生命周期监听
场景:监听应用的生命周期
1. 监听器-SpringApplicationRunListener
- 自定义SpringApplicationRunListener来监听事件;
1.1. 编写SpringApplicationRunListener 实现类
1.2. 在 META-INF/spring.factories 中配置 org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=自己的Listener,还可以指定一个有参构造器,接受两个参数(SpringApplication application, String[] args)
1.3. springboot 在spring-boot.jar中配置了默认的 Listener,如下
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListenner=\org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
/**
* Listener先要从 META-INF/spring.factories 读到
*
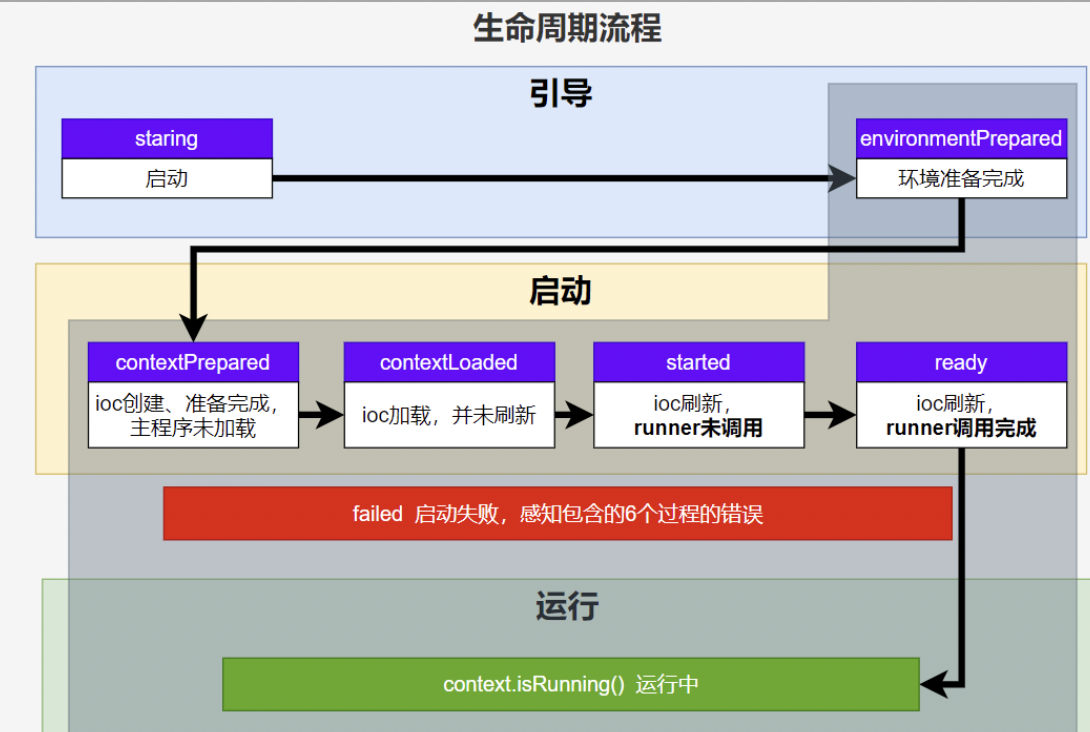
* 1、引导: 利用 BootstrapContext 引导整个项目启动
* starting: 应用开始,SpringApplication的run方法一调用,只要有了 BootstrapContext 就执行
* environmentPrepared: 环境准备好(把启动参数等绑定到环境变量中),但是ioc还没有创建;【调一次】
* 2、启动:
* contextPrepared: ioc容器创建并准备好,但是sources(主配置类)没加载。并关闭引导上下文;组件都没创建 【调一次】
* contextLoaded: ioc容器加载。主配置类加载进去了。但是ioc容器还没刷新(我们的bean没创建)。
* =======截止以前,ioc容器里面还没造bean呢=======
* started: ioc容器刷新了(所有bean造好了),但是 runner 没调用。
* ready: ioc容器刷新了(所有bean造好了),所有 runner 调用完了。
* 3、运行
* 以前步骤都正确执行,代表容器running。
*/
2. 生命周期全流程
事件触发时机
1. 各种回调监听器
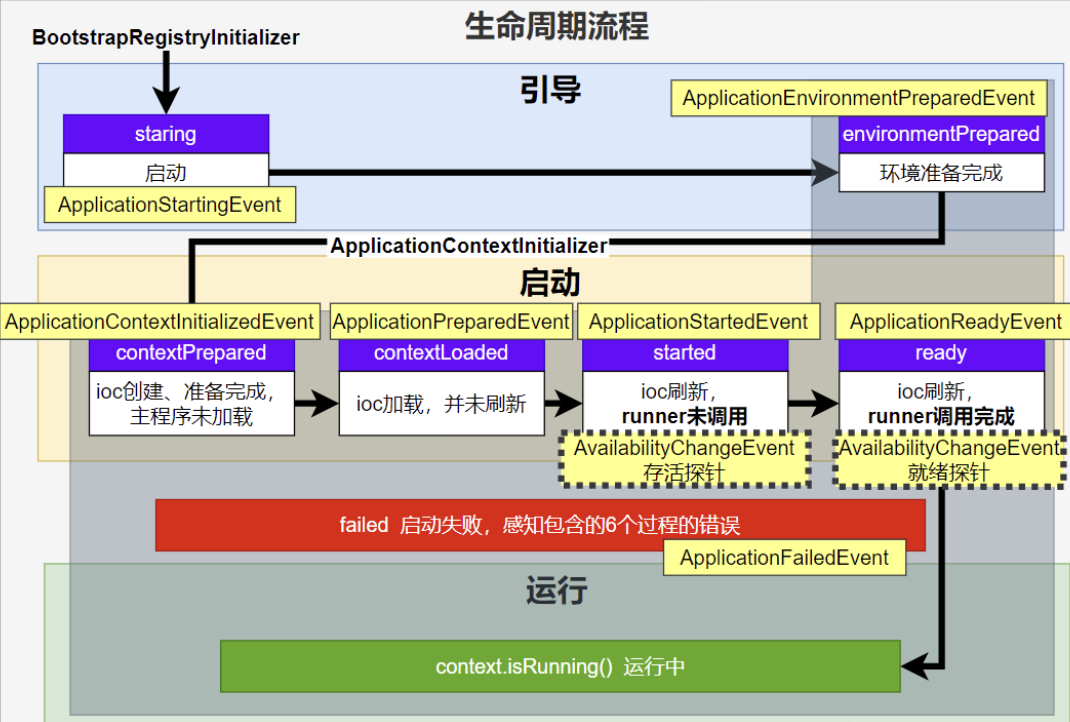
● BootstrapRegistryInitializer: 感知特定阶段:感知引导初始化
○ META-INF/spring.factories
○ 创建引导上下文bootstrapContext的时候触发。
○ application.addBootstrapRegistryInitializer();
○ 场景:进行密钥校对授权。
● ApplicationContextInitializer: 感知特定阶段: 感知ioc容器初始化
○ META-INF/spring.factories
○ application.addInitializers();
● ApplicationListener: 感知全阶段:基于事件机制,感知事件。 一旦到了哪个阶段可以做别的事
○ @Bean或@EventListener: 事件驱动
○ SpringApplication.addListeners(…)或 SpringApplicationBuilder.listeners(…)
○ META-INF/spring.factories
● SpringApplicationRunListener: 感知全阶段生命周期 + 各种阶段都能自定义操作; 功能更完善。
○ META-INF/spring.factories
● ApplicationRunner: 感知特定阶段:感知应用就绪Ready。卡死应用,就不会就绪
○ @Bean
● CommandLineRunner: 感知特定阶段:感知应用就绪Ready。卡死应用,就不会就绪
○ @Bean
最佳实战:
● 如果项目启动前做事: BootstrapRegistryInitializer 和 ApplicationContextInitializer
● 如果想要在项目启动完成后做事:ApplicationRunner和 CommandLineRunner
● 如果要干涉生命周期做事:SpringApplicationRunListener
● 如果想要用事件机制:ApplicationListener
2. 完整触发流程
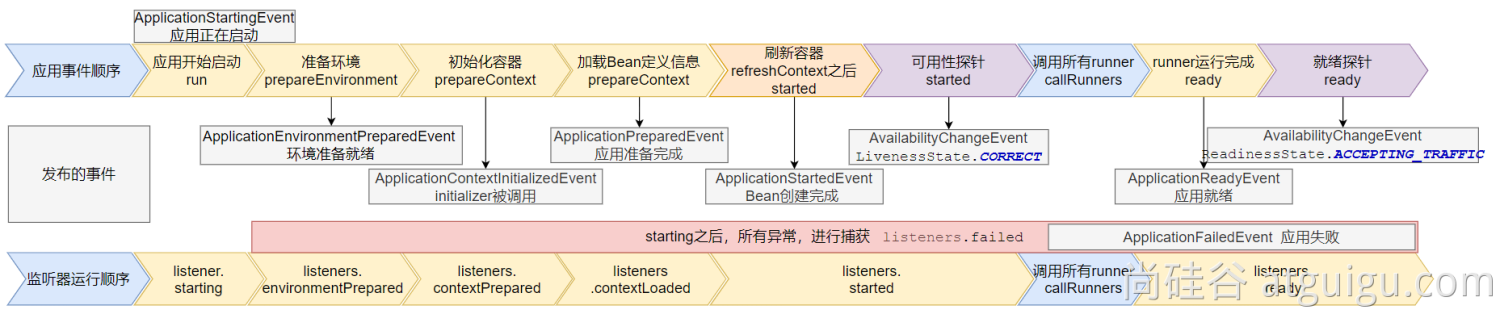
9大事件触发顺序&时机
- ApplicationStartingEvent:应用启动但未做任何事情, 除过注册listeners and initializers.
- ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent: Environment 准备好,但context 未创建.
- ApplicationContextInitializedEvent: ApplicationContext 准备好,ApplicationContextInitializers 调用,但是任何bean未加载
- ApplicationPreparedEvent: 容器刷新之前,bean定义信息加载
- ApplicationStartedEvent: 容器刷新完成, runner未调用
=以下就开始插入了探针机制==== - AvailabilityChangeEvent: LivenessState.CORRECT应用存活; 存活探针
- ApplicationReadyEvent: 任何runner被调用
- AvailabilityChangeEvent:ReadinessState.ACCEPTING_TRAFFIC就绪探针,可以接请求
- ApplicationFailedEvent :启动出错
应用事件发送顺序如下:
感知应用是否存活了:可能植物状态,虽然活着但是不能处理请求。
应用是否就绪了:能响应请求,说明确实活的比较好。
3. SpringBoot 事件驱动开发
应用启动过程生命周期事件感知(9大事件)、应用运行中事件感知(无数种)。
● 事件发布:ApplicationEventPublisherAware或注入:ApplicationEventMulticaster
● 事件监听:组件 + @EventListener


事件发布者
@Service
public class EventPublisher implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware {
/**
* 底层发送事件用的组件,SpringBoot会通过ApplicationEventPublisherAware接口自动注入给我们
* 事件是广播出去的。所有监听这个事件的监听器都可以收到
*/
ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
/**
* 所有事件都可以发
* @param event
*/
public void sendEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
//调用底层API发送事件
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event);
}
/**
* 会被自动调用,把真正发事件的底层组组件给我们注入进来
* @param applicationEventPublisher event publisher to be used by this object
*/
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;
}
}
事件订阅者
@Service
public class CouponService {
@Order(1)
@EventListener
public void onEvent(LoginSuccessEvent loginSuccessEvent){
System.out.println("===== CouponService ====感知到事件"+loginSuccessEvent);
UserEntity source = (UserEntity) loginSuccessEvent.getSource();
sendCoupon(source.getUsername());
}
public void sendCoupon(String username){
System.out.println(username + " 随机得到了一张优惠券");
}
}
自动配置原理
入门理解:应用关注的三大核心:场景、配置、组件
1. 自动配置流程

- 导入starter
- 依赖导入autoconfigure
- 寻找类路径下 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports文件
- 启动,加载所有 自动配置类 xxxAutoConfiguration
a. 给容器中配置功能组件
b. 组件参数绑定到 属性类中。xxxProperties
c. 属性类和配置文件前缀项绑定
d. @Contional派生的条件注解进行判断是否组件生效 - 效果:
a. 修改配置文件,修改底层参数
b. 所有场景自动配置好直接使用
c. 可以注入SpringBoot配置好的组件随时使用
2. SPI机制
● Java中的SPI(Service Provider Interface)是一种软件设计模式,用于在应用程序中动态地发现和加载组件。SPI的思想是,定义一个接口或抽象类,然后通过在classpath中定义实现该接口的类来实现对组件的动态发现和加载。
● SPI的主要目的是解决在应用程序中使用可插拔组件的问题。例如,一个应用程序可能需要使用不同的日志框架或数据库连接池,但是这些组件的选择可能取决于运行时的条件。通过使用SPI,应用程序可以在运行时发现并加载适当的组件,而无需在代码中硬编码这些组件的实现类。
● 在Java中,SPI的实现方式是通过在META-INF/services目录下创建一个以服务接口全限定名为名字的文件,文件中包含实现该服务接口的类的全限定名。当应用程序启动时,Java的SPI机制会自动扫描classpath中的这些文件,并根据文件中指定的类名来加载实现类。
● 通过使用SPI,应用程序可以实现更灵活、可扩展的架构,同时也可以避免硬编码依赖关系和增加代码的可维护性。
在SpringBoot中,META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
3. 功能开关
● 自动配置:全部都配置好,什么都不用管。 自动批量导入
○ 项目一启动,spi文件中指定的所有都加载。
● @EnableXxxx:手动控制哪些功能的开启; 手动导入。
○ 开启xxx功能
○ 都是利用 @Import 把此功能要用的组件导入进去
进阶理解
1. @SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootConfiguration
就是: @Configuration ,容器中的组件,配置类。spring ioc启动就会加载创建这个类对象
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置
开启自动配置
@AutoConfigurationPackage:扫描主程序包:加载自己的组件
● 利用 @Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) 想要给容器中导入组件。
● 把主程序所在的包的所有组件导入进来。
● 为什么SpringBoot默认只扫描主程序所在的包及其子包
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):加载所有自动配置类:加载starter导入的组件
List<String> configurations = ImportCandidates.load(AutoConfiguration.class, getBeanClassLoader())
.getCandidates();
扫描SPI文件:META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
@ComponentScan
组件扫描:排除一些组件(哪些不要)
排除前面已经扫描进来的配置类、和自动配置类。
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
2. 完整启动加载流程
生命周期启动加载流程
自定义starter
场景:抽取聊天机器人场景,它可以打招呼。
效果:任何项目导入此starter都具有打招呼功能,并且问候语中的人名需要可以在配置文件中修改
● 1. 创建自定义starter项目,引入spring-boot-starter基础依赖
● 2. 编写模块功能,引入模块所有需要的依赖。
● 3. 编写xxxAutoConfiguration自动配置类,帮其他项目导入这个模块需要的所有组件
● 4. 编写配置文件META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports指定启动需要加载的自动配置
● 5. 其他项目引入即可使用
1. 业务代码
自定义配置有提示。导入以下依赖重启项目,再写配置文件就有提示
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "robot") //此属性类和配置文件指定前缀绑定
@Component
@Data
public class RobotProperties {
private String name;
private String age;
private String email;
}
<!-- 导入配置处理器,配置文件自定义的properties配置都会有提示-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
2. 基本抽取
● 创建starter项目,把公共代码需要的所有依赖导入
● 把公共代码复制进来
● 自己写一个 RobotAutoConfiguration,给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件
○ 为什么这些组件默认不会扫描进去?
○ starter所在的包和 引入它的项目的主程序所在的包不是父子层级
● 别人引用这个starter,直接导入这个 RobotAutoConfiguration,就能把这个场景的组件导入进来
● 功能生效。
● 测试编写配置文件
3. 使用@EnableXxx机制
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({
ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Import(RobotAutoConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableRobot {
}
别人引入starter需要使用 @EnableRobot开启功能
4. 完全自动配置
● 依赖SpringBoot的SPI机制
●METAINF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports 文件中编写好我们自动配置类的全类名即可
● 项目启动,自动加载我们的自动配置类