To improve the boomerang throwing skills of the animals, Zookeeper has set up an n×nn×n grid with some targets, where each row and each column has at most 22 targets each. The rows are numbered from 11 to nn from top to bottom, and the columns are numbered from 11 to nn from left to right.
For each column, Zookeeper will throw a boomerang from the bottom of the column (below the grid) upwards. When the boomerang hits any target, it will bounce off, make a 9090 degree turn to the right and fly off in a straight line in its new direction. The boomerang can hit multiple targets and does not stop until it leaves the grid.
![]()
正在上传…重新上传取消
In the above example, n=6n=6 and the black crosses are the targets. The boomerang in column 11 (blue arrows) bounces 22 times while the boomerang in column 33 (red arrows) bounces 33 times.
The boomerang in column ii hits exactly aiai targets before flying out of the grid. It is known that ai≤3ai≤3.
However, Zookeeper has lost the original positions of the targets. Thus, he asks you to construct a valid configuration of targets that matches the number of hits for each column, or tell him that no such configuration exists. If multiple valid configurations exist, you may print any of them.
Input
The first line contains a single integer nn (1≤n≤105)(1≤n≤105).
The next line contains nn integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an (0≤ai≤3)(0≤ai≤3).
Output
If no configuration of targets exist, print −1−1.
Otherwise, on the first line print a single integer tt (0≤t≤2n)(0≤t≤2n): the number of targets in your configuration.
Then print tt lines with two spaced integers each per line. Each line should contain two integers rr and cc (1≤r,c≤n)(1≤r,c≤n), where rr is the target's row and cc is the target's column. All targets should be different.
Every row and every column in your configuration should have at most two targets each.
Examples
input
Copy
6 2 0 3 0 1 1
output
Copy
5 2 1 2 5 3 3 3 6 5 6
input
Copy
1 0
output
Copy
0
input
Copy
6 3 2 2 2 1 1
output
Copy
-1
Note
For the first test, the answer configuration is the same as in the picture from the statement.
For the second test, the boomerang is not supposed to hit anything, so we can place 00 targets.
For the third test, the following configuration of targets matches the number of hits, but is not allowed as row 33 has 44 targets.
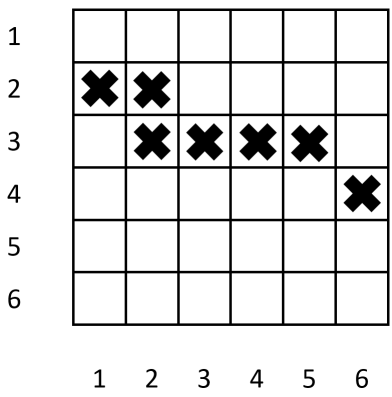
It can be shown for this test case that no valid configuration of targets will result in the given number of target hits.
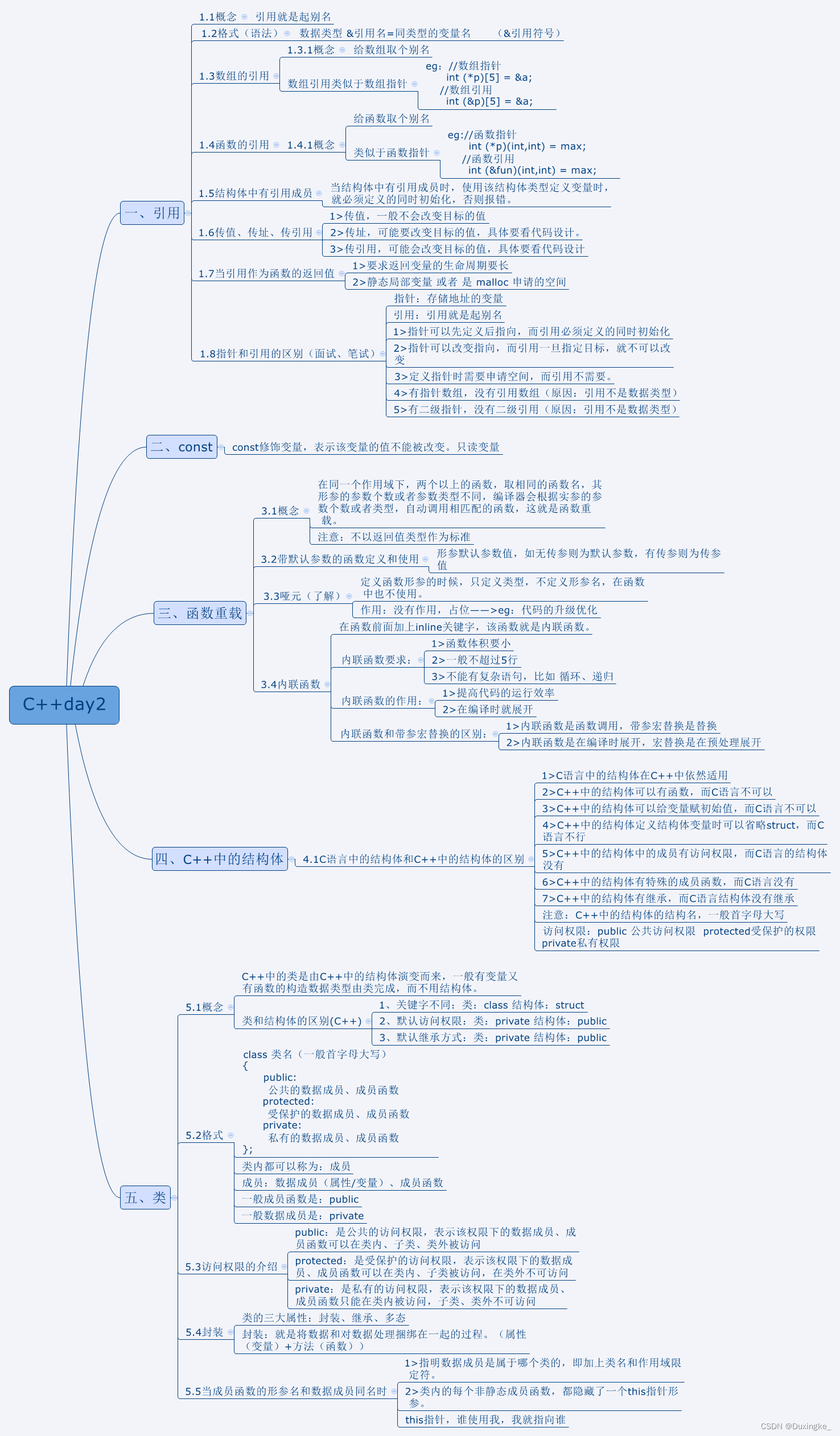
思路:
构造题,具体思路请看代码。
代码:
int a[maxj];
int r[maxj],c[maxj];
void solve(){//构造题,受后边影响,从后往前
int n;cin>>n;
vector<pii>ans;
queue<pii>que1,que2;//分情况去存数
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
cin>>a[i];
}
bool ff=0;
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){//构造的是梯子
if(a[i]==0)continue;
else if(a[i]==1){
ans.push_back({i,i});
// if(!que1.size())que1.pop();
que1.push({i,i});
r[i]++,c[i]++;
}else if(a[i]==2){
if(que1.size()==0){
ff=1;
break;
}
pii x=que1.front();que1.pop();
ans.push_back({x.first,i});//不是x.second,因为中间可能会有0
r[x.first]++,c[i]++;
que2.push({x.first,i});
}else if(a[i]==3){
if(que2.size()){
pii x=que2.front();
que2.pop();
int rr=x.first-1;
while(rr>=1&&r[rr]){rr--;}
if(rr<=0){break;}
ans.push_back({rr,i});//中间可能会有0
ans.push_back({rr,x.second});
r[rr]+=2;c[i]++;
que2.push({rr,i});//添加一次,ai为2的情况
}else if(que1.size()){//!
pii x=que1.front();
que1.pop();
int rr=x.first-1;
while(rr>=1&&r[rr]){rr--;}
if(rr<=0){break;}//
ans.push_back({rr,i});
ans.push_back({rr,x.second});
r[rr]+=2;c[i]++;
que2.push({rr,i});
}else{
ff=1;
break;
}
}
}
if(!ff){
cout<<ans.size()<<'\n';
for(auto i:ans){
cout<<i.first<<' '<<i.second<<'\n';
}
}else cout<<-1<<'\n';
}




















![【C语言_指针[2]_复习篇】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7cd869c2fa91405c9c39004eba103d8c.png)