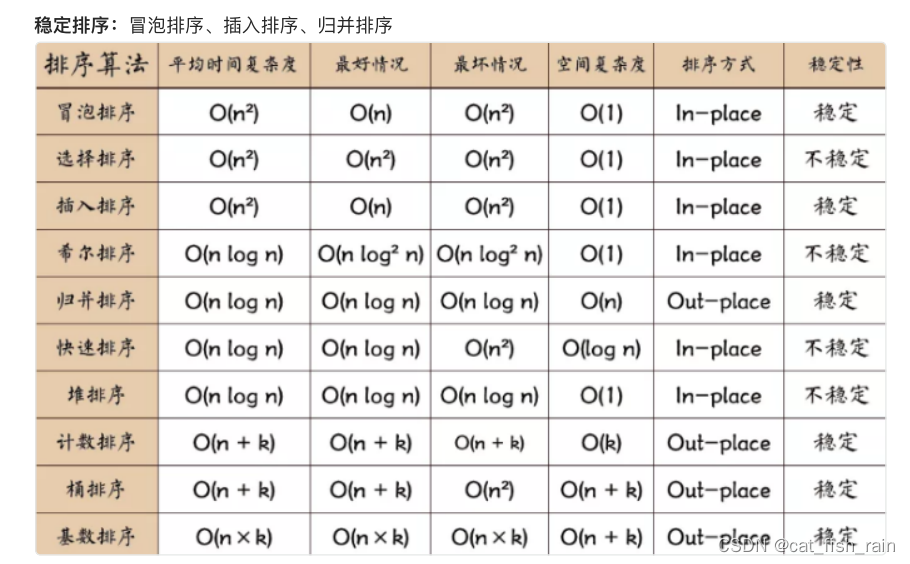
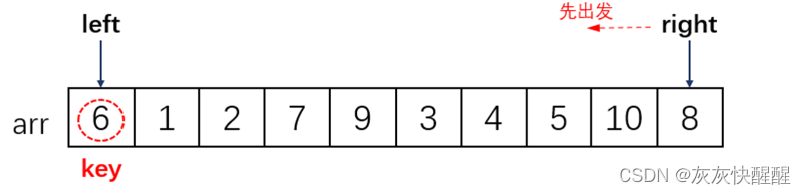
博主学习历程:
首先,思想不难,代码更是简单,仅仅是非递归快排和循环归并略有难度(个人认为难度集中在边界条件上)
学习方法:这里博主是听老师细细讲解(各种排序思想,老师演示手撕和注意事项,顺带学习手撕技巧和各种排序的价值和历史),
理解思想和技巧,课上讲完之后,完全可以时隔半周仍能按思路手撕,第一次手撕可能略有缓慢,切记不要行照抄,比较找错之事,那样不如不学!!
手撕技巧:
1.请脑子里清楚知道排序的思想,是怎样把数组里的值排序的。这都不知道的话,根本手撕不了一点。
2.博主理解里,排序可分两种。一是,可以看成几个步骤,如:计数排序等,这种排序简单,直直按着思想写就行;二是,循环套循环一样的排序,如:希尔排序,归并排序等,这种一般操作(第一次手撕时)是根据先写单趟(单次,或者说是排“第一个”),然后再套个循环把数组每个排,然后再套——总之是先完成"每一轮"的,再产生每一轮的初始条件(套循环)
3.相信自己,自己手撕的时候,别别别别别别看别人的代码,全程自己写,出错请使用调试+打印小技巧。
代码:
堆排用到了向下调整,非递归快排用到了栈结构,以int类型为例
栈stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdlib.h>
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);
stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"stack.h"
#include<assert.h>
// 初始化栈 栈顶代表的下标存数据
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_a = NULL;
ps->_capacity = 0;
ps->_top = -1;
}
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->_capacity == (ps->_top + 1)) {
ps->_capacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->_capacity * 2;
STDataType* ptmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->_a, sizeof(STDataType) * ps->_capacity);
assert(ptmp);
ps->_a = ptmp;
}
++(ps->_top);
ps->_a[ps->_top] = data;
}
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->_top > -1) {
--(ps->_top);
}
}
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->_top > -1) {
return ps->_a[ps->_top];
}
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top + 1;
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->_top == -1) {
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->_a);
ps->_a = NULL;
ps->_capacity = 0;
ps->_top = -1;
}sort.h
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
// 选择排序
void SelectSort(int* a, int n);
// 堆排序
void AdjustDwon(int* a, int n, int root);
void HeapSort(int* a, int n);
// 插入排序
void InsertSort(int* a, int n);
// 希尔排序
void ShellSort(int* a, int n);
// 冒泡排序
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n);
// 快排非递归
void QuickSortNonR(int* a, int n);
// 归并
void MergeSort(int* a, int n);
//计数,hash
void CountSort(int* a, int n);
sort.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"sort.h"
#include"stack.h"
//两个指针,先用int做测试;
int SortCmp(int* p1, int* p2)//p1大于p2 为升序
{
assert(p1);
assert(p2);
if (*p1 > *p2) return 1;
else return 0;
}
void Swap(int* p1, int* p2)
{
assert(p1);
assert(p2);
int tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
// 选择排序
void SelectSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
while (left < right) {
int tmp = left;//记录交换下标
for (int i = left; i <= right; ++i) {
if (!SortCmp(&a[i], &a[tmp])) {
tmp = i;
}
}
Swap(&a[tmp], &a[left]);
++left;
}
}
// 堆排序
void AdjustDwon(int* a, int n, int root)
{
assert(a);
int father = root;
int swapSon = father * 2 + 1;
while (swapSon < n)
{
if (swapSon + 1 < n && SortCmp(&a[swapSon + 1], &a[swapSon])) {
++swapSon;
}
if (SortCmp(&a[swapSon], &a[father])) {
Swap(&a[swapSon], &a[father]);
father = swapSon;
swapSon = father * 2 + 1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int father = (n - 1 - 1) / 2;
while (father >= 0) {
AdjustDwon(a, n, father);
--father;
}
while (n != 1) {
Swap(&a[0], &a[n - 1]);
--n;
AdjustDwon(a, n, 0);//每次从top开始向下check
}
}
// 插入排序
void InsertSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
//先搞个升序
//单次
int spacer = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n - spacer; ++i) {
int end = i;//单次范围下标_right
int tmp = a[end + spacer];
while (end >= 0) {
if (SortCmp(&tmp, &a[end])) {
break;
}
a[end + spacer] = a[end];
end -= spacer;
}
a[end + spacer] = tmp;
}
}
// 希尔排序
void ShellSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int spacer = n;
while (spacer > 1) {//预排序到最后一次排序的循环
spacer = spacer / 3 + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n - spacer; ++i) {//从下标0到这一次排序末端的一次排序或预排序
int end = i;//单次范围下标_right
int tmp = a[end + spacer];
while (end >= 0) {//一组的循环
if (SortCmp(&tmp, &a[end])) {//比较
break;
}
a[end + spacer] = a[end];
end -= spacer;
}
a[end + spacer] = tmp;
}
}
}
// 冒泡排序
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; --i) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if (SortCmp(&a[j], &a[j + 1]) ){
Swap(&a[j], &a[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
//快排,非递归,栈实现
void QuickSortNonR(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
srand((size_t)time(NULL));
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
Stack tmp;
StackInit(&tmp);
StackPush(&tmp, left);
StackPush(&tmp, right);
while (!StackEmpty(&tmp)) {
//取元素
right = StackTop(&tmp);
StackPop(&tmp);
left = StackTop(&tmp);
StackPop(&tmp);
int begin = left;
int end = right;
int mid = rand() % (end - begin + 1);//随机数做比较值
/*printf("mid = %d \n", mid);
Print(a, left, right);*/
Swap(&a[left + mid], &a[left]);
while (begin < end) {
while (begin < end && SortCmp(&a[end], &a[left])) {//等于的在左边
--end;
}
while (begin < end && !SortCmp(&a[begin], &a[left])) {
++begin;
}
Swap(&a[begin], &a[end]);
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[end]);
//mid = end;//分割数组
//[left, mid - 1][mid + 1, right]
if (left < end - 1) {
StackPush(&tmp, left);
StackPush(&tmp, end - 1);
}
if (end + 1 < right) {
StackPush(&tmp, end + 1);
StackPush(&tmp, right);
}
}
StackDestroy(&tmp);
}
//归并,循环实现,二路归并
void MergeSort(int* a, int n)
{
int gap = 1;
int* atmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
int i = 0;
while (gap < n) {
i = 0;
//[left1, right1 - 1][left2, right2 - 1]
int left1 = 0, right1 = gap;
int left2 = gap, right2 = gap + gap;
if (right2 > n) {
right2 = n;
}
while (left1 != n) {//每行的循环
//printf("%d ", left1);
while (left1 < right1 && left2 < right2) {//每两个小区间的循环
if (!SortCmp(&a[left1], &a[left2])) {
atmp[i++] = a[left1];
++left1;
}
else {
atmp[i++] = a[left2];
++left2;
}
}
while (left1 < right1) {
atmp[i++] = a[left1++];
}
while (left2 < right2) {
atmp[i++] = a[left2++];
}
left1 = right2;
right1 += gap * 2;
left2 = right1;
right2 += gap * 2;
if (right1 > n) {
right1 = n;
left2 = n;
}
if (right2 > n) {
right2 = n;
}
}
memmove(a, atmp, sizeof(int) * n);
gap *= 2;
}
}
//计数,hash
void CountSort(int* a, int n)
{
//先找到数组里的最大,最小值,以确定数据范围
int max = a[0];
int min = a[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (a[i] > max) {
max = a[i];
}
if (a[i] < min) {
min = a[i];
}
}
int* ptmp = (int*)calloc((max - min + 1), sizeof(int) );
if (ptmp == NULL) {
perror("ptmp:malloc");
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ptmp[a[i] - min]++;
}
int cur = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (max - min + 1); ++i) {
while (ptmp[i]) {
a[cur++] = i + min;
--ptmp[i];
}
}
}sortTest.c
//简单的测试用例
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"sort.h"
void print(int* a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void test01()
{
int a1[] = { 3, 5, 8, 1, 2, 6, 9, 7, 0, 4 };
//int a1[] = { 2, 7, 1, 6 , 3 , 9, 5, 4, 0, 8, 51, 20, 11, -11, 2,33 ,3,4,6,7 };
int a2[] = { 2, 7, 1, 6 , 3 , 9, 5, 4, 0, 8, 51, 20, 11, -11, 2,33 ,3,4,6,7 };
//SelectSort(a1, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
//HeapSort(a2, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
//InsertSort(a1, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
//ShellSort(a1, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
//BubbleSort(a1, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
//QuickSortNonR(a1, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
//print(a1, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
//print(a2, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
//MergeSort(a1, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
CountSort(a1, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
//printf("\n");
print(a1, sizeof(a1) / sizeof(int));
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}