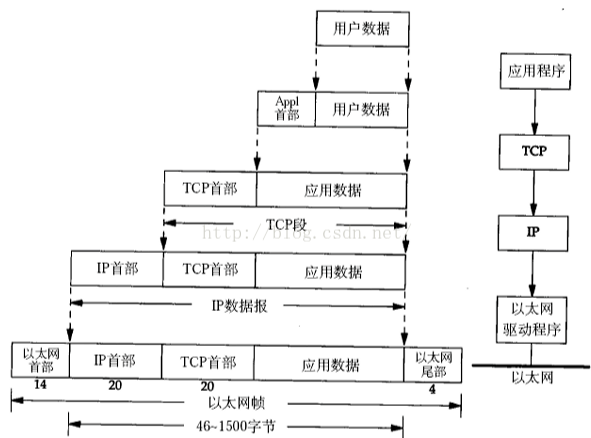
判断是否是完全二叉树
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root){
if (root == null){
return true;
}
//创建队列
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//把根放进队列里
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
//把出队列的放进cur里
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
//当cur不等于空时,把cur的左子树和右子树放进队列
if (cur != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
queue.offer(cur.right);
}else{
//如果cur放进了null,说明要跳出队列进入判断环节
break;
}
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode tmp = queue.peek();//瞄一眼队列的数
if (tmp == null){
queue.poll();
}else{
//遇到不为空的说明不是完全二叉树
return false;
}
}
//来到这里说明tmp全部是空的,是完全二叉树
return true;
}
找出p和q的最近的公共祖先
1.root节点是p或q其中的一个,那么root就是最近的公共祖先
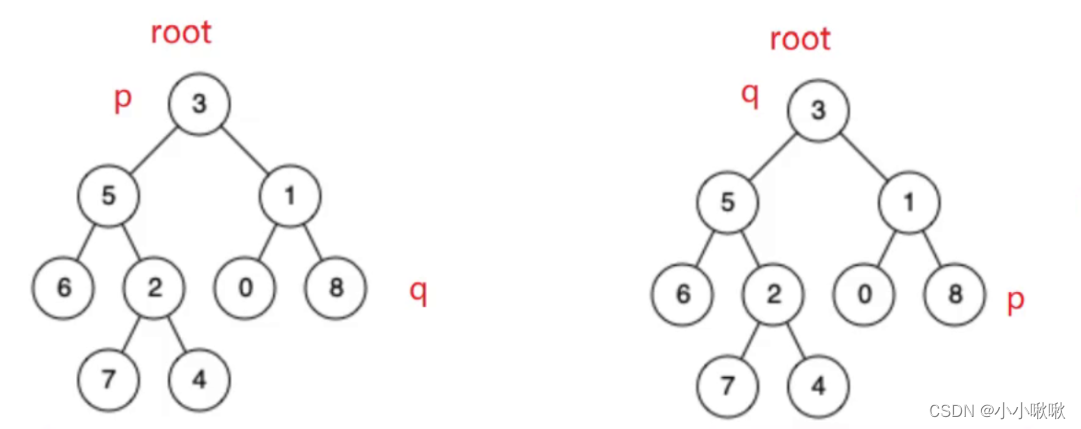
2.p和q分别在root的两侧,那么root是最近的公共祖先
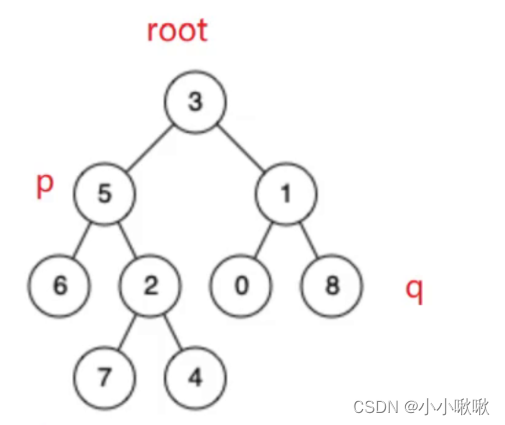
3.p和q在root的同一侧
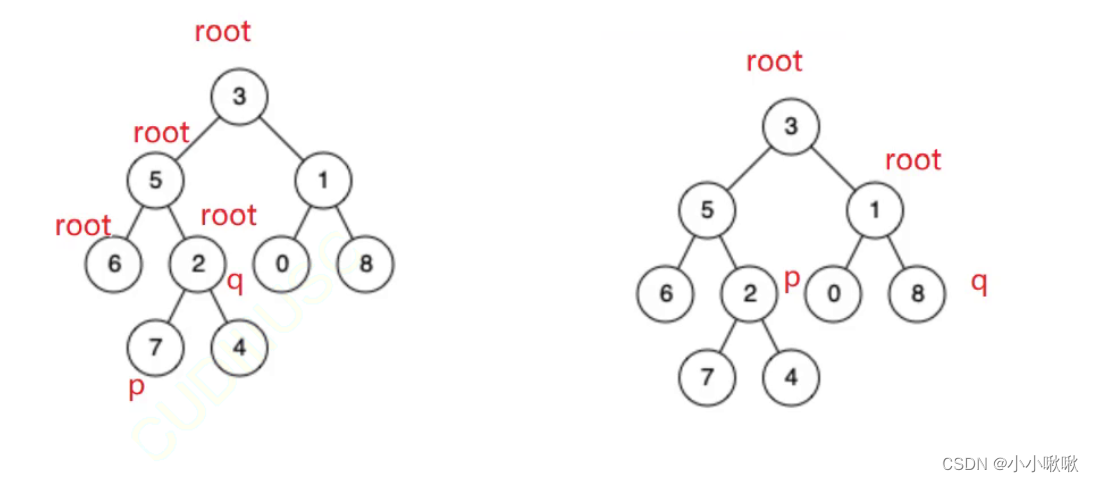
原理:root还是在遍历这棵树,遇到p或q就返回。
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode leftTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode rightTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
if (leftTree != null && rightTree != null) {
return root;
} else if (leftTree != null) {
return leftTree;
} else {
return rightTree;
}
}
还有第二种方法
大概意思就是:找p那条路径,和q那条路径出现的节点,然后放进两个栈里,保证两个栈的数相同,多的去掉,然后栈中相同的元素就是他们最近的公共祖先。
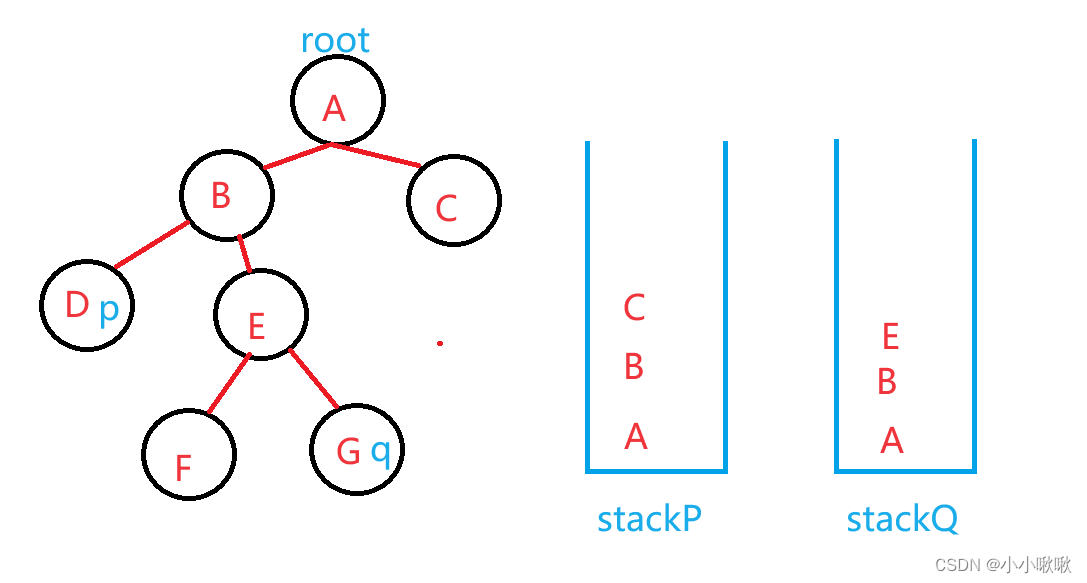
public class BinaryTree {
static class TreeNode{
public char val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public TreeNode creatTree(){
TreeNode A = new TreeNode('A');
TreeNode B = new TreeNode('B');
TreeNode C = new TreeNode('C');
TreeNode D = new TreeNode('D');
TreeNode E = new TreeNode('E');
TreeNode F = new TreeNode('F');
TreeNode G = new TreeNode('G');
TreeNode H = new TreeNode('H');
A.left = B;
A.right = C;
B.left = D;
B.right = E;
C.left = F;
C.right = G;
E.right = H;
return A;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor2(TreeNode root,TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(root == null) return null;
//创建两个栈
Stack<TreeNode> stackP = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stackQ = new Stack<>();
//两条路径
getPath(root,p,stackP);
getPath(root,q,stackQ);
//大小
int sizeP = stackP.size();
int sizeQ = stackP.size();
if (sizeP > sizeQ){
int size = sizeP - sizeQ;
while (size != 0){
stackP.pop();
size--;
}
}else {
int size = sizeQ - sizeP;
while (size != 0){
stackQ.pop();
size--;
}
}
//两个栈元素一样多
while(!stackP.isEmpty() && !stackQ.isEmpty()){
if (stackP.peek() == stackQ.peek()){
return stackP.peek() ;
}else{
stackP.pop();
stackQ.pop();
}
}
return null;
}
private boolean getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode node, Stack<TreeNode> stack){
if (root == null || node == null){
return false;
}
stack.push(root);
if (root == node){
return true;
}
boolean flg1 = getPath(root.left, node, stack);
if(flg1){
return true;
}
boolean flg2 = getPath(root.right, node, stack);
if(flg2){
return true;
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}
}
非递归实现前序遍历
//递归实现前序遍历
void preOrder(TreeNode root){
//根左右
if(root == null){
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
//非递归实现前序遍历
void preOrderNor(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
cur = top.right;
//1.为空,返回;不为空创建栈,让cur=root;
//当cur!=null时,把cur放进栈里,并打印cur.val;再让cur=root.left。
//当cur==null时,让top=栈顶元素,然后让cur=top.right
}
}
非递归实现中序遍历
//中序遍历
void inOrder(TreeNode root){
//左根右
if(root == null){
return;
}
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inOrder(root.right);
}
//非递归中序遍历
void inorderNor(TreeNode root){
if (root == null){
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
System.out.print(top.val+" ");
cur = top.right;
}
//不为空,创建栈,让cur=root,把cur放进栈里,然后遍历cur的左边。
//直到cur遇到空,说明cur的左边遍历完了
//让top=栈顶元素,并打印top的值,让cur=top.right。
}
非递归实现后序遍历
//后序遍历
void postOrder(TreeNode root){
//左右根
if(root == null){
return;
}
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
}
//非递归后序遍历
void postOrderNor(TreeNode root){
if (root == null){
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
if (top.right == null || top.right == prev){
System.out.print(top.val+" ");
stack.pop();
prev = top;
}else{
cur = top.right;
}
//先创建栈,让cur=root,cur不等于空或者栈不为空,当cur不等于空时,让cur入栈,然后让cur=cur.left,
//直到当cur等于空时,定义prev=null;让top=瞄一眼栈顶元素,如果等于空或者top.right=prev进入循环,
// 循环内打印top.val,并且出栈,然后让prev=top,否则让cur=cur.right
}























![[AI]文心一言出圈的同时,NLP处理下的ChatGPT-4.5最新资讯](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0422b4369a3549b3a39da19588ab88f4.png)