🏠个人主页:尘觉主页
文章目录
算法 - 符号表
前言
符号表(Symbol Table)是一种存储键值对的数据结构,可以支持快速查找操作。
符号表分为有序和无序两种,有序符号表主要指支持 min()、max() 等根据键的大小关系来实现的操作。
有序符号表的键需要实现 Comparable 接口。
public interface UnorderedST<Key, Value> {
int size();
Value get(Key key);
void put(Key key, Value value);
void delete(Key key);
}
public interface OrderedST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
int size();
void put(Key key, Value value);
Value get(Key key);
Key min();
Key max();
int rank(Key key);
List<Key> keys(Key l, Key h);
}
初级实现
1. 链表实现无序符号表
public class ListUnorderedST<Key, Value> implements UnorderedST<Key, Value> {
private Node first;
private class Node {
Key key;
Value value;
Node next;
Node(Key key, Value value, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
int cnt = 0;
Node cur = first;
while (cur != null) {
cnt++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cnt;
}
@Override
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
Node cur = first;
// 如果在链表中找到节点的键等于 key 就更新这个节点的值为 value
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key.equals(key)) {
cur.value = value;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 否则使用头插法插入一个新节点
first = new Node(key, value, first);
}
@Override
public void delete(Key key) {
if (first == null)
return;
if (first.key.equals(key))
first = first.next;
Node pre = first, cur = first.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key.equals(key)) {
pre.next = cur.next;
return;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public Value get(Key key) {
Node cur = first;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key.equals(key))
return cur.value;
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
}
2. 二分查找实现有序符号表
使用一对平行数组,一个存储键一个存储值。
二分查找的 rank() 方法至关重要,当键在表中时,它能够知道该键的位置;当键不在表中时,它也能知道在何处插入新键。
二分查找最多需要 logN+1 次比较,使用二分查找实现的符号表的查找操作所需要的时间最多是对数级别的。但是插入操作需要移动数组元素,是线性级别的。
public class BinarySearchOrderedST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> implements OrderedST<Key, Value> {
private Key[] keys;
private Value[] values;
private int N = 0;
public BinarySearchOrderedST(int capacity) {
keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[capacity];
values = (Value[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@Override
public int size() {
return N;
}
@Override
public int rank(Key key) {
int l = 0, h = N - 1;
while (l <= h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
int cmp = key.compareTo(keys[m]);
if (cmp == 0)
return m;
else if (cmp < 0)
h = m - 1;
else
l = m + 1;
}
return l;
}
@Override
public List<Key> keys(Key l, Key h) {
int index = rank(l);
List<Key> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (keys[index].compareTo(h) <= 0) {
list.add(keys[index]);
index++;
}
return list;
}
@Override
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
int index = rank(key);
// 如果找到已经存在的节点键为 key,就更新这个节点的值为 value
if (index < N && keys[index].compareTo(key) == 0) {
values[index] = value;
return;
}
// 否则在数组中插入新的节点,需要先将插入位置之后的元素都向后移动一个位置
for (int j = N; j > index; j--) {
keys[j] = keys[j - 1];
values[j] = values[j - 1];
}
keys[index] = key;
values[index] = value;
N++;
}
@Override
public Value get(Key key) {
int index = rank(key);
if (index < N && keys[index].compareTo(key) == 0)
return values[index];
return null;
}
@Override
public Key min() {
return keys[0];
}
@Override
public Key max() {
return keys[N - 1];
}
}
二叉查找树
二叉树 是一个空链接,或者是一个有左右两个链接的节点,每个链接都指向一颗子二叉树。
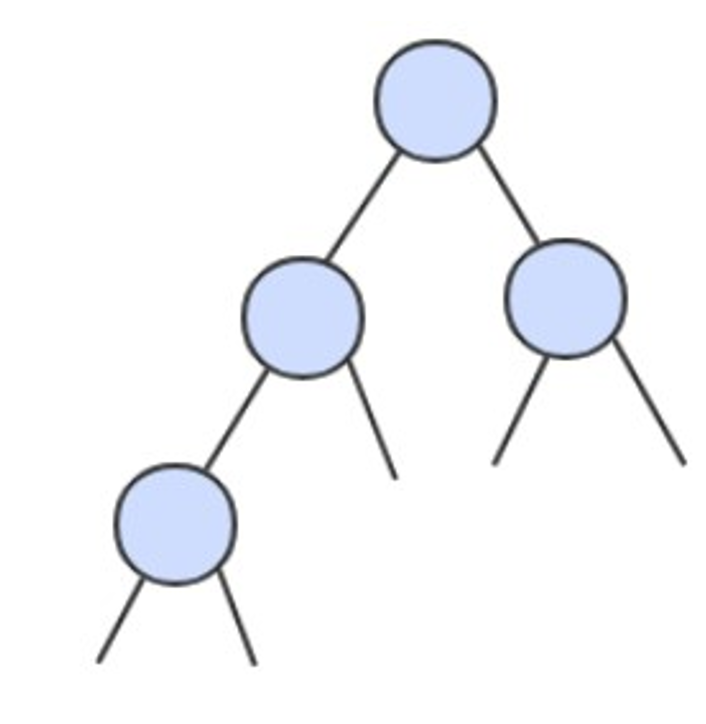
二叉查找树 (BST)是一颗二叉树,并且每个节点的值都大于等于其左子树中的所有节点的值而小于等于右子树的所有节点的值。
BST 有一个重要性质,就是它的中序遍历结果递增排序。
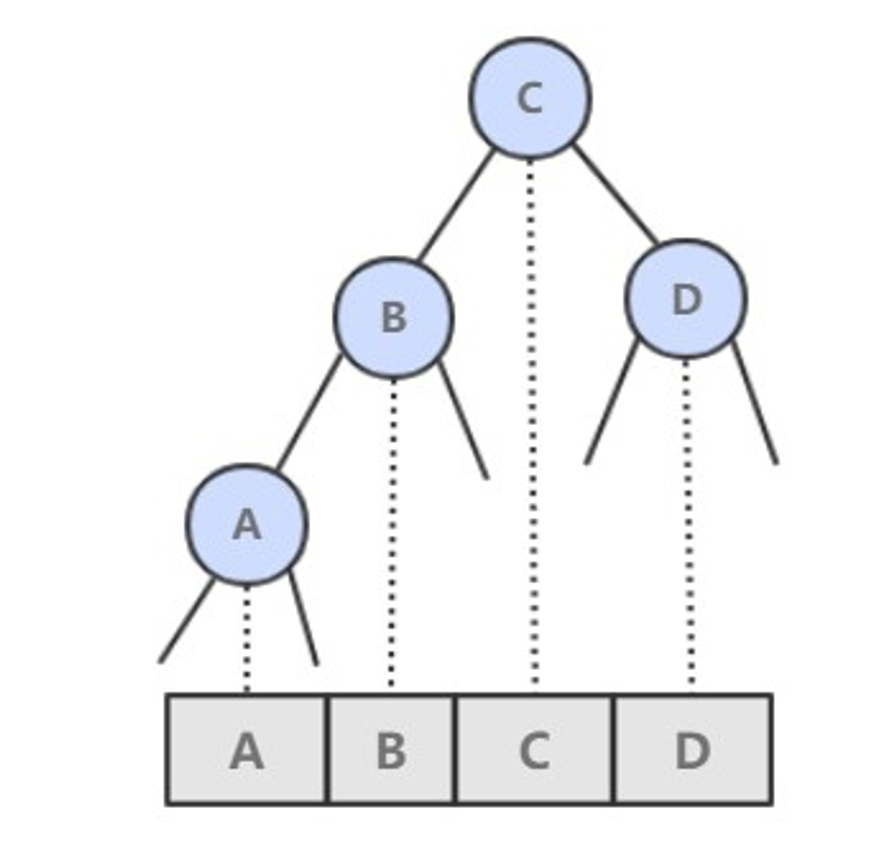
基本数据结构:
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> implements OrderedST<Key, Value> {
protected Node root;
protected class Node {
Key key;
Value val;
Node left;
Node right;
// 以该节点为根的子树节点总数
int N;
// 红黑树中使用
boolean color;
Node(Key key, Value val, int N) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.N = N;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size(root);
}
private int size(Node x) {
if (x == null)
return 0;
return x.N;
}
protected void recalculateSize(Node x) {
x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
}
}
为了方便绘图,下文中二叉树的空链接不画出来。
1. get()
- 如果树是空的,则查找未命中;
- 如果被查找的键和根节点的键相等,查找命中;
- 否则递归地在子树中查找:如果被查找的键较小就在左子树中查找,较大就在右子树中查找。
@Override
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
private Value get(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null)
return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0)
return x.val;
else if (cmp < 0)
return get(x.left, key);
else
return get(x.right, key);
}
2. put()
当插入的键不存在于树中,需要创建一个新节点,并且更新上层节点的链接指向该节点,使得该节点正确地链接到树中。
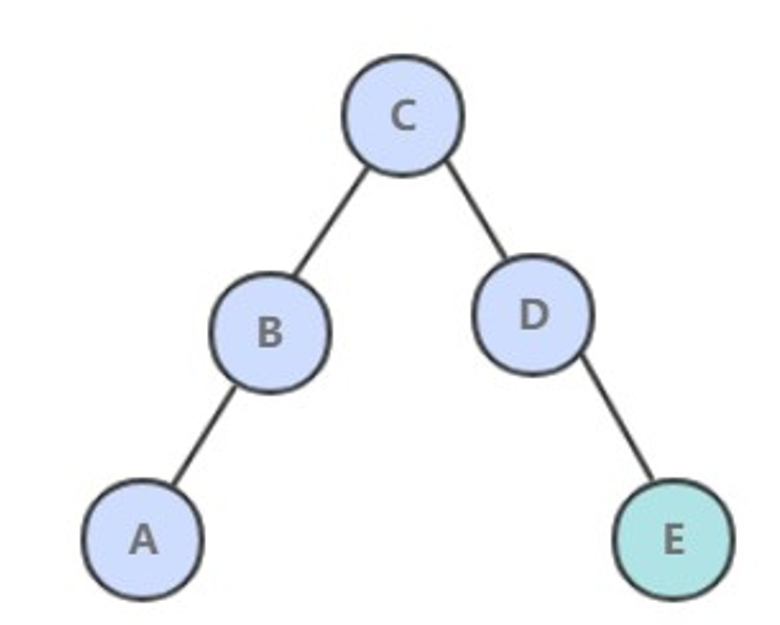
@Override
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
root = put(root, key, value);
}
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value value) {
if (x == null)
return new Node(key, value, 1);
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0)
x.val = value;
else if (cmp < 0)
x.left = put(x.left, key, value);
else
x.right = put(x.right, key, value);
recalculateSize(x);
return x;
}
3. 分析
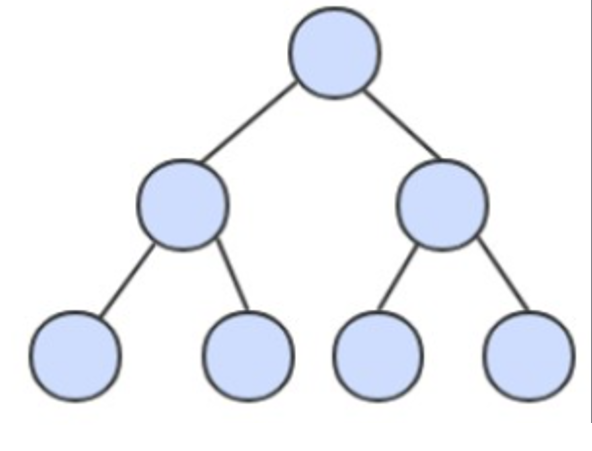
二叉查找树的算法运行时间取决于树的形状,而树的形状又取决于键被插入的先后顺序。
最好的情况下树是完全平衡的,每条空链接和根节点的距离都为 logN。
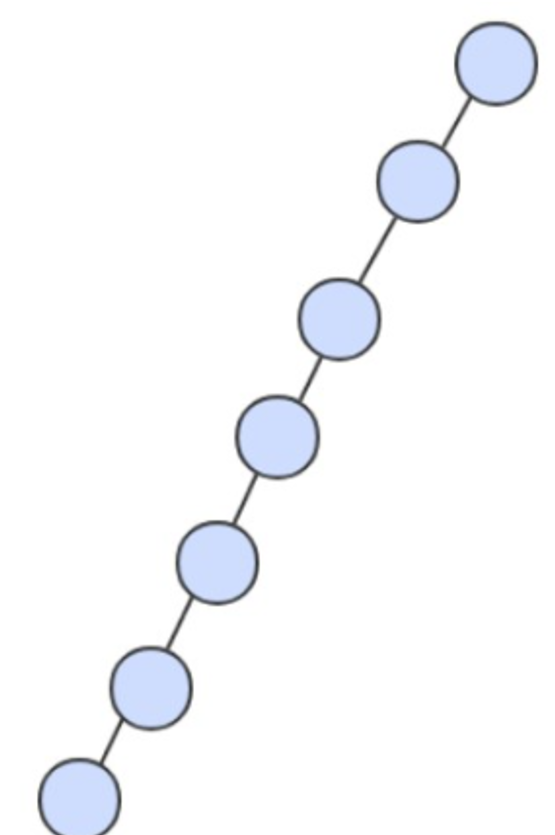
在最坏的情况下,树的高度为 N。
4. floor()
floor(key):小于等于键的最大键
- 如果键小于根节点的键,那么 floor(key) 一定在左子树中;
- 如果键大于根节点的键,需要先判断右子树中是否存在 floor(key),如果存在就返回,否则根节点就是 floor(key)。
public Key floor(Key key) {
Node x = floor(root, key);
if (x == null)
return null;
return x.key;
}
private Node floor(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null)
return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0)
return x;
if (cmp < 0)
return floor(x.left, key);
Node t = floor(x.right, key);
return t != null ? t : x;
}
5. rank()
rank(key) 返回 key 的排名。
- 如果键和根节点的键相等,返回左子树的节点数;
- 如果小于,递归计算在左子树中的排名;
- 如果大于,递归计算在右子树中的排名,加上左子树的节点数,再加上 1(根节点)。
@Override
public int rank(Key key) {
return rank(key, root);
}
private int rank(Key key, Node x) {
if (x == null)
return 0;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp == 0)
return size(x.left);
else if (cmp < 0)
return rank(key, x.left);
else
return 1 + size(x.left) + rank(key, x.right);
}
6. min()
@Override
public Key min() {
return min(root).key;
}
private Node min(Node x) {
if (x == null)
return null;
if (x.left == null)
return x;
return min(x.left);
}
7. deleteMin()
令指向最小节点的链接指向最小节点的右子树。
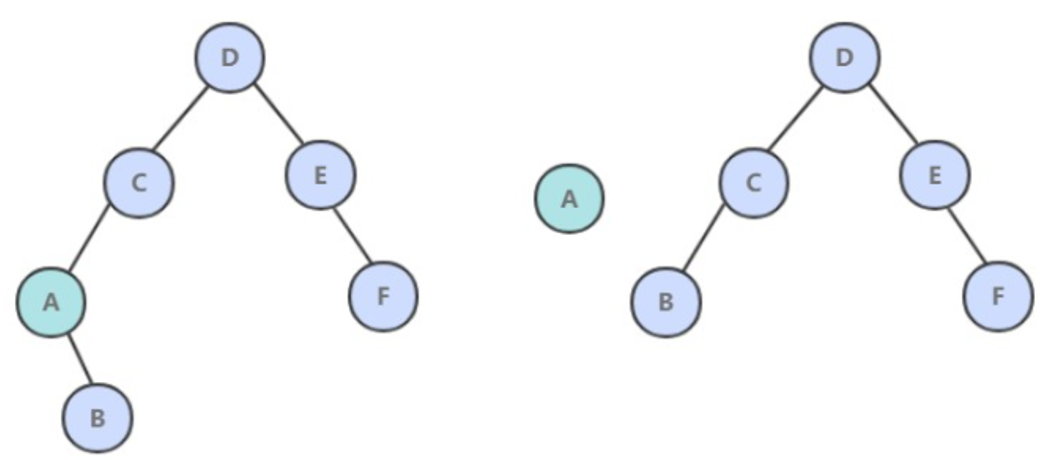
public void deleteMin() {
root = deleteMin(root);
}
public Node deleteMin(Node x) {
if (x.left == null)
return x.right;
x.left = deleteMin(x.left);
recalculateSize(x);
return x;
}
8. delete()
- 如果待删除的节点只有一个子树, 那么只需要让指向待删除节点的链接指向唯一的子树即可;
- 否则,让右子树的最小节点替换该节点。
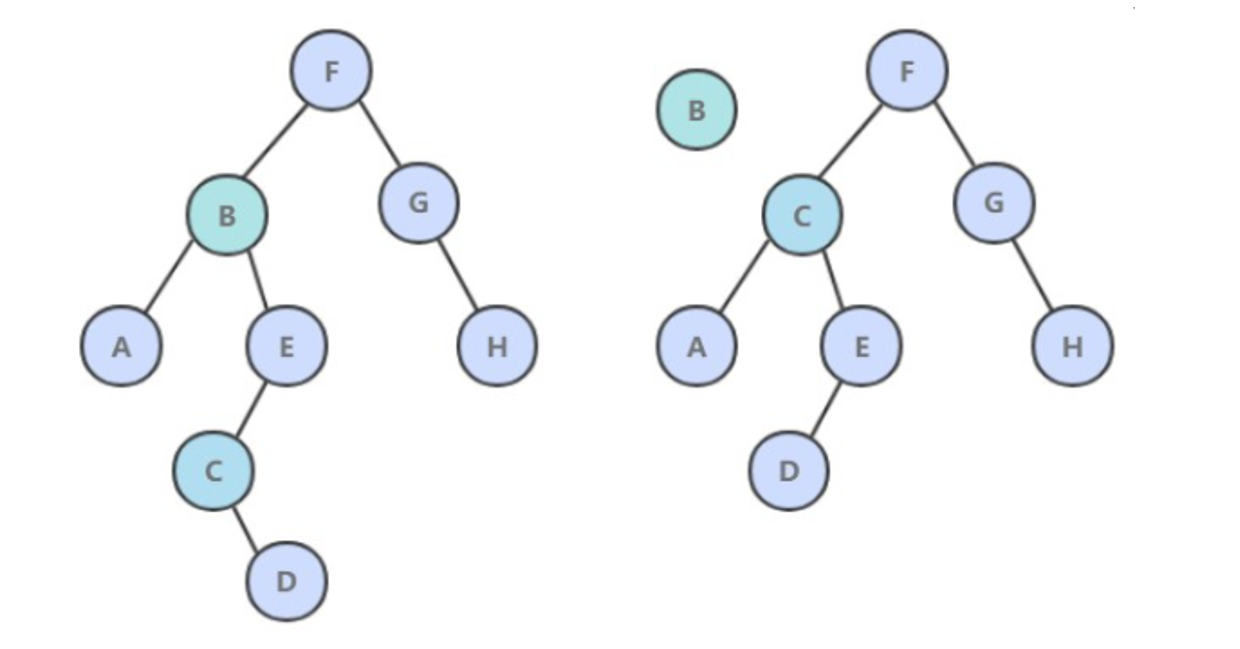
public void delete(Key key) {
root = delete(root, key);
}
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null)
return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x.left = delete(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0)
x.right = delete(x.right, key);
else {
if (x.right == null)
return x.left;
if (x.left == null)
return x.right;
Node t = x;
x = min(t.right);
x.right = deleteMin(t.right);
x.left = t.left;
}
recalculateSize(x);
return x;
}
9. keys()
利用二叉查找树中序遍历的结果为递增的特点。
@Override
public List<Key> keys(Key l, Key h) {
return keys(root, l, h);
}
private List<Key> keys(Node x, Key l, Key h) {
List<Key> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (x == null)
return list;
int cmpL = l.compareTo(x.key);
int cmpH = h.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmpL < 0)
list.addAll(keys(x.left, l, h));
if (cmpL <= 0 && cmpH >= 0)
list.add(x.key);
if (cmpH > 0)
list.addAll(keys(x.right, l, h));
return list;
}
10. 分析
二叉查找树所有操作在最坏的情况下所需要的时间都和树的高度成正比。
😁热门专栏推荐
想学习vue的可以看看这个
等等等还有许多优秀的合集在主页等着大家的光顾感谢大家的支持
🤔欢迎大家加入我的社区 尘觉社区
文章到这里就结束了,如果有什么疑问的地方请指出,诸佬们一起来评论区一起讨论😁
希望能和诸佬们一起努力,今后我们一起观看感谢您的阅读🍻
如果帮助到您不妨3连支持一下,创造不易您们的支持是我的动力🤞
























![纯初中数学!快速幂[mod]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c1a64cc71eb047bebf6d3bd84eb961f7.png)