一、简述
您可以在数组数据结构中存储相同类型的多个变量。您可以通过指定数组元素的类型来声明数组。如果您希望数组存储任何类型的元素,您可以指定object其类型。在 C# 的统一类型系统中,所有类型(预定义的和用户定义的、引用类型和值类型)都直接或间接继承自Object。
type[] arrayName;
数组具有以下属性:
1、数组可以是单维、多维或锯齿状的。
2、维数是在声明数组变量时设置的。
3、每个维度的长度是在创建数组实例时确定的。这些值在实例的生命周期内无法更改。
4、交错数组是数组的数组,每个成员数组都有默认值null。
5、数组的索引为零:包含n元素的数组的索引从0到n-1。
6、数组元素可以是任何类型,包括数组类型。
7、数组类型是从抽象基类型Array派生的引用类型。所有数组都实现IList和IEnumerable。您可以使用foreach语句来迭代数组。一维数组还实现IList<T>和IEnumerable<T>。
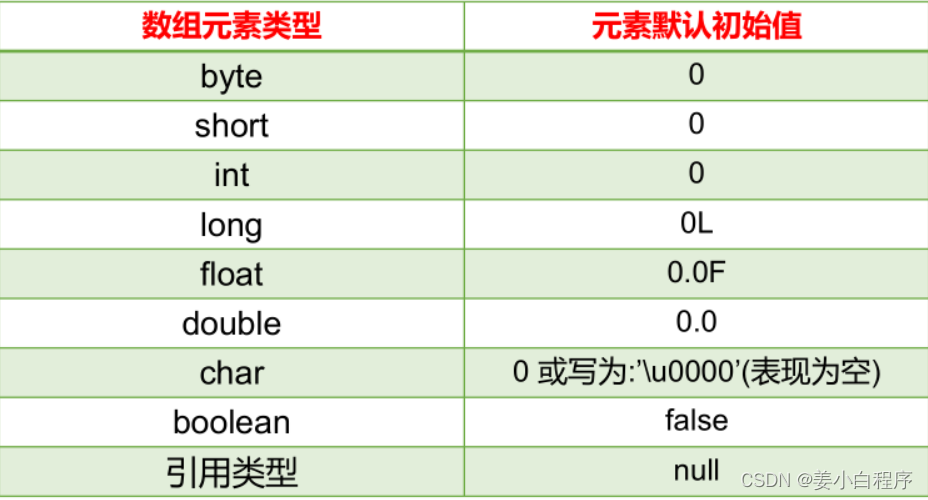
创建数组时,可以将数组的元素初始化为已知值。从 C# 12 开始,所有集合类型都可以使用Collection 表达式进行初始化。未初始化的元素将设置为默认值。默认值是 0 位模式。所有引用类型(包括不可为 null 的类型)都具有值null。所有值类型都具有 0 位模式。这意味着Nullable<T>.HasValue属性是false,而Nullable<T>.Value属性未定义。在 .NET 实现中,该Value属性会引发异常。
二、数组创建示例
// Declare a single-dimensional array of 5 integers.
int[] array1 = new int[5];
// Declare and set array element values.
int[] array2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
// Declare a two dimensional array.
int[,] multiDimensionalArray1 = new int[2, 3];
// Declare and set array element values.
int[,] multiDimensionalArray2 = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
// Declare a jagged array.
int[][] jaggedArray = new int[6][];
// Set the values of the first array in the jagged array structure.
jaggedArray[0] = [1, 2, 3, 4];1、一维数组
一维数组是相似元素的序列。您可以通过索引访问元素。索引是其在序列中的顺序位置。数组中的第一个元素位于索引处0。您可以使用指定数组元素类型和元素数量的new运算符创建一维数组。以下示例声明并初始化一维数组:
int[] array = new int[5];
string[] weekDays = ["Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat"];
Console.WriteLine(weekDays[0]);
Console.WriteLine(weekDays[1]);
Console.WriteLine(weekDays[2]);
Console.WriteLine(weekDays[3]);
Console.WriteLine(weekDays[4]);
Console.WriteLine(weekDays[5]);
Console.WriteLine(weekDays[6]);
/*Output:
Sun
Mon
Tue
Wed
Thu
Fri
Sat
*/第一个声明声明了一个由五个整数组成的未初始化数组,从array[0]到array[4]。数组的元素被初始化为元素类型的默认值0(对于整数)。第二个声明声明一个字符串数组并初始化该数组的所有七个值。foreach语句迭代数组的元素weekday并打印所有值。对于一维数组,该foreach语句按递增索引顺序处理元素,从索引 0 开始,以索引 结束Length - 1。
2、传递一维数组作为参数
您可以将初始化的一维数组传递给方法。在以下示例中,初始化了一个字符串数组,并将其作为参数传递给DisplayArray字符串方法。该方法显示数组的元素。接下来,该ChangeArray方法反转数组元素,然后该ChangeArrayElements方法修改数组的前三个元素。每个方法返回后,该DisplayArray方法都会显示按值传递数组不会阻止对数组元素的更改。
class ArrayExample
{
static void DisplayArray(string[] arr) => Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", arr));
// Change the array by reversing its elements.
static void ChangeArray(string[] arr) => Array.Reverse(arr);
static void ChangeArrayElements(string[] arr)
{
// Change the value of the first three array elements.
arr[0] = "Mon";
arr[1] = "Wed";
arr[2] = "Fri";
}
static void Main()
{
// Declare and initialize an array.
string[] weekDays = ["Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat"];
// Display the array elements.
DisplayArray(weekDays);
Console.WriteLine();
// Reverse the array.
ChangeArray(weekDays);
// Display the array again to verify that it stays reversed.
Console.WriteLine("Array weekDays after the call to ChangeArray:");
DisplayArray(weekDays);
Console.WriteLine();
// Assign new values to individual array elements.
ChangeArrayElements(weekDays);
// Display the array again to verify that it has changed.
Console.WriteLine("Array weekDays after the call to ChangeArrayElements:");
DisplayArray(weekDays);
}
}
// The example displays the following output:
// Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat
//
// Array weekDays after the call to ChangeArray:
// Sat Fri Thu Wed Tue Mon Sun
//
// Array weekDays after the call to ChangeArrayElements:
// Mon Wed Fri Wed Tue Mon Sun3、多维数组
数组可以有多个维度。例如,以下声明创建四个数组:两个具有二维,两个具有三个维度。前两个声明声明每个维度的长度,但不初始化数组的值。后两个声明使用初始值设定项来设置多维数组中每个元素的值。
int[,] array2DDeclaration = new int[4, 2];
int[,,] array3DDeclaration = new int[4, 2, 3];
// Two-dimensional array.
int[,] array2DInitialization = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } };
// Three-dimensional array.
int[,,] array3D = new int[,,] { { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } },
{ { 7, 8, 9 }, { 10, 11, 12 } } };
// Accessing array elements.
System.Console.WriteLine(array2DInitialization[0, 0]);
System.Console.WriteLine(array2DInitialization[0, 1]);
System.Console.WriteLine(array2DInitialization[1, 0]);
System.Console.WriteLine(array2DInitialization[1, 1]);
System.Console.WriteLine(array2DInitialization[3, 0]);
System.Console.WriteLine(array2DInitialization[3, 1]);
// Output:
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 7
// 8
System.Console.WriteLine(array3D[1, 0, 1]);
System.Console.WriteLine(array3D[1, 1, 2]);
// Output:
// 8
// 12
// Getting the total count of elements or the length of a given dimension.
var allLength = array3D.Length;
var total = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < array3D.Rank; i++)
{
total *= array3D.GetLength(i);
}
System.Console.WriteLine($"{allLength} equals {total}");
// Output:
// 12 equals 12对于多维数组,遍历元素时首先递增最右侧维度的索引,然后递增下一个左侧维度,依此类推,直至最左侧索引。以下示例枚举 2D 和 3D 数组:
int[,] numbers2D = { { 9, 99 }, { 3, 33 }, { 5, 55 } };
foreach (int i in numbers2D)
{
System.Console.Write($"{i} ");
}
// Output: 9 99 3 33 5 55
int[,,] array3D = new int[,,] { { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } },
{ { 7, 8, 9 }, { 10, 11, 12 } } };
foreach (int i in array3D)
{
System.Console.Write($"{i} ");
}
// Output: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12在二维数组中,您可以将左索引视为行,将右索引视为列。 但是,对于多维数组,使用嵌套for循环可以让您更好地控制处理数组元素的顺序:
int[,,] array3D = new int[,,] { { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } },
{ { 7, 8, 9 }, { 10, 11, 12 } } };
for (int i = 0; i < array3D.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < array3D.GetLength(1); j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < array3D.GetLength(2); k++)
{
System.Console.Write($"{array3D[i, j, k]} ");
}
System.Console.WriteLine();
}
System.Console.WriteLine();
}
// Output (including blank lines):
// 1 2 3
// 4 5 6
//
// 7 8 9
// 10 11 12
//4、将多维数组作为参数传递
将初始化的多维数组传递给方法的方式与传递一维数组的方式相同。以下代码显示了 print 方法的部分声明,该方法接受二维数组作为其参数。您可以一步初始化并传递一个新数组,如以下示例所示。在以下示例中,初始化了一个二维整数数组并将其传递给该Print2DArray方法。该方法显示数组的元素。
static void Print2DArray(int[,] arr)
{
// Display the array elements.
for (int i = 0; i < arr.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < arr.GetLength(1); j++)
{
System.Console.WriteLine("Element({0},{1})={2}", i, j, arr[i, j]);
}
}
}
static void ExampleUsage()
{
// Pass the array as an argument.
Print2DArray(new int[,] { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 }, { 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } });
}
/* Output:
Element(0,0)=1
Element(0,1)=2
Element(1,0)=3
Element(1,1)=4
Element(2,0)=5
Element(2,1)=6
Element(3,0)=7
Element(3,1)=8
*/5、交错数组
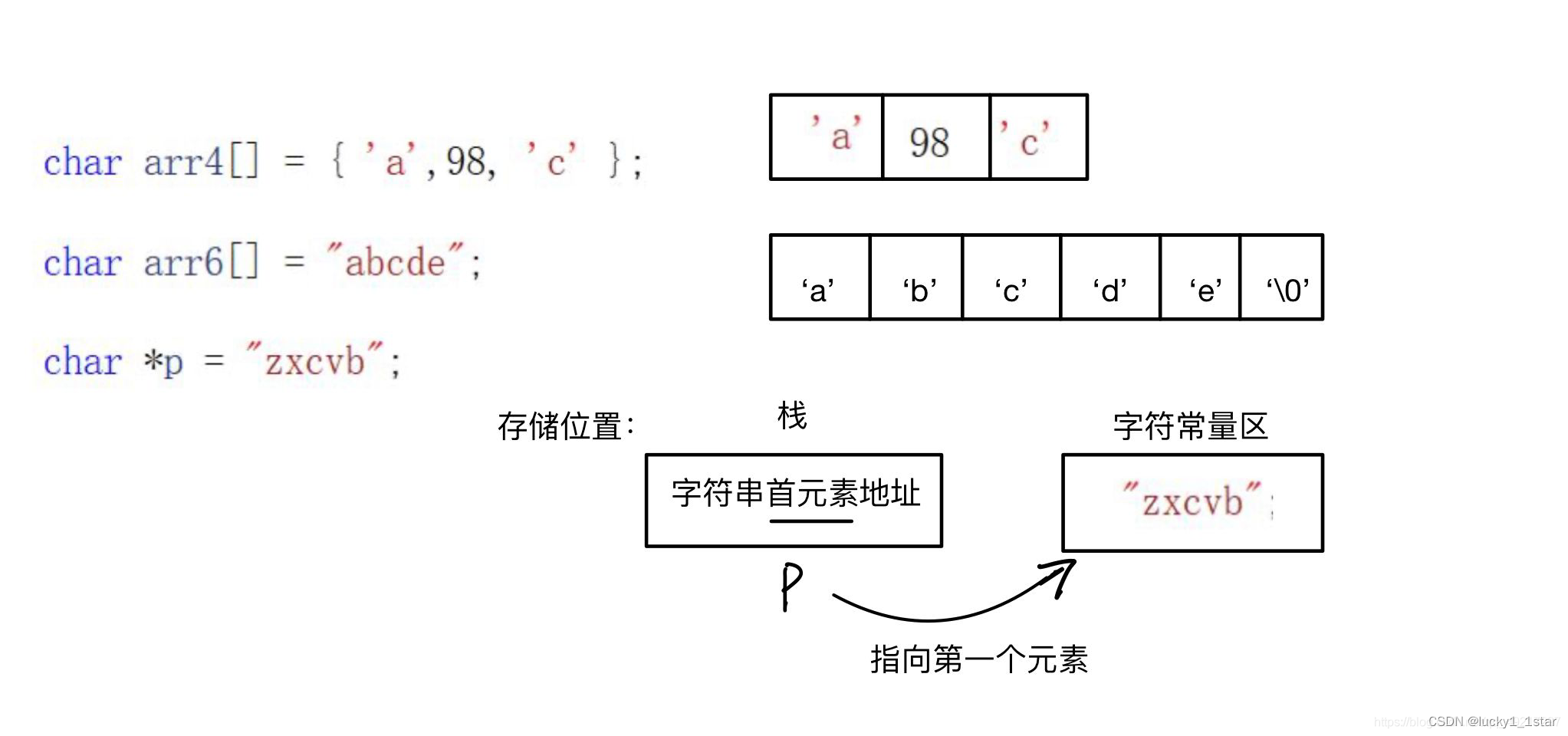
交错数组是一种其元素为数组且大小可能不同的数组。锯齿状数组有时称为“数组的数组”。它的元素是引用类型并初始化为null. 以下示例演示如何声明、初始化和访问交错数组。
第一个示例jaggedArray是在一条语句中声明的。每个包含的数组都是在后续语句中创建的。
第二个示例jaggedArray2是在一条语句中声明和初始化的。可以混合锯齿状数组和多维数组。
最后一个示例jaggedArray3是一个单维交错数组的声明和初始化,该数组包含三个不同大小的二维数组元素。
int[][] jaggedArray = new int[3][];
jaggedArray[0] = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9];
jaggedArray[1] = [0, 2, 4, 6];
jaggedArray[2] = [11, 22];
int[][] jaggedArray2 =
[
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9],
[0, 2, 4, 6],
[11, 22]
];
// Assign 77 to the second element ([1]) of the first array ([0]):
jaggedArray2[0][1] = 77;
// Assign 88 to the second element ([1]) of the third array ([2]):
jaggedArray2[2][1] = 88;
int[][,] jaggedArray3 =
[
new int[,] { {1,3}, {5,7} },
new int[,] { {0,2}, {4,6}, {8,10} },
new int[,] { {11,22}, {99,88}, {0,9} }
];
Console.Write("{0}", jaggedArray3[0][1, 0]);
Console.WriteLine(jaggedArray3.Length);交错数组的元素必须先初始化,然后才能使用它们。每个元素本身就是一个数组。还可以使用初始值设定项来用值填充数组元素。使用初始值设定项时,不需要数组大小。
此示例构建一个数组,其元素本身就是数组。每个数组元素都有不同的大小。
// Declare the array of two elements.
int[][] arr = new int[2][];
// Initialize the elements.
arr[0] = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9];
arr[1] = [2, 4, 6, 8];
// Display the array elements.
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
System.Console.Write("Element({0}): ", i);
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].Length; j++)
{
System.Console.Write("{0}{1}", arr[i][j], j == (arr[i].Length - 1) ? "" : " ");
}
System.Console.WriteLine();
}
/* Output:
Element(0): 1 3 5 7 9
Element(1): 2 4 6 8
*/6、隐式类型数组
您可以创建一个隐式类型数组,其中数组实例的类型是根据数组初始值设定项中指定的元素推断出来的。任何隐式类型变量的规则也适用于隐式类型数组。
以下示例展示了如何创建隐式类型数组:
int[] a = new[] { 1, 10, 100, 1000 }; // int[]
// Accessing array
Console.WriteLine("First element: " + a[0]);
Console.WriteLine("Second element: " + a[1]);
Console.WriteLine("Third element: " + a[2]);
Console.WriteLine("Fourth element: " + a[3]);
/* Outputs
First element: 1
Second element: 10
Third element: 100
Fourth element: 1000
*/
var b = new[] { "hello", null, "world" }; // string[]
// Accessing elements of an array using 'string.Join' method
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", b));
/* Output
hello world
*/
// single-dimension jagged array
int[][] c =
[
[1,2,3,4],
[5,6,7,8]
];
// Looping through the outer array
for (int k = 0; k < c.Length; k++)
{
// Looping through each inner array
for (int j = 0; j < c[k].Length; j++)
{
// Accessing each element and printing it to the console
Console.WriteLine($"Element at c[{k}][{j}] is: {c[k][j]}");
}
}
/* Outputs
Element at c[0][0] is: 1
Element at c[0][1] is: 2
Element at c[0][2] is: 3
Element at c[0][3] is: 4
Element at c[1][0] is: 5
Element at c[1][1] is: 6
Element at c[1][2] is: 7
Element at c[1][3] is: 8
*/
// jagged array of strings
string[][] d =
[
["Luca", "Mads", "Luke", "Dinesh"],
["Karen", "Suma", "Frances"]
];
// Looping through the outer array
int i = 0;
foreach (var subArray in d)
{
// Looping through each inner array
int j = 0;
foreach (var element in subArray)
{
// Accessing each element and printing it to the console
Console.WriteLine($"Element at d[{i}][{j}] is: {element}");
j++;
}
i++;
}
/* Outputs
Element at d[0][0] is: Luca
Element at d[0][1] is: Mads
Element at d[0][2] is: Luke
Element at d[0][3] is: Dinesh
Element at d[1][0] is: Karen
Element at d[1][1] is: Suma
Element at d[1][2] is: Frances
*/ 在前面的示例中,请注意,对于隐式类型数组,初始化语句的左侧没有使用方括号。此外,交错数组的初始化方式与new []一维数组类似。
当您创建包含数组的匿名类型时,该数组必须在该类型的对象初始值设定项中隐式类型化。在以下示例中,contacts是一个匿名类型的隐式类型数组,每个匿名类型都包含一个名为 的数组PhoneNumbers。该var关键字不在对象初始值设定项内部使用。
var contacts = new[]
{
new
{
Name = "Eugene Zabokritski",
PhoneNumbers = new[] { "206-555-0108", "425-555-0001" }
},
new
{
Name = "Hanying Feng",
PhoneNumbers = new[] { "650-555-0199" }
}
};
![<span style='color:red;'>C</span>++静态<span style='color:red;'>数</span><span style='color:red;'>组</span>和<span style='color:red;'>C</span>语言静态<span style='color:red;'>数</span><span style='color:red;'>组</span><span style='color:red;'>的</span>区别( array,int a[])](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/b5081660510144898787447195b9ac79.png)





























![[备赛笔记]——5G大唐杯(5G考试等级考考试基础试题)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/38ef97fb3d5a4aa4ac7fedf7032966f5.gif)