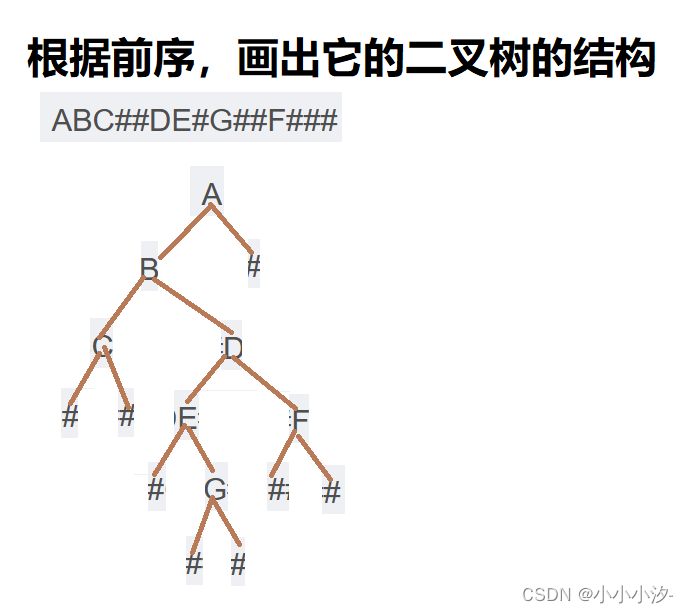
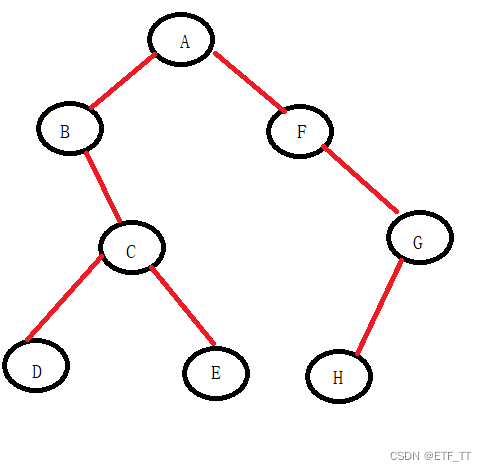
从根节点往下查找,先找左子树、直至左子树为空(左子节点逐个入栈、直至左子节点为空),再找右子树(出栈找右子节点)
前序遍历:根左右,第一次经过节点即打印,直到打印null,往回溯,打印右子树
中序遍历:左根右,第二次经过该节点时进行打印,即左边回溯时
后序遍历:左右根,第三次经过该节点时进行打印,即右边回溯时
层序遍历:按照层级,从上往下,从左到右。使用广度优先搜索算法。
一、递归遍历:
public static void preorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//System.out.println(root.val);//前序 第一次成为栈顶
preorder(root.left);
System.out.println(root.val);//中序 第二次成为栈顶
preorder(root.right);
//System.out.println(root.val);//后序 第三次成为栈顶
}
二、迭代遍历:
public int largestPerimeter(int[] A) {
Arrays.sort(A);
for (int i = A.length - 1; i >= 2; --i) {
if (A[i - 2] + A[i - 1] > A[i]) {
return A[i - 2] + A[i - 1] + A[i];
}
}
return 0;
}
public static void preorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//System.out.println(root.val);//前序 第一次成为栈顶
preorder(root.left);
System.out.println(root.val);//中序 第二次成为栈顶
preorder(root.right);
//System.out.println(root.val);//后序 第三次成为栈顶
}
三、前序遍历
前序:使用stack记录递归路径,左子节点后添加保证先出栈
public static void preOrder2(TreeNode head) {
if (head != null) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
stack.add(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
head = stack.pop();
if(head != null){
System.out.println(head.val);
stack.push(head.right);
stack.push(head.left);
}
}
}
}
四、中序遍历
中序:将左子节点入栈,出栈打印值,然后添加右子节点
public static void preOrder3(TreeNode head) {
if (head != null) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) {
if (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
} else {
head = stack.pop();
System.out.println(head.val);
head = head.right;
}
}
}
}
五、后序遍历
public static void postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return ;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode prev = null;
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();//root的左子节点为null
if (root.right == null || root.right == prev) {//右子节点为null,或者右子节
点已打印
System.out.println(root.val);
prev = root;
root = null;
} else {//右子节点有值,重新入栈
stack.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
}
}
六、层序遍历:
public static void levelTraversal(Node root) {
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node temp = q.poll();
if (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.value + " ");
q.add(temp.left);
q.add(temp.right);
}
}
}
public static void deepOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return ;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 1; i <= queue.size(); ++i) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
System.out.println(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
}
private static List order(TreeNode root, int i, ArrayList list) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
int length = list.size();
if(length <= i){
for(int j=0; j<= i-length; j++){
list.add(length+j,null);
}
}
list.set(i,root.val);
order(root.left, 2 * i,list);
order(root.right, 2 * i + 1,list);
return list;
}
七、线索二叉树:
在N个节点的二叉树中,每个节点有2个指针,所以一共有2N个指针,除了根节点以外,每一个节点都有一个指针从它的父节点指向它,所以一共使用了N-1个指针,所以剩下2N-(N-1)也就是N+1个空指针;
如果能利用这些空指针域来存放指向该节点的直接前驱或是直接后继的指针,则可由此信息直接找到在该遍历次序下的前驱节点或后继节点,从而比递归遍历提高了遍历速度,节省了建立系统递归栈所使用的存储空间;
这些被重新利用起来的空指针就被称为线索(Thread),加上了线索的二叉树就是线索二叉树
实现思路:按某种次序遍历二叉树,在遍历过程中用线索取代空指针即可。以中序遍历为例,首先找到中序遍历的开始节点,然后利用线索依次查找后继节点即可。
由于它充分利用了空指针域的空间(等于节省了空间),又保证了创建时的一次遍历就可以终生受用前驱、后继的信息(这意味着节省了时间),所以在实际问题中,如果所使用的二叉树需要经常遍历或查找节点时需要某种遍历中的前驱和后继,那么采用线索二叉链表的存储结构就是不错的选择
morris遍历:构建中序线索二叉树的过程中,如果发现前驱节点的右指针指向自身,则将指针(线索)
删除
public static void morrisPre(Node cur) {
if(head == null){
return;
}
Node mostRight = null;
while (cur != null){
// cur表示当前节点,mostRight表示cur的左孩子的最右节点
mostRight = cur.left;
if(mostRight != null){
// cur有左孩子,找到cur左子树最右节点
while (mostRight.right !=null && mostRight.right != cur){
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
// mostRight的右孩子指向空,让其指向cur,cur向左移动
if(mostRight.right == null){
mostRight.right = cur;
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
cur = cur.left;
continue;
}else {
// mostRight的右孩子指向cur,让其指向空,cur向右移动
mostRight.right = null;
}
}else {
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
}
cur = cur.right;
}
}
public static void morrisIn(Node cur) {
if(head == null){
return;
}
Node mostRight = null;
while (cur != null){
mostRight = cur.left;
if(mostRight != null){
while (mostRight.right !=null && mostRight.right != cur){
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if(mostRight.right == null){
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
continue;
}else {
mostRight.right = null;
}
}
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
cur = cur.right;
}
}
public static void morrisPos(TreeNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
TreeNode head = cur;
TreeNode mostRight = null;
while (cur != null) {
mostRight = cur.left;
if (mostRight != null) {
while (mostRight.right != null && mostRight.right != cur) {
mostRight = mostRight.right;
}
if (mostRight.right == null) {
mostRight.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
continue;
} else {
mostRight.right = null;
printEdge(cur.left);
}
}
cur = cur.right;
}
printEdge(head);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printEdge(TreeNode head) {
TreeNode tail = reverseEdge(head);
TreeNode cur = tail;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
reverseEdge(tail);
}
public static TreeNode reverseEdge(TreeNode from) {
TreeNode pre = null;
TreeNode next = null;
while (from != null) {
next = from.right;
from.right = pre;
pre = from;
from = next;
}
return pre;
}
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode prev = null;
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if (root.right == null || root.right == prev) {
res.add(root.val);
prev = root;
root = null;
} else {
stack.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}