Spring 注解编程之 AnnotationMetadata
这篇文章我们主要深入 AnnotationMetadata,了解其底层原理。
Spring 版本为 5.1.8-RELEASE
AnnotationMetadata 结构
使用 IDEA 生成 AnnotationMetadata 类图,如下:
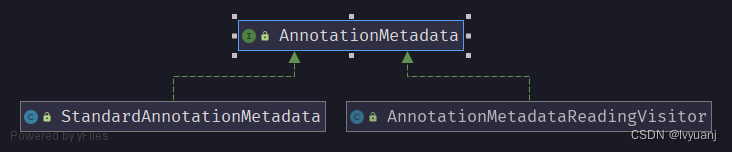
AnnotationMetadata 存在两个实现类分别为 StandardAnnotationMetadata与 AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor。StandardAnnotationMetadata主要使用 Java 反射原理获取元数据,而 AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor 使用 ASM 框架获取元数据。
Java 反射原理大家一般比较熟悉,而 ASM 技术可能会比较陌生,下面主要篇幅介绍 AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor 实现原理。
基于 AnnotationMetadata#getMetaAnnotationTypes方法,查看两者实现区别。
AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor
ASM 是一个通用的 Java 字节码操作和分析框架。它可以用于修改现有类或直接以二进制形式动态生成类。 ASM 虽然提供与其他 Java 字节码框架如 Javassist,CGLIB 类似的功能,但是其设计与实现小而快,且性能足够高。
Spring 直接将 ASM 框架核心源码内嵌于 Spring-core中,目前 Spring 5.1 使用 ASM 7 版本。
ASM框架简单应用
Java 源代码经过编译器编译之后生成了 .class 文件。
Class文件是有8个字节为基础的字节流构成的,这些字节流之间都严格按照规定的顺序排列,并且字节之间不存在任何空隙,对于超过8个字节的数据,将按 照Big-Endian的顺序存储的,也就是说高位字节存储在低的地址上面,而低位字节存储到高地址上面,其实这也是class文件要>跨平台的关键,因为 PowerPC架构的处理采用Big-Endian的存储顺序,而x86系列的处理器则采用Little-Endian的存储顺序,因此为了Class文 件在各中处理器架构下保持统一的存储顺序,虚拟机规范必须对起进行统一。
Class 文件中包含类的所有信息,如接口,字段属性,方法,在内部这些信息按照一定规则紧凑排序。ASM 框会以文件流的形式读取 class 文件,然后解析过程中使用观察者模式(Visitor),当解析器碰到相应的信息委托给观察者(Visitor)。使用 ASM 框架首先需要继承 ClassVisitor,完成解析相应信息,如解析方法,字段等。
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Message {
private Header header;
private String content;
public Message(Header header, String content) {
this.header = header;
this.content = content;
}
public Header getHeader() {
return header;
}
public void setHeader(Header header) {
this.header = header;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("[version=%d,contentLength=%d,sessionId=%s,content=%s]",
header.getVersion(),
header.getContentLength(),
header.getSessiongId(),
content);
}
}
import com.lvyuanj.core.mytest.netty.model.Message;
import org.springframework.asm.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyClassPrinter extends ClassVisitor {
public MyClassPrinter() {
super(7 << 16 | 0 << 8);
}
@Override
public void visit(int version, int access, String name, String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) {
System.out.println(name + " extends "+ superName + " {");
}
@Override
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String descriptor, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
System.out.println("method:"+" "+ name + descriptor);
return null;
}
@Override
public AnnotationVisitor visitAnnotation(String desc, boolean visible) {
System.out.println("Annotation:"+" "+ desc + " ");
return null;
}
@Override
public FieldVisitor visitField(int access, String name, String desc, String signature, Object value) {
System.out.println("field:"+" "+ desc + " "+ name + " "+ Type.getType(desc).getClass());
return null;
}
@Override
public void visitEnd() {
System.out.println("}");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
MyClassPrinter myClassPrinter = new MyClassPrinter();
ClassReader reader = new ClassReader(Message.class.getName());
reader.accept(myClassPrinter, 0);
}
}
然后使用 ClassReader 读取类文件,然后再使用 ClassReader#accpet 接受 ClassVisitor。
输出结果:
com/lvyuanj/core/mytest/netty/model/Message extends java/lang/Object {
Annotation: Lorg/springframework/stereotype/Component;
field: Lcom/lvyuanj/core/mytest/netty/model/Header; header class org.springframework.asm.Type
field: Ljava/lang/String; content class org.springframework.asm.Type
method: <init>(Lcom/lvyuanj/core/mytest/netty/model/Header;Ljava/lang/String;)V
method: getHeader()Lcom/lvyuanj/core/mytest/netty/model/Header;
method: setHeader(Lcom/lvyuanj/core/mytest/netty/model/Header;)V
method: getContent()Ljava/lang/String;
method: setContent(Ljava/lang/String;)V
method: toString()Ljava/lang/String;
}
可以看到 ClassVisitor 相应方法可以用来解析类的相关信息,这里我们主要关注解析类上注解信息。解析注解将会在 ClassVisitor#visitAnnotation完成解析。 该方法返回了一个 AnnotationVisitor 对象,其也是一个 Visitor 对象。后续解析器会继续调用 AnnotationVisitor内部方法进行再次解析。
以上实现采用 ASM Core API ,而 ASM 框架还提供 Tree API 用法。具体用法参考:https://asm.ow2.io/
AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor#getMetaAnnotationTypes 源码解析
AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor#getMetaAnnotationTypes 方法实现非常简单,直接从 metaAnnotationMap 根据注解类名称获取其上面所有元注解。注解相关信息解析由 AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor#visitAnnotation 完成。
@Override
public Set<String> getMetaAnnotationTypes(String annotationName) {
Set<String> metaAnnotationTypes = this.metaAnnotationMap.get(annotationName);
return (metaAnnotationTypes != null ? metaAnnotationTypes : Collections.emptySet());
}
在 visitAnnotation 方法中,metaAnnotationMap当做构造参数传入了 AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor 对象中,metaAnnotationMap会在这里面完成赋值。
@Override
public AnnotationVisitor visitAnnotation(String desc, boolean visible) {
String className = Type.getType(desc).getClassName();
this.annotationSet.add(className);
return new AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor(
className, this.attributesMap, this.metaAnnotationMap, this.classLoader);
}
AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor#visitEnd 将会排除 java.lang.annotation 下的注解,然后通过递归调用 recursivelyCollectMetaAnnotations获取元注解,不断将元注解置入 metaAnnotationMap中。
public void visitEnd() {
super.visitEnd();
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass = this.attributes.annotationType();
if (annotationClass != null) {
List<AnnotationAttributes> attributeList = this.attributesMap.get(this.annotationType);
if (attributeList == null) {
this.attributesMap.add(this.annotationType, this.attributes);
}
else {
attributeList.add(0, this.attributes);
}
if (!AnnotationUtils.isInJavaLangAnnotationPackage(annotationClass.getName())) {
try {
Annotation[] metaAnnotations = annotationClass.getAnnotations();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(metaAnnotations)) {
Set<Annotation> visited = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (Annotation metaAnnotation : metaAnnotations) {
recursivelyCollectMetaAnnotations(visited, metaAnnotation);
}
if (!visited.isEmpty()) {
Set<String> metaAnnotationTypeNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(visited.size());
for (Annotation ann : visited) {
metaAnnotationTypeNames.add(ann.annotationType().getName());
}
this.metaAnnotationMap.put(annotationClass.getName(), metaAnnotationTypeNames);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to introspect meta-annotations on " + annotationClass + ": " + ex);
}
}
}
}
}
private void recursivelyCollectMetaAnnotations(Set<Annotation> visited, Annotation annotation) {
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = annotation.annotationType();
String annotationName = annotationType.getName();
if (!AnnotationUtils.isInJavaLangAnnotationPackage(annotationName) && visited.add(annotation)) {
try {
// Only do attribute scanning for public annotations; we'd run into
// IllegalAccessExceptions otherwise, and we don't want to mess with
// accessibility in a SecurityManager environment.
if (Modifier.isPublic(annotationType.getModifiers())) {
this.attributesMap.add(annotationName,
AnnotationUtils.getAnnotationAttributes(annotation, false, true));
}
for (Annotation metaMetaAnnotation : annotationType.getAnnotations()) {
recursivelyCollectMetaAnnotations(visited, metaMetaAnnotation);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to introspect meta-annotations on " + annotation + ": " + ex);
}
}
}
}
最后使用 UML 时序图中,概括以上调用流程。
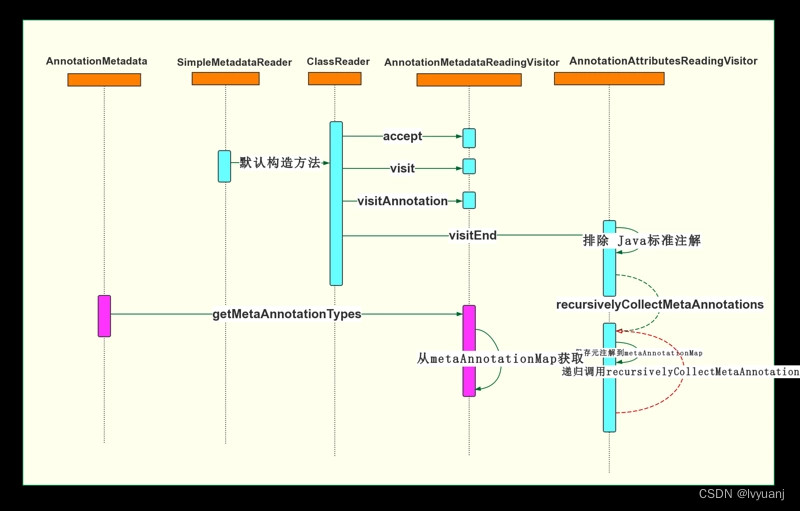
Spring 4 之后版本才有递归查找元注解的方法。各位同学可以翻阅 Spring3 的版本作为比较,可以看出 Spring 的代码功能也是逐渐迭代升级的。
StandardAnnotationMetadata
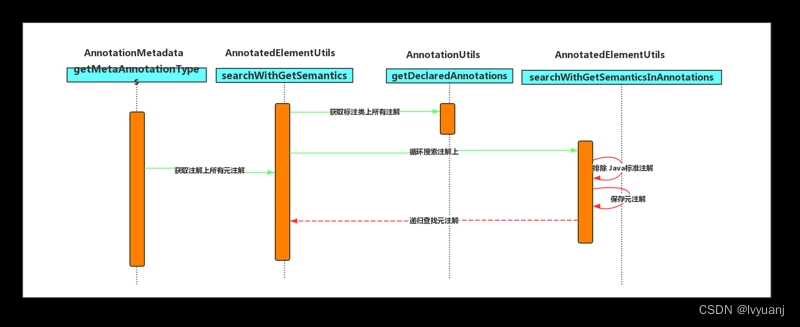
StandardAnnotationMetadata 主要使用 Java 反射原理获取相关信息。在 Spring 中封装很多了反射工具类用于操作。StandardAnnotationMetadata#getMetaAnnotationTypes 通过使用 Spring 工具类 AnnotatedElementUtils.getMetaAnnotationTypes方法获取。源码调用比较清晰,各位同学可以自行翻阅理解,可以参考下面时序图理解,这里不再叙述。
StandardAnnotationMetadata standardAnnotationMetadata = new StandardAnnotationMetadata(Message.class);
MergedAnnotations annotations = standardAnnotationMetadata.getAnnotations();
annotations.forEach(o-> System.out.println(o.getType()));
结果:
interface org.springframework.stereotype.Component
interface org.springframework.stereotype.Indexed
总结
本文介绍了 AnnotationMetadata两种实现方案,一种基于 Java 反射,另一种基于 ASM 框架。两种实现方案适用于不同场景。StandardAnnotationMetadata 基于 Java 反射,需要加载类文件。而 AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor基于 ASM 框架无需提前加载类,所以适用于 Spring 应用扫描指定范围内模式注解时使用。