目录
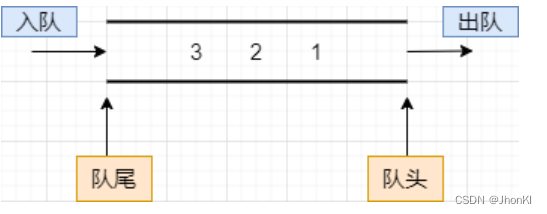
队列定义:
队列是一个先进先出的数据结构(First in First out)。只能对表尾进行插入,对表头进行结点的删除,这样强限制性的链表,这就是所说的队列。也就是说,队列是限定在表的一端进行插入,表的另一端进行删除的数据结构。
图解:

如同日常生活中去买票排队,每一列队伍都有一个队尾和队首,先来的先买票,后来的后买,买好的就从队首出去,新来买票的就需要从队尾继续排队。
为了使用的方便,咱们将队头位置的指针命名为head,队尾为tail

队列的声明与头文件的包含:
队列的声明:
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue//定义类型为QNode的指向队头和队尾的指针
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;这里通过单链表实现队列,需要一个单链表的结构QueueNode。然后头尾指针需要另外开辟一个结构体,指针的类型是QNode*. 通过指针head和tail来查询队列中的队头和队尾数据。
头文件的包含:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>队列的基本操作:
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//摧毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//返回队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//返回队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//返回队列当前大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//判空操作
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);

初始化队列 :
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//将指向队头和队尾的指针置空
}摧毁队列:
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;//保存下一个节点的指针,释放当亲位置的空间
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//释放完后将队头和队尾指针都置空
}入队列:
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)//为新节点开辟空间
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;//为新节点赋值
if (pq->tail == NULL)//若当前尾为空,就将队头,尾指针指向newnode
{
pq->tail = pq->head = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;//否则队尾指针的next指向newnode
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}1.入队列前需要开辟一个新节点,同时进行判空操作
2.进行入队操作的时候,首先需要判断队列是否为空,如果队列为空的话,需要将头指针和尾指针一同指向第一个结点
3.如果不为空,就进行队列的尾插操作,同时移动tail的位置以便于下一次的插入

出队列:
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//一个
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//多个
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}出队列是需要判断当前队列中的节点个数,分为一个和多个进行讨论。如果只有一个,就将头节点内存释放,接着将头尾指针置空,防止野指针的出现。如果是多个节点,就需要将头节点的下一个节点保存,以免找不到。接着将头节点内存释放,释放后,移动头指针head的位置,使其指向下一个节点。
返回队头数据:
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}返回队尾数据:
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->data;
}返回队列当前大小:
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}判空操作:
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}测试数据:


最后,完整代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue//定义类型为QNode的指向队头和队尾的指针
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//将指向队头和队尾的指针置空
}
//摧毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;//保存下一个节点的指针,释放当亲位置的空间
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//释放完后将队头和队尾指针都置空
}
//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)//为新节点开辟空间
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;//为新节点赋值
if (pq->tail == NULL)//若当前尾为空,就将队头,尾指针指向newnode
{
pq->tail = pq->head = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;//否则队尾指针的next指向newnode
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//一个
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//多个
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
//返回队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
//返回队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->data;
}
//返回队列当前大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
//判空操作
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
void QueueTest()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestory(&q);
}
int main()
{
QueueTest();
return 0;
}博客到这里也是结束了,喜欢的小伙伴可以点赞加关注支持下博主,这对我真的很重要~~