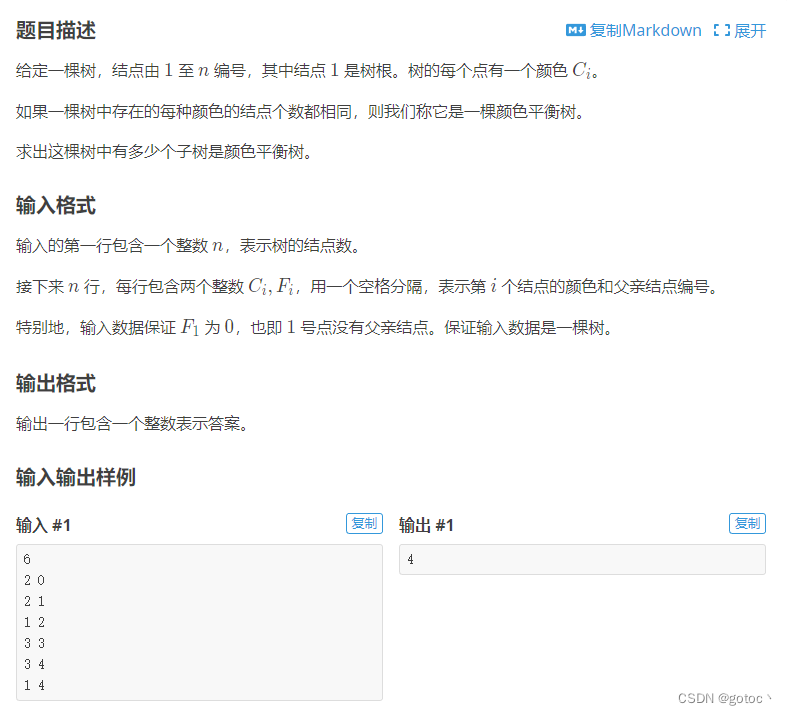
题目
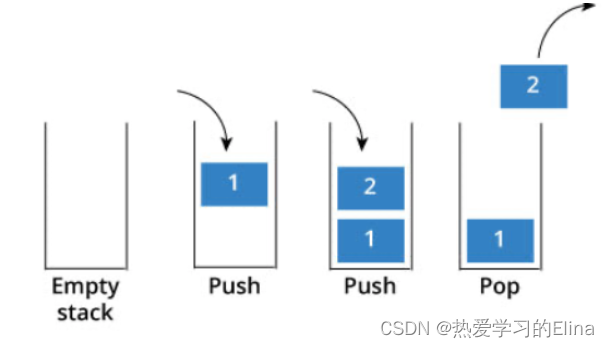
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈
- pop() -- 移除栈顶元素
- top() -- 获取栈顶元素
- empty() -- 返回栈是否为空
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
- 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
思路
(这里要强调是单向队列)
有点人可能依然想着用一个输入队列,一个输出队列,就可以模拟栈的功能,仔细想一下还真不行!队列模拟栈,其实一个队列就够了,那么我们先说一说两个队列来实现栈的思路。
队列是先进先出的规则,把一个队列中的数据导入另一个队列中,数据的顺序并没有变,并没有变成先进后出的顺序。
所以用栈实现队列, 和用队列实现栈的思路还是不一样的,这取决于这两个数据结构的性质。
但是依然还是要用两个队列来模拟栈,只不过没有输入和输出的关系,而是另一个队列完全用来备份的!
如下面动画所示,用两个队列que1和que2实现队列的功能,que2其实完全就是一个备份的作用,把que1最后面的元素以外的元素都备份到que2,然后弹出最后面的元素,再把其他元素从que2导回que1。
模拟的队列执行语句如下:
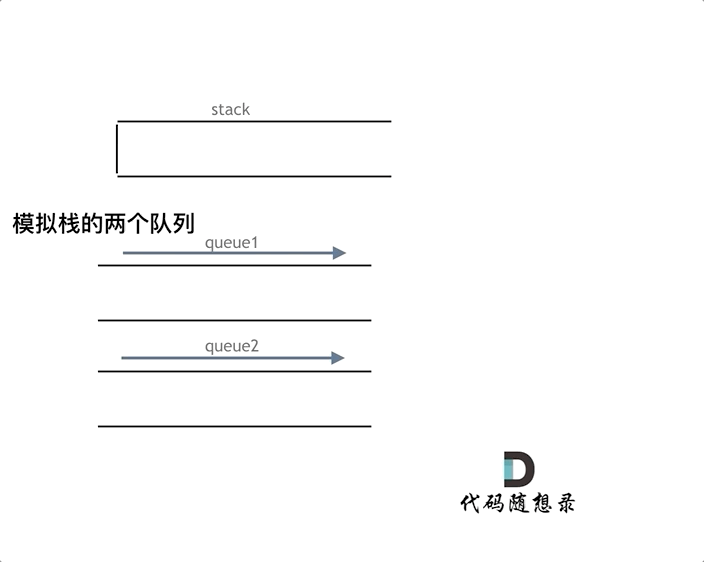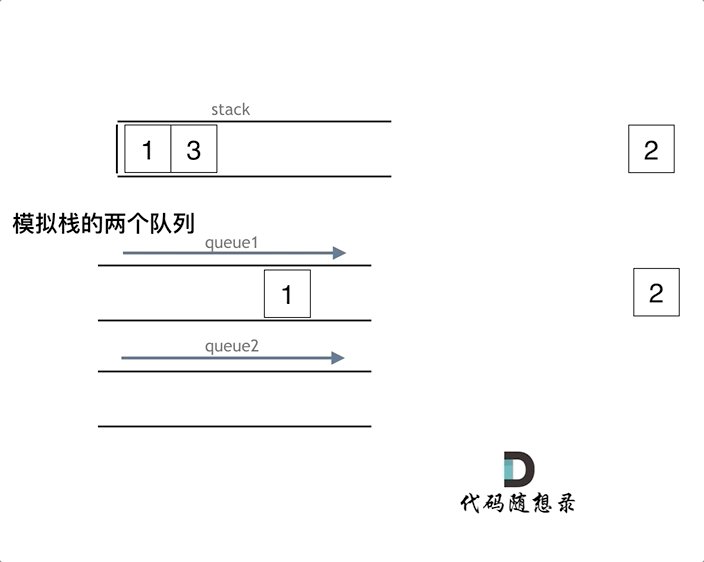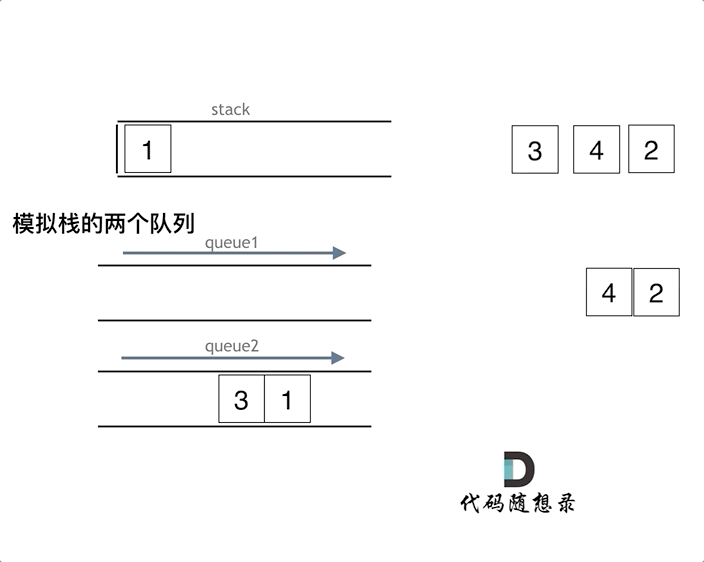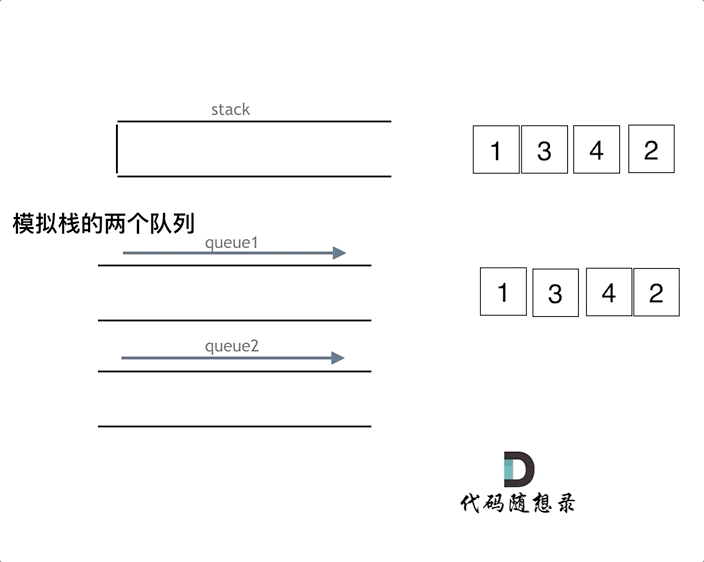
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.pop(); // 注意弹出的操作
queue.push(3);
queue.push(4);
queue.pop(); // 注意弹出的操作
queue.pop();
queue.pop();
queue.empty();
c++代码如下:
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que1;
queue<int> que2; // 辅助队列,用来备份
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
que1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int size = que1.size();
size--;
while (size--) { // 将que1 导入que2,但要留下最后一个元素
que2.push(que1.front());
que1.pop();
}
int result = que1.front(); // 留下的最后一个元素就是要返回的值
que1.pop();
que1 = que2; // 再将que2赋值给que1
while (!que2.empty()) { // 清空que2
que2.pop();
}
return result;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return que1.back();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que1.empty();
}
};
- 时间复杂度: pop为O(n),其他为O(1)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
优化
其实这道题目就是用一个队列就够了。
一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部,此时再去弹出元素就是栈的顺序了。
C++代码
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
que.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int size = que.size();
size--;
while (size--) { // 将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部
que.push(que.front());
que.pop();
}
int result = que.front(); // 此时弹出的元素顺序就是栈的顺序了
que.pop();
return result;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return que.back();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};
- 时间复杂度: pop为O(n),其他为O(1)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)