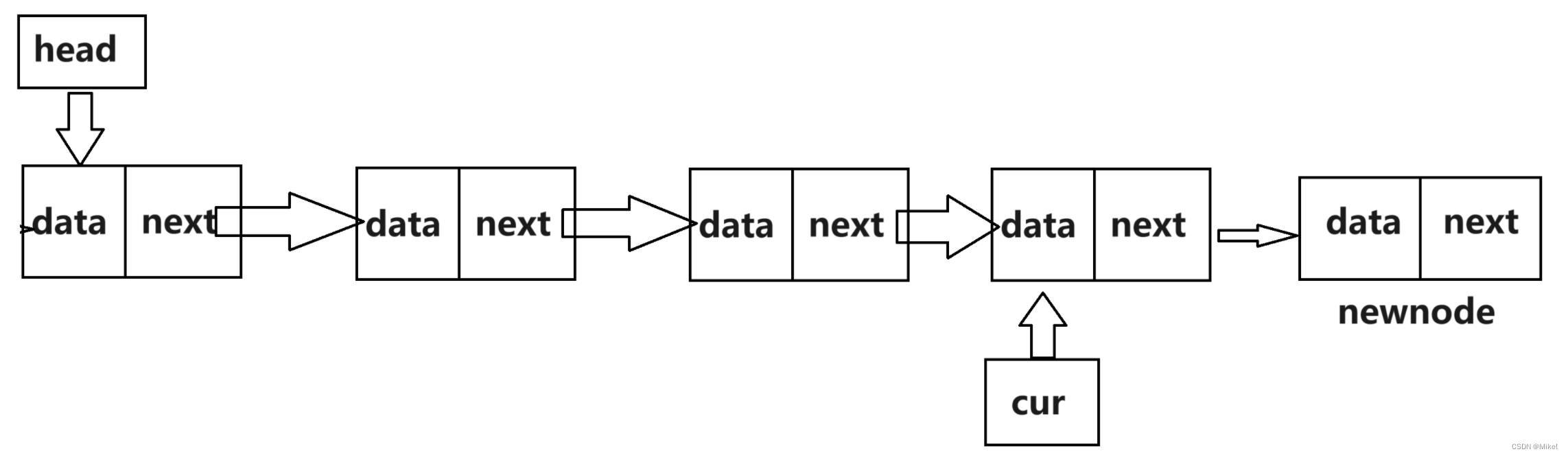
2.2.5 Popfront()头删函数
void Popfront(List** head)
{
if (head == NULL || (*head) == NULL)
{
printf("ls is empty!\n");
return;
}
List* cur = (*head)->next;
free(*head);
(*head) = cur;
}(1).新定义一个结构体指针cur,使cur指向头结点的下一个结点。
(2).再把现在的头节点释放。
(3).再使得头节点指向cur。
图文:
第一步:
List* cur = (*head)->next;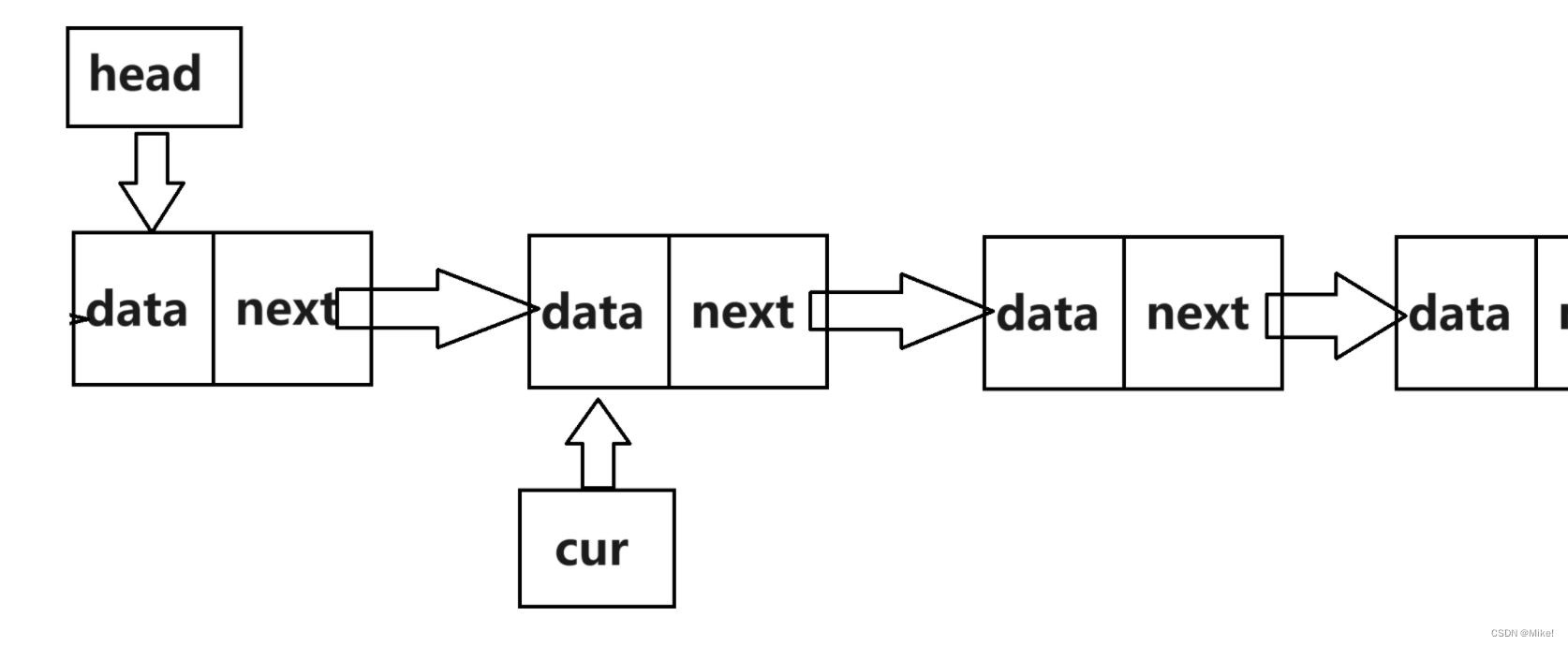
第二步:
free(*head);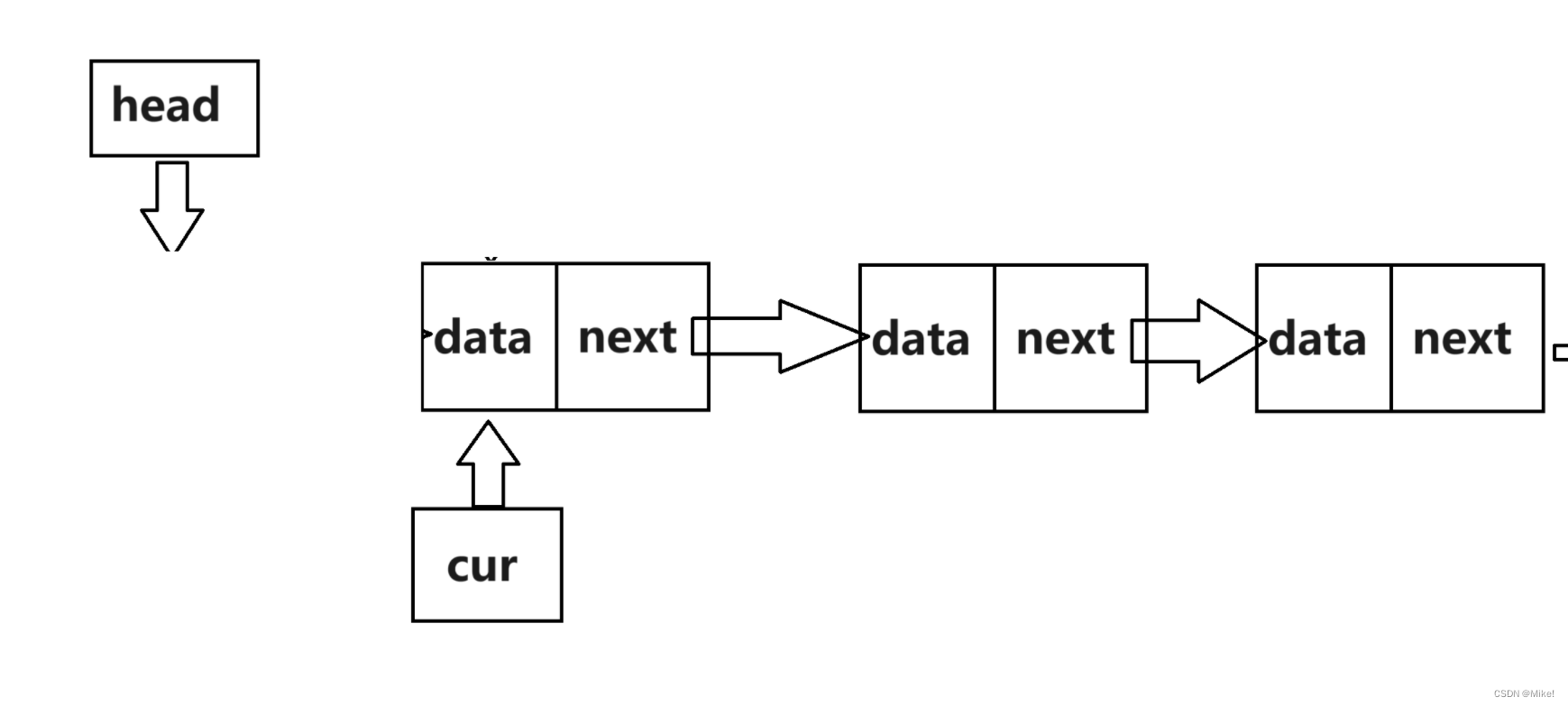
第三步:
(*head) = cur;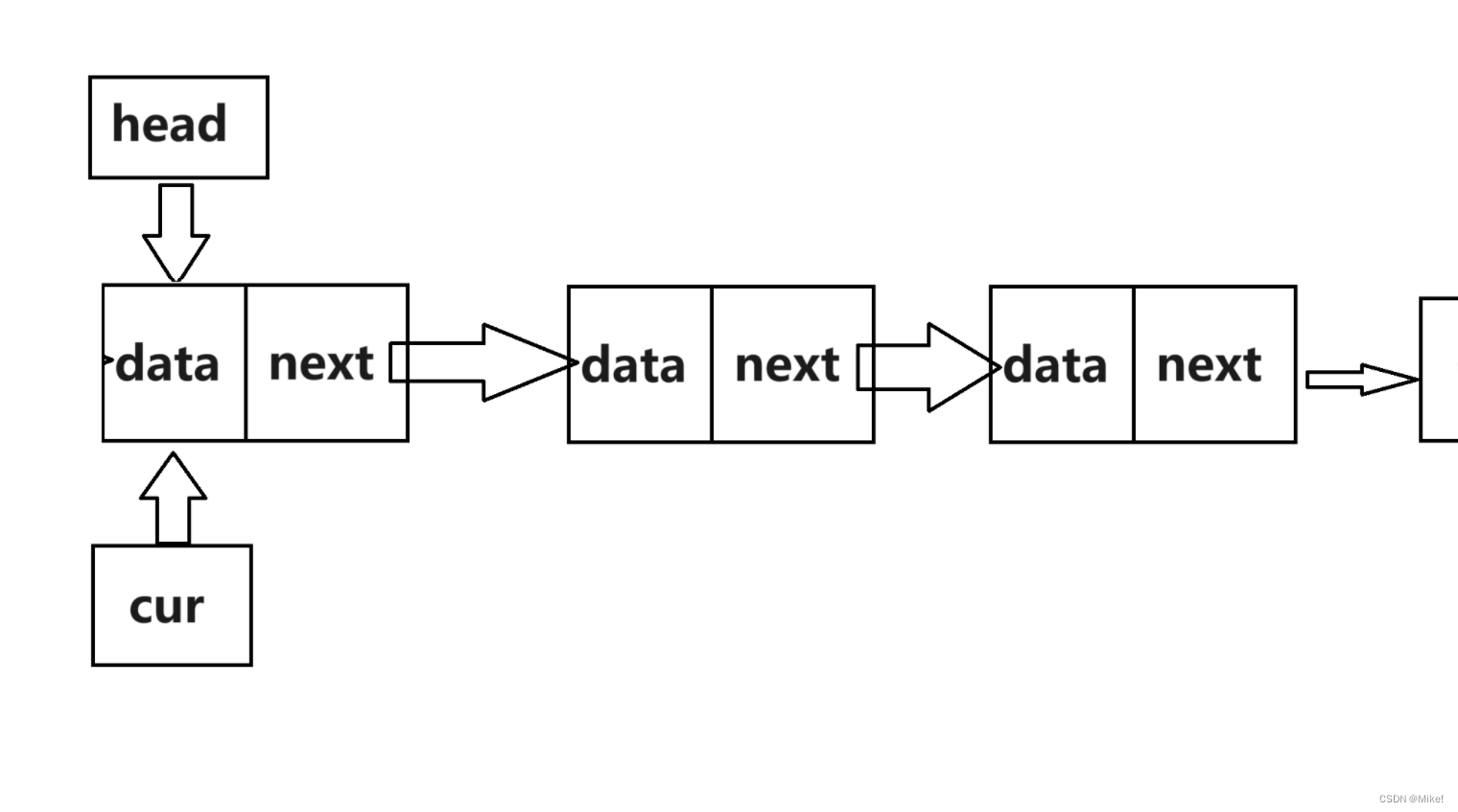
2.2.6 Popback()尾删函数
void Popback(List** head)
{
if (head== NULL || (*head) == NULL)
{
printf("headis empty!\n");
return;
}
List* pre = NULL; List* cur = (*head);
if ((*head)->next == NULL)
{
free(*head);
*head= NULL;
}
else
{
while (cur->next)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
pre->next = NULL;
}
}
(1).如果链表中只有一个结点,则直接释放头结点即可。
(2).如果不只有一个结点,则需要定义两个结构体指针,pre和cur,使pre始终在cur之前的一位,则当cur到达最后一个结点时,pre在倒数第二个结点,此时,释放cur结点,再令pre的next指针指向NULL。
图文:
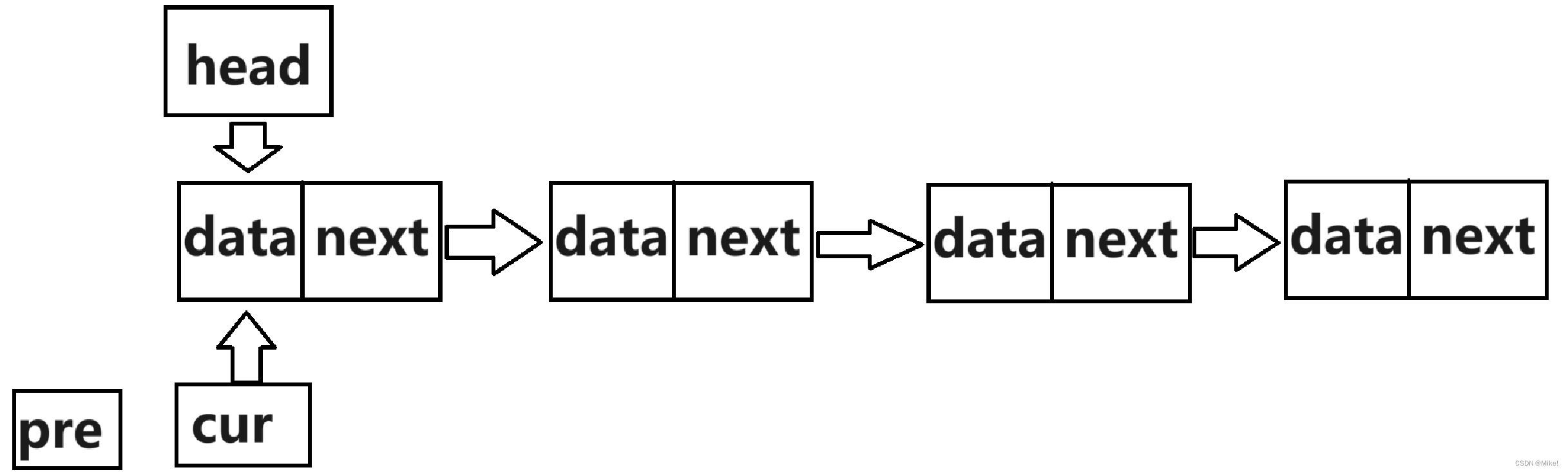
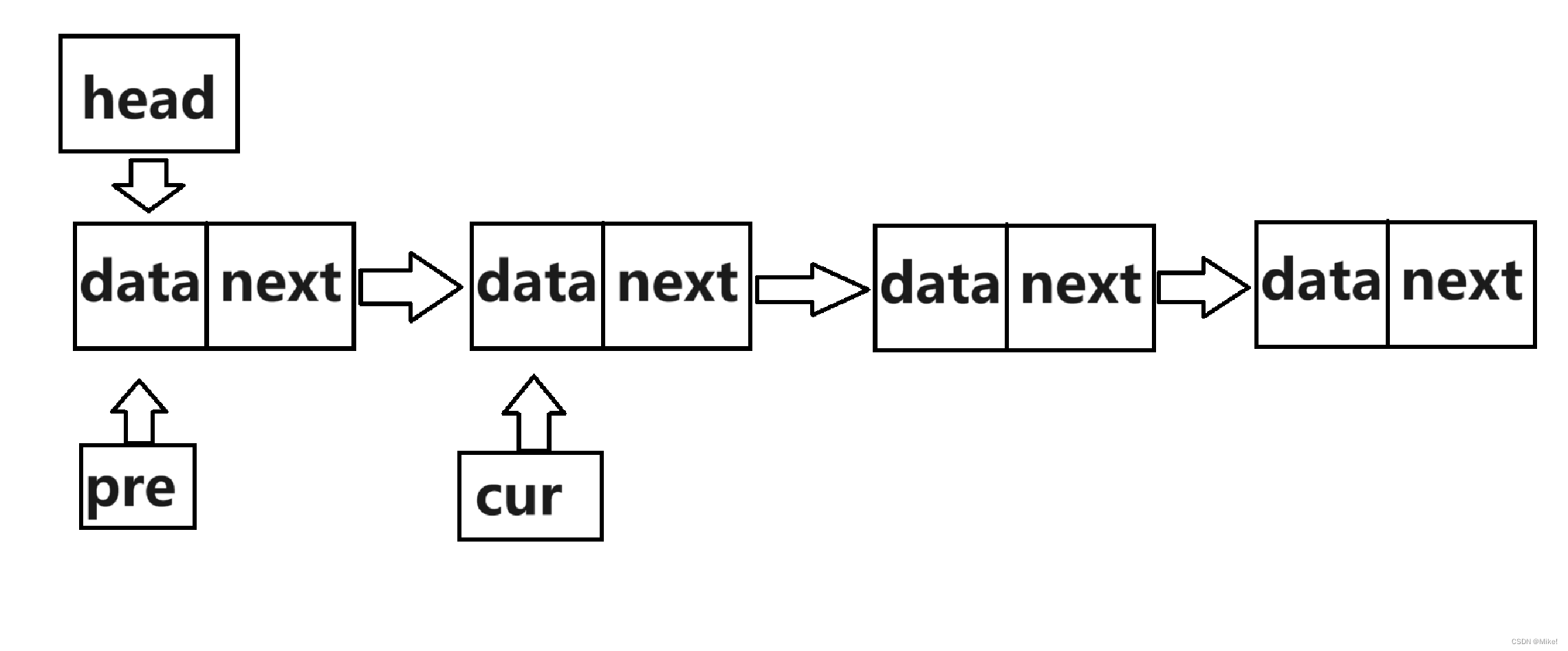


2.2.7 Find()查找函数
List* Find(List* head, Datatype x)
{
List* cur = head;
while (cur && cur->data != x)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur == NULL)
{
printf("not have x\n");
return NULL;
}
return cur;
}(1).定义结构体指针cur,循环查找,条件为cur不为空指针,并且cur所指的结点的值不等于要查找的值。
(2).当cur为空时并且在这之前都没有匹配到x,则此时cur指到了链表尾部,说明链表中不存在要查找的值。反之则找到了,返回该结点的地址。
2.2.8 Insertfront()在指定位置之前插入元素
void Insertfront(List** head, List* pos, Datatype x)//指定位置之前
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("sl is NULL\n");
return;
}
List* node = Newnode(x);
List* pre = NULL;
List* cur = (*head);
if (pos == *head)
{
Pushfront(head, x);
}
else
{
while (cur != pos)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
pre->next = node;
node->next = pos;
}
}
(1).首先创建新结点,再创建pre和cur,pre始终在cur之前的一位。
(2).如果要插入的位置(pos)刚好在头结点处,则直接调用头插即可。
(3).如果(pos)不在头结点,则使cur循环至pos的位置,此时pre位于pos前一位,使pre的next指向新结点,再使新结点的next指向pos。
图文:
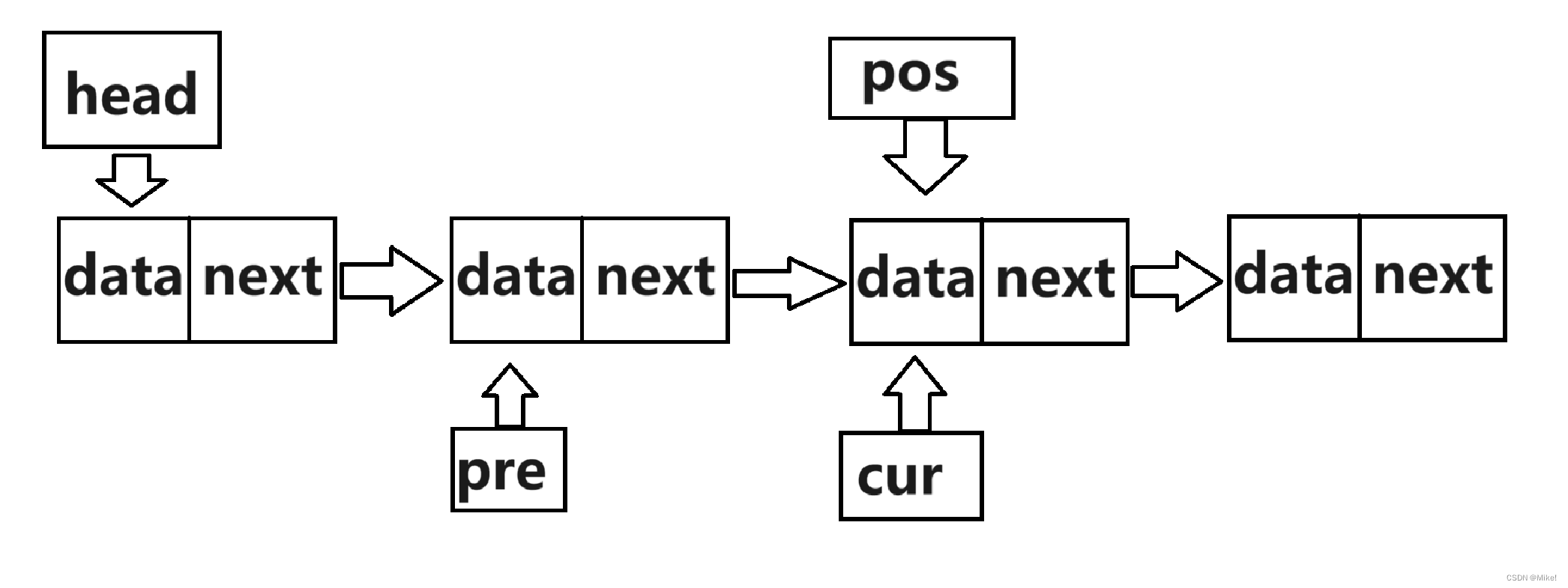

2.2.9 Insertback()指定位置之后插入元素
void Insertback(List** head, List* pos, Datatype x)//指定位置之后
{
if (head== NULL)
{
printf("head is NULL\n");
return;
}
List* node = Newnode(x);
node->next = pos->next;
pos->next = node;
}
(1).创建新结点。
(2).令新结点的next指向pos的next,再让pos的next指向新结点。
图文:
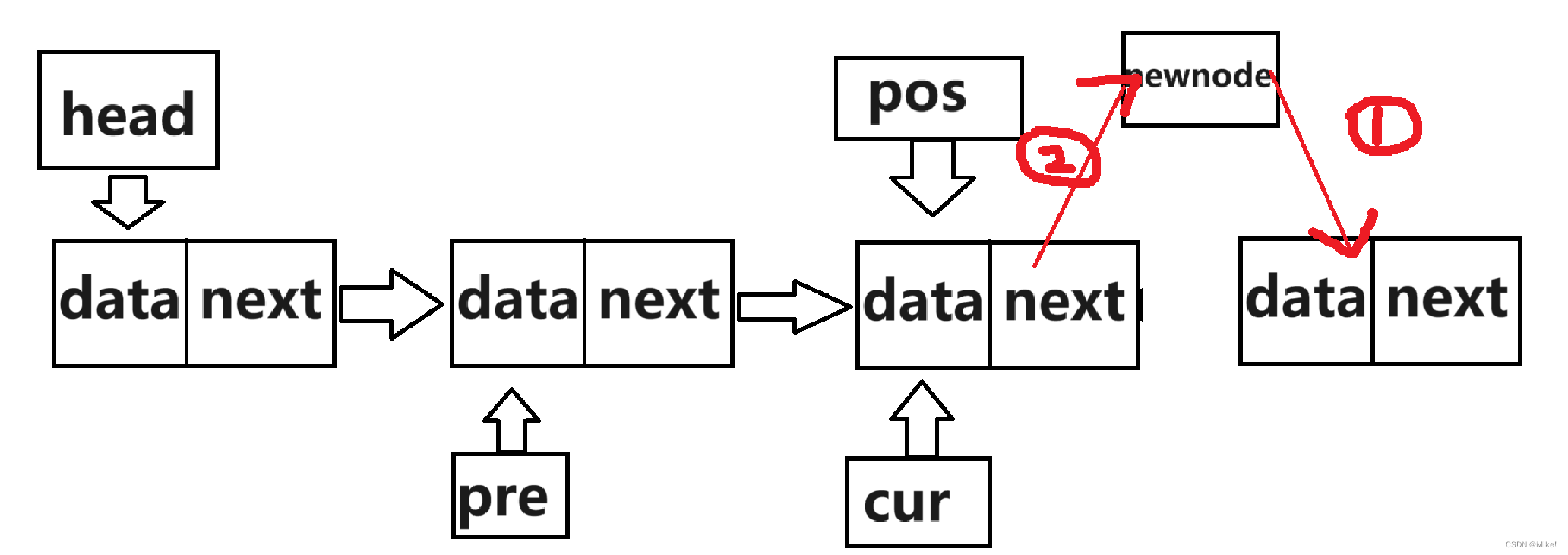
2.2.10 Erasepos() 删除指定位置的元素
void Erasepos(List** sl, List* pos)//删除指定位置
{
if (sl == NULL)
{
printf("sl is NULL\n");
return;
}
if ((*sl) == NULL)
{
printf("sl is empty\n");
return;
}
List* cur = (*sl);
if (pos == *sl)
{
Popfront(sl);
}
else
{
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
}
(1).如果pos与头结点相同,则直接调用头删。
(2).定义一个cur指针,循环至pos结点之前的一个结点,再让cur的next指向pos
的next,最后释放pos。
图文: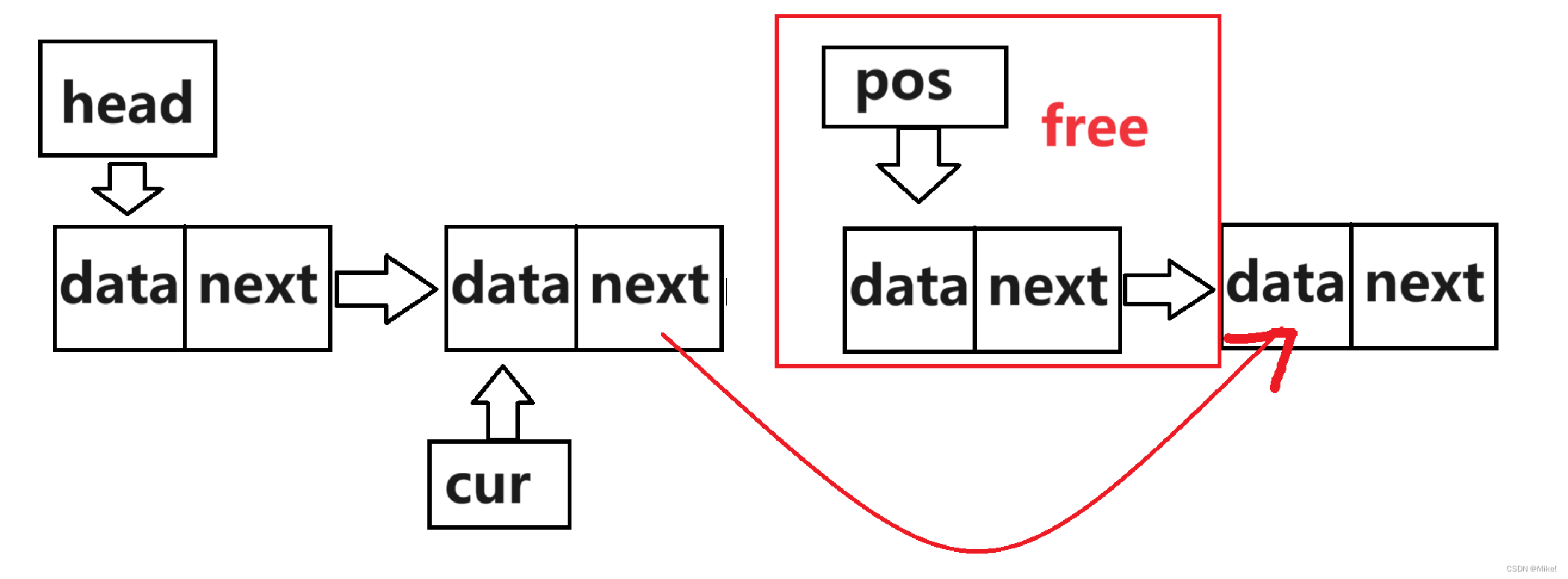
2.2.11 Destory()单链表的销毁
void Destory(List** sl)
{
if (sl == NULL)
{
printf("sl is destory\n");
return;
}
List* cur = *sl;
List* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
cur = NULL;
next = NULL;
*sl = NULL;
}
(1).要使得单链表中全部的结点销毁,就要遍历单链表。
(2).先使得next 保存cur的下一个结点地址,然后释放cur,再使得cur指向next,循环往复。
图文:
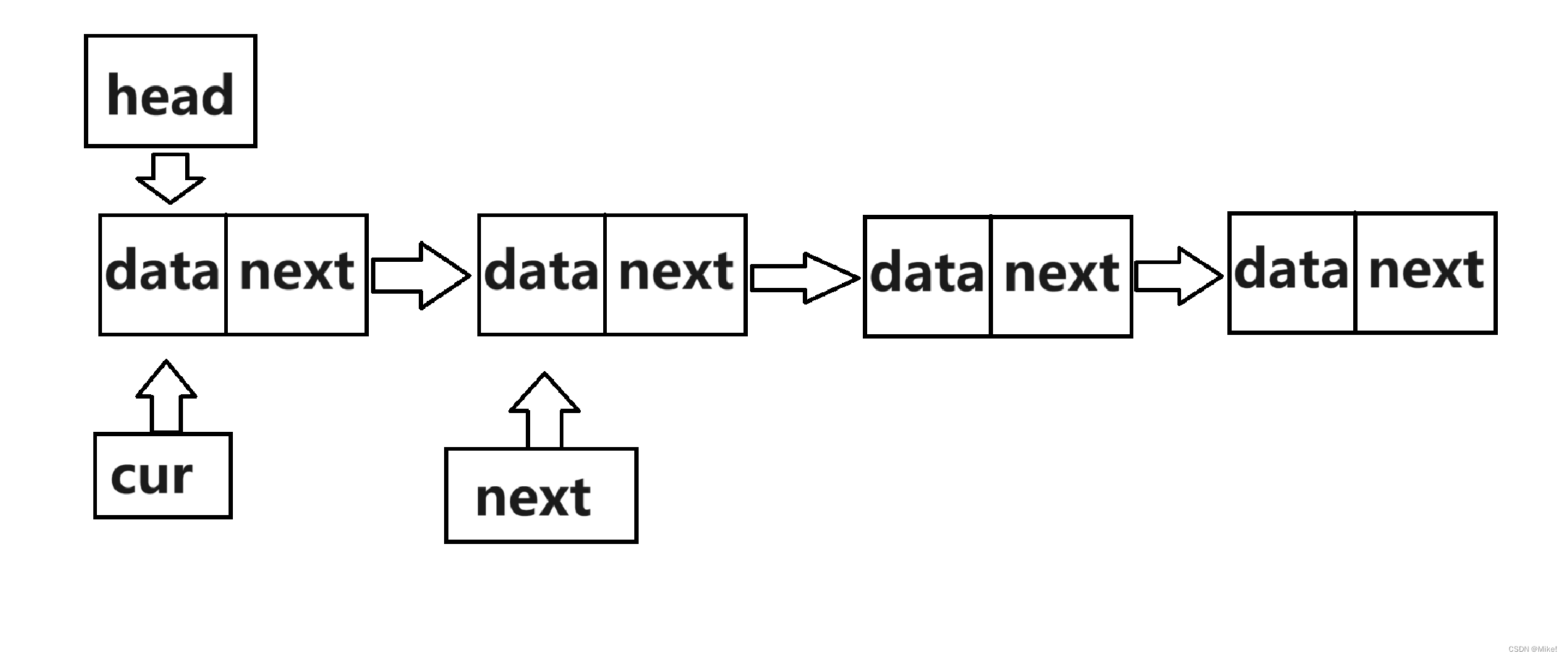
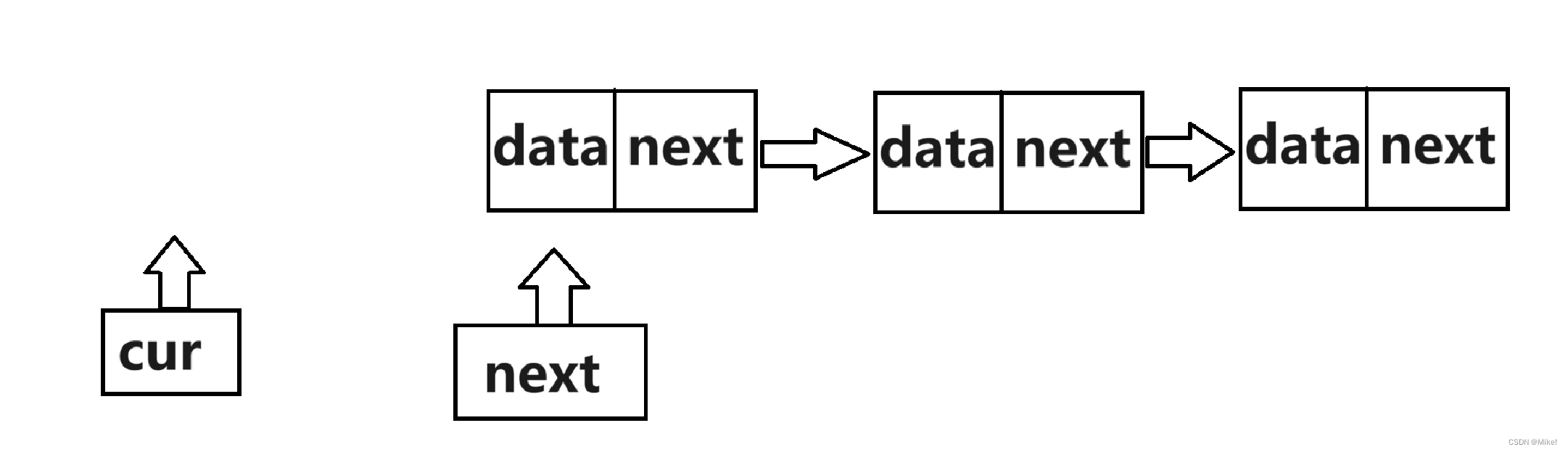


2.2.12 print()单链表的打印
void print(List* ls)//打印
{
if (ls == NULL)
{
printf("ls is NULL\n");
return;
}
List* cur = ls;
while (cur)
{
cout << cur->data << ' ';
cur = cur->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
(1).只需遍历单链表,依次打印每个结点存储的值即可。
2.3 test.cpp
源码:
#include"List.h"
int main()
{
List* node = NULL;
//init(&node);
Datatype x;
Datatype y;
List* POS = NULL;
int op;
int n;
do
{
menu();
printf("input option \n");
cin >> op;
switch (op)
{
case 1:
printf("input element number\n");
cin >> n;
while (n--)
{
cin >> x;
Pushfront(&node, x);
}
break;
case 2:
printf("input element number\n");
cin >> n;
while (n--)
{
cin >> x;
Pushback(&node, x);
}
break;
case 3:
Popfront(&node);
break;
case 4:
Popback(&node);
break;
case 5:
printf("input insert position \n");
cin >> y;
POS = Find(node,y);
if (POS == NULL)
{
printf("y is not in List\n");
}
else
{
printf("input insert element\n");
cin >> x;
Insertfront(&node, POS, x);
}
break;
case 6:
printf("input insert position \n");
cin >> y;
POS = Find(node, y);
if (POS == NULL)
{
printf("y is not in List\n");
}
else
{
printf("input insert element\n");
cin >> x;
Insertback(&node, POS, x);
}
break;
case 7:
printf("input insert position \n");
cin >> y;
POS = Find(node, y);
if (POS == NULL)
{
printf("y is not in List\n");
}
else
{
Erasepos(&node,POS);
}
break;
case 8:
printf("input insert position \n");
cin >> y;
POS = Find(node, y);
if (POS == NULL)
{
printf("y is not in List\n");
}
else
{
Eraseposback(&node, POS);
}
break;
case 9:
Destory(&node);
break;
case 10:
print(node);
break;
case 0:
break;
default:
printf("please reinput \n");
break;
}
} while (op);
return 0;
}
3.运行结果:
以上就是单链表的知识啦,如果你喜欢博主的文章,请给博主点点赞吧👍