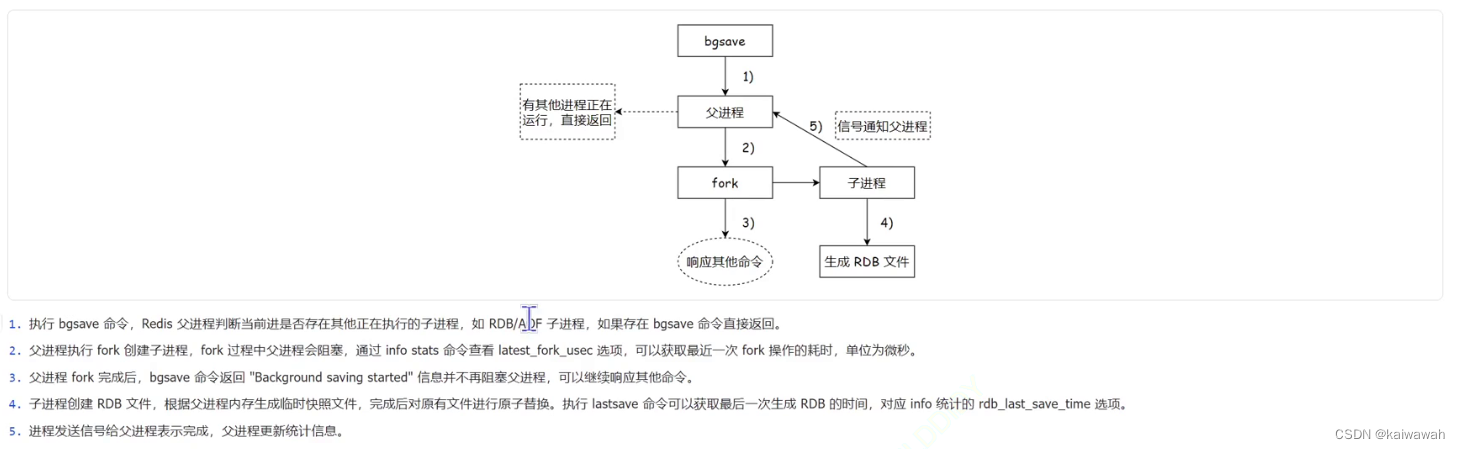
1.递归求平衡二叉树
2.递归法求二叉树的所有路径
3.左叶子之和
1.递归求平衡二叉树
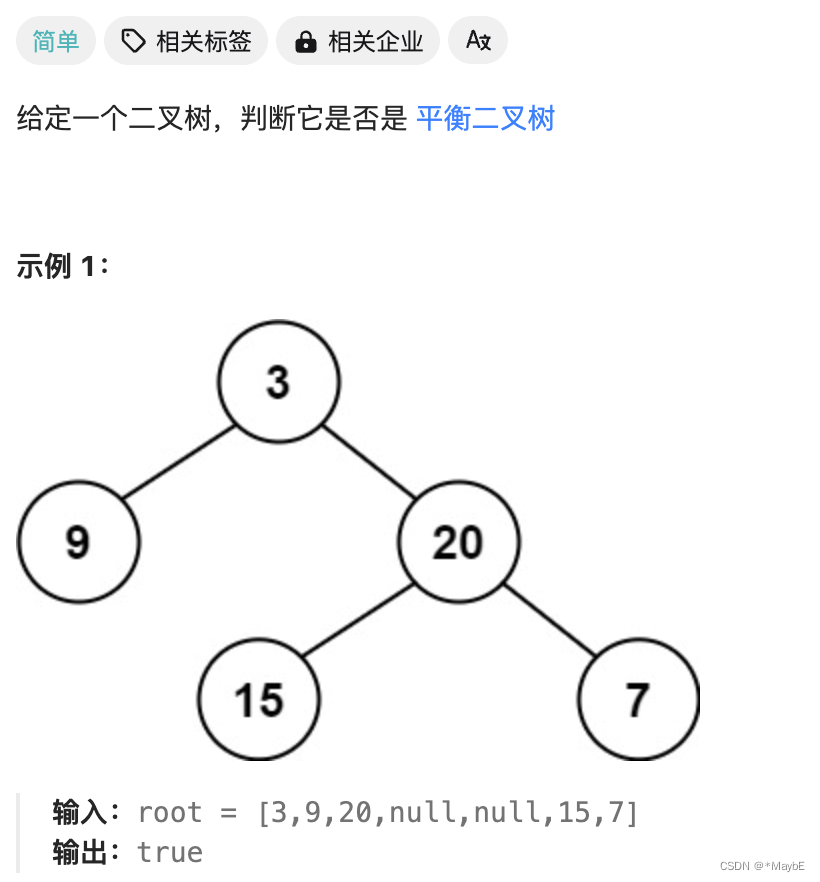
平衡二叉树定义:每个节点的左右子树高度相差小于等于1。
思路:求高度的题和求深度题不一样的地方在于,高度是用左右中,也就是后序遍历,而深度是前序遍历,为什么呢?因为高度是从下往上计算节点的个数,而后序遍历就是从下往上传数据,所以用来求高度,反之,求深度的前序遍历也是一样的道理。
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(getHeight(root) == -1) return false;
return true;
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return 0;
//左右中
//左
int left = getHeight(root.left);
if(left == -1) return -1;
//右
int right = getHeight(root.right);
if(right == -1) return -1;
//中
int res = 0;
if(Math.abs(left - right) > 1) res = -1;
else{
res = Math.max(left,right) + 1;
}
return res;
}
}2.二叉树的所有路径
思路:采用前序遍历从上往下搜索,当判断是叶子节点的时候就加入答案集,如果不是叶子节点,就继续往下搜索,但要注意回溯,因为传入的数据List采用了同一个地址,所以结果会保存。
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return res;
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
findPath(root,path,res);
return res;
}
public void findPath(TreeNode root,List<Integer> path , List<String> res){
//中
path.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
String temp = "";
for (int i = 0; i < path.size()-1; i++) {
temp += path.get(i) + "->";
}
temp += path.get(path.size()-1);
res.add(temp);
}
//左
if(root.left != null){
findPath(root.left,path,res);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
//右
if(root.right != null){
findPath(root.right,path,res);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}这是没有采用同一个path集合的代码,更加简洁,是代码里利用新建tep的String对象传入给下一个节点,他们的tmp地址是不共享的,这样就达到了不用回溯的效果
//方式二
class Solution {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
deal(root, "");
return result;
}
public void deal(TreeNode node, String s) {
if (node == null)
return;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
result.add(new StringBuilder(s).append(node.val).toString());
return;
}
String tmp = new StringBuilder(s).append(node.val).append("->").toString();
deal(node.left, tmp);
deal(node.right, tmp);
}
}3.左叶子之和
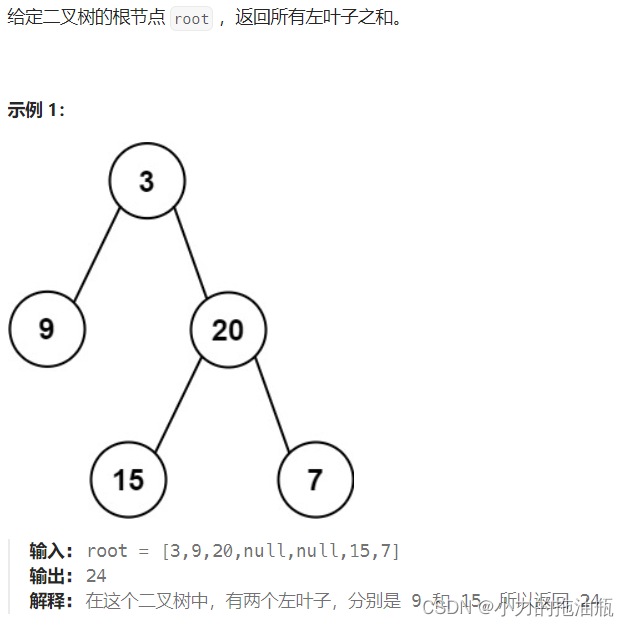
思路:首先要明白左叶子的定义:是父节点的左孩子并且是叶子节点。这就告诉了我们,我们要找的是父节点,所以判断return的条件多了一个 if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return 0; 因为这时候的节点不是父节点所以直接返回。
在判断的时候,如果满足左孩子是叶子节点的情况,就要更新以当前节点为根节点的二叉树的左叶子之和的情况,当前左叶子之和就是左孩子的值。
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return 0;
//左右中
//左
int left = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
if(root.left!=null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right==null){
left = root.left.val;
}
//右
int right = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
//中
return left + right;
}
}